|
Surgical Incisions
A surgical incision is a cut made through the skin and soft tissue to facilitate an operation or procedure. Often, multiple incisions are possible for an operation. In general, a surgical incision is made as small and unobtrusive as possible to facilitate safe and timely operating conditions and recovery. Anatomy Surgical incisions are planned based on the expected extent of exposure needed for the specific operation planned. Within each region of the body, several incisions are common. Head and neck * Wilde's incision – This post-aural incision is used for a variant mastoiditis drainage, and was named after Sir William Wilde, an ENT surgeon in Dublin who first described it at the end of the nineteenth century. His son, Oscar Wilde's, death was stated by his doctors to be due to meningitis stemming from an ear infection. He had recently had an operation, believed by some to be a mastoidectomy. Chest * Median sternotomy – This is the primary incision used for cardiac pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/ os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at the front an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherney Incision
The Cherney incision is an incision used in gynecologic surgery. It is similar to the Pfannenstiel incision but allows access to the space of Retzius and gives a larger area in which to operate. __TOC__ Technique The Cherney incision begins when the skin is cut 2-3 centimeters above the pubic symphysis and the surgeon dissects down to the rectus abdominis muscle. The surgeon then uses blunt dissection with the fingers to separate the tendons from the overlying fascia before cutting the tendons 1-2 centimeters above the pubic symphysis. The muscles are then lifted away, toward the patient's head (cephalad). Then, the peritoneum can be cut and the surgery can proceed. Complications Complications can ensue. If surgical retractors are not placed carefully under the edges of the incision, they can damage the femoral nerve or other nerves in the area. If during wound closure, tendons are sewn directly to the pubic symphysis, osteitis pubis or osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis (OM) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
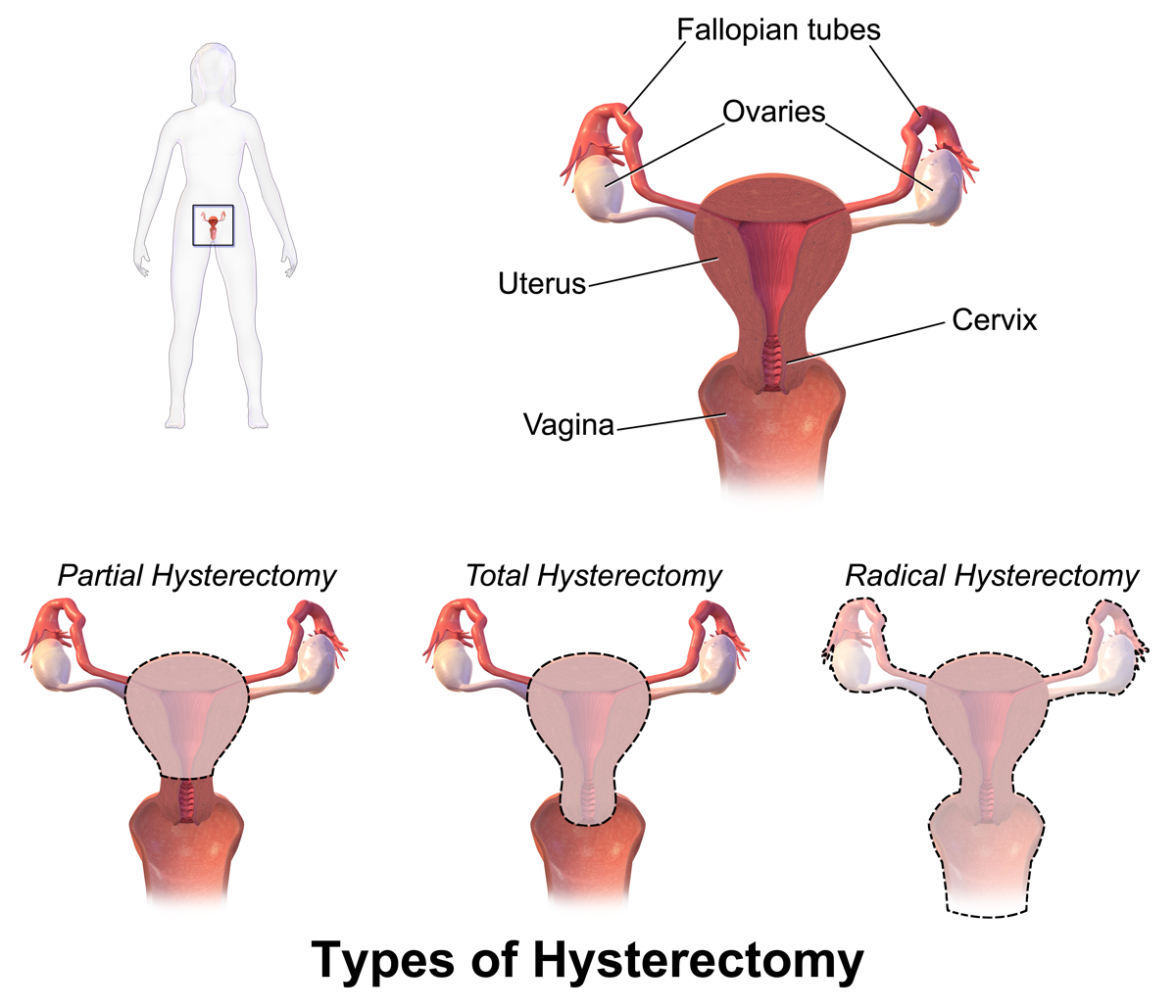
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. Supracervical hysterectomy refers to removal of the uterus while the cervix is spared. These procedures may also involve removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy), fallopian tubes ( salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. The term “partial” or “total” hysterectomy are lay-terms that incorrectly describe the addition or omission of oophorectomy at the time of hysterectomy. These procedures are usually performed by a gynecologist. Removal of the uterus is a form of sterilization, rendering the patient unable to bear children (as does removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) and has surgical risks as well as long-term effects, so the surgery is normally recommended only when other treatment options are not available or have failed. It is the second most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure, after