|
Taiyuan
Taiyuan; Mandarin pronunciation: (Jin Chinese, Taiyuan Jin: /tʰai˦˥ ye˩˩/) is the capital of Shanxi, China. Taiyuan is the political, economic, cultural and international exchange center of Shanxi Province. It is an industrial base focusing on energy and heavy chemicals. Throughout its long history, Taiyuan was the capital or provisional capital of many dynasties in China, hence the name ( zh, s=龙城, p=Dragon City, labels=no). As of 2021, the city governs 6 districts, 3 counties, and hosts a county-level city with a total area of 6,988 square kilometers and a permanent population of 5,390,957. Taiyuan is located roughly in the centre of Shanxi, with the Fen River flowing through the central city. Etymology and names The two Chinese characters of the city's name are (, "great") and (, "plain"), referring to the location where the Fen River leaves the mountains and enters a relatively flat plain. Throughout its long history, the city had various names, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi and Datong. Its one-character abbreviation is (), after the Jin (Chinese state), state of Jin that existed there during the Spring and Autumn period (). The name ''Shanxi'' means 'west of the mountains', a reference to its location west of the Taihang Mountains. Shanxi borders Hebei to the east, Henan to the south, Shaanxi to the west and Inner Mongolia to the north. Shanxi's terrain is characterised by a plateau bounded partly by mountain ranges. Shanxi's culture is largely dominated by the ethnic Han Chinese, Han majority, who make up over 99% of its population. Jin Chinese is considered by some linguists to be a distinct language from Mandarin and its geographical range covers most of Shanxi. Both Jin and Mandarin are spoken in Shanxi. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fen River
The Fen River drains the center of Shanxi Province, China. It originates in the Guancen Mountains of Ningwu County in northeast Shanxi, flows southeast into the basin of Taiyuan, and then south through the central valley of Shanxi before turning west to join the Yellow River west of Hejin. The Fen and the Wei Rivers are the two largest tributaries of the Yellow River. The river is long and drains an area of , 25.3% of Shanxi's area. The Fen River is the longest in Shanxi. It is also the second-longest tributary of the Yellow River. Within Taiyuan, the Fen runs from north to south; the prefecture includes one-seventh of the river's course. History Legend The Fen is usually identified with the said by Sima Qian and others to have flowed beside the home of the Yellow Emperor. The ''Guoyu (book), Discourses of the States'' states that the Ji was the home of the Yellow Emperor's clan before he fought the clan of Yan Emperor, Yandi (the "Flame Emperor"). Its name is identical with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
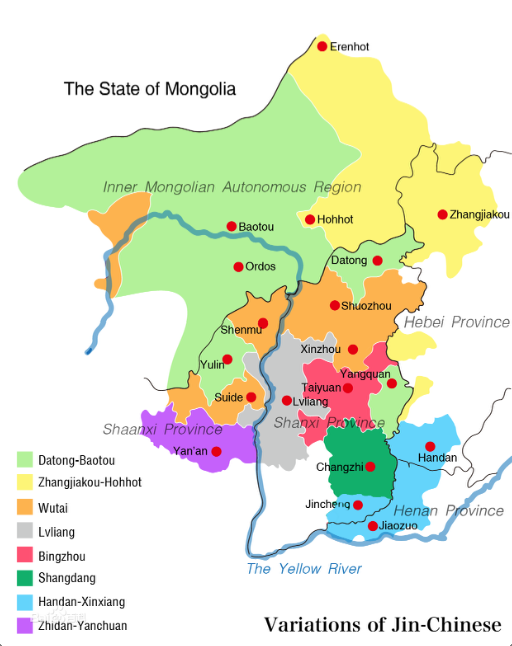
Jin Chinese
Jin () is a group of Chinese linguistic varieties spoken by roughly 48 million people in northern China, including most of Shanxi province, much of central Inner Mongolia, and adjoining areas in Hebei, Henan, and Shaanxi provinces. The status of Jin is disputed among linguists; some prefer to include it within Mandarin, but others set it apart as a closely related but separate sister group. Classification After the concept of Mandarin Chinese was proposed, the Jin dialects were universally included within it, mainly because Chinese linguists paid little attention to these dialects at the time. In order to promote Standard Mandarin in the early days of People's Republic of China, linguists started to research various dialects in Shanxi, comparing these dialects with Standard Mandarin for helping the locals to learn it more quickly. During this period, a few linguists discovered some unique features of Jin Chinese that do not exist in other northern Mandarin dialects, planting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinci
The Jinci or Jin Temple (晉祠) is the most prominent temple complex in Shanxi, China. It is located 16 miles (25 km) southwest of Taiyuan at the foot of Xuanweng Mountain at the Jin Springs. It was founded about 1,400 years ago and expanded during the following centuries, resulting in a diverse collection of more than 100 sculptures, buildings, terraces, and bridges. The best known structure at Jinci is the Hall of the Holy Mother (圣母殿, Shèngmǔdiàn), which was constructed from 1023 to 1032 during the Song dynasty The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv .... It has carved wooden dragons coiled around the eight pillars that support its upward-curving double-eave roof. Inside the Hall of the Holy Mother are 43 Song-dynasty clay sculptures, including a seated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinghualing District
Xinghualing District () is one of six districts of the prefecture-level city of Taiyuan, the capital of Shanxi Province, North China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after .... It is located in the urban core of Taiyuan. References External links www.xzqh.org County-level divisions of Shanxi {{Shanxi-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianlongshan Grottoes