cesarean section, in the United States. Nearly 68 percent were performed for conditions such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesarian Section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, cesarean, or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen. It is often performed because vaginal delivery would put the mother or child at risk (of paralysis or even death). Reasons for the operation include, but are not limited to, obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, breech birth, shoulder presentation, and problems with the placenta or umbilical cord. A caesarean delivery may be performed based upon the shape of the mother's pelvis or history of a previous C-section. A trial of vaginal birth after C-section may be possible. The World Health Organization recommends that caesarean section be performed only when medically necessary. A C-section typically takes 45 minutes to an hour. It may be done with a spinal block, where the woman is awake, or under general anesthesia. A urinary catheter is used to drain the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfannenstiel Incision
A Pfannenstiel incision , Kerr incision, Pfannenstiel-Kerr incision or pubic incision is a type of abdominal surgical incision that allows access to the abdomen. It is used for gynecologic and orthopedics surgeries, and it is the most common method for performing Caesarian sections today. This incision is also used in Stoppa approach for orthopedics surgeries to treat pelvic fractures. The Pfannenstiel incision offers a large view of the central pelvis but limits exposure to the lateral pelvis and upper abdomen, factors that limit the usefulness of this incision for gynecologic cancer surgery. This incision is commonly called the " bikini line incision". Some common reasons for this surgical access are obstetric delivery and hernia repair. It is often used in preference to other incision types for the sake of aesthetics, because the scar will be hidden by the pubic hair. The incision does not distort the belly button and heals faster than the traditional vertical incision. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trauma Surgery
Trauma surgery is a surgical specialty that utilizes both operative and non-operative management to treat traumatic injuries, typically in an acute setting. Trauma surgeons generally complete residency training in general surgery and often fellowship training in trauma or surgical critical care. The trauma surgeon is responsible for initially resuscitating and stabilizing and later evaluating and managing the patient. The attending trauma surgeon also leads the trauma team, which typically includes nurses and support staff, as well as resident physicians in teaching hospitals. Training Most United States trauma surgeons practice in larger centers and complete a 1- to 2-year trauma-surgery fellowship, which often includes a surgical critical-care fellowship. They may therefore sit for the American Board of Surgery (ABS) certifying examination in surgical critical care. National surgical boards usually supervise European training programs; they also certify for subspecia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