The Tianlongshan Grottoes (, English translation: Mountain of the Heavenly Dragon) are caves located in Taiyuan, Shanxi Province, China, that are notable for the Buddhist temples located within them. The temple complex spans two mountains: there are eight grottoes on the eastern mountain and 13 on the western mountain. The complex was constructed over a number of centuries, from the northern Qi dynasty until the Tang dynasty, and contains Buddhist art of high historic importance. The majority of the caves date to the Tang dynasty. The caves have been designated by the government as a Major Historical and Cultural Site Protected at the National Level. Artwork A number of works of Buddhist sculpture survived in the caves, including over 1,500 statues and 1,144 reliefs sculptures. Many of the sculptures are of painted stone. The subject matter includes images of Buddha and bodhisattvas. The caves' Tang sculptures are noted for their soft modeling, sensuous drapery, and naturalism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Pagoda Temple
The Twin Pagoda Temple (), officially known as Yongzuo Temple (), of Taiyuan, Shanxi Province, China, is a temple containing two pagodas dating from the Ming dynasty. History The East pagoda was built in 1597, and the West one in 1612. In charge of the pagoda’s construction was a high ranking monk, named Fodeng (佛灯). By the 20th century, deterioration since construction had caused the East pagoda to slant from its center of gravity by 2.87 meters. In 1995, experts set about trying to correct the slant. They removed earth from underneath the pagoda and successfully corrected the pagoda's tilt. Pagodas The pagodas are the tallest set of twin pagodas in China. They are both eight-cornered, with the lowest floor being comparatively taller than the rest, the size of the upper floors progressively decreasing. The West Pagoda is 54.78 meters tall, with the lowest floor’s circumference being 4.16 meters. The pagoda’s eaves are painted with emerald green glaze. The East Pagoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globalization And World Cities Research Network
The Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) is a British think tank that studies the relationships between world cities in the context of globalization. It is based in the geography department of Loughborough University in Leicestershire, United Kingdom. GaWC was founded by Peter J. Taylor in 1998. Together with Jon Beaverstock and Richard G. Smith, they create the GaWC's biennial categorization of world cities into "Alpha", "Beta" and "Gamma" tiers. The three tiers are further divided into subgroupings using plus and minus signs. The categorization is based upon the author's views of "international connectedness", primarily shown through a regions advanced services firms, such as in accountancy, finance and law). GaWC city classification The GaWC examines cities worldwide to narrow them down to a roster of world cities, then ranks these based on their connectivity through four "advanced producer services": accountancy, advertising, banking/finance, and law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhao (state)
Zhao () was one of the seven major State (Ancient China), states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It emerged from the Partition of Jin, tripartite division of Jin, along with Han (Warring States), Han and Wei (state), Wei, in the 5th century BC. Zhao gained considerable strength from the military reforms initiated during the reign of King Wuling of Zhao, King Wuling, but suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of Qin (state), Qin at the Battle of Changping. Its territory included areas in the modern provinces of Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi. It bordered the states of Qin, Wei, and Yan (state), Yan, as well as various nomadic peoples including the Donghu people, Hu and Xiongnu. Its capital was Handan, in modern Hebei province. Zhao was home to the Chinese Legalism, administrative philosopher Shen Dao, Confucian Xun Kuang, and Gongsun Long, who is affiliated to the school of names. Origins and ascendancy The Zhao (surname), Zhao clan within Jin ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of China
Provinces ( zh, c=省, p=Shěng) are the most numerous type of province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions in the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). There are currently 22 provinces administered by the PRC and one province that is claimed, but not administered, which is Taiwan Province, People's Republic of China, Taiwan, currently administered by the Taiwan, Republic of China (ROC). The local governments of Chinese provinces consists of a Provincial People's Government headed by a Governor (China), governor that acts as the executive, a Provincial People's Congress with legislative powers, and a parallel provincial branch of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) that elects a Chinese Communist Party Committee Secretary, party secretary and a Chinese Communist Party Provincial Standing Committee, provincial standing committee. Government Provinces are the most common form of province-level governments. The legislative bodies of the provinces are the Prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |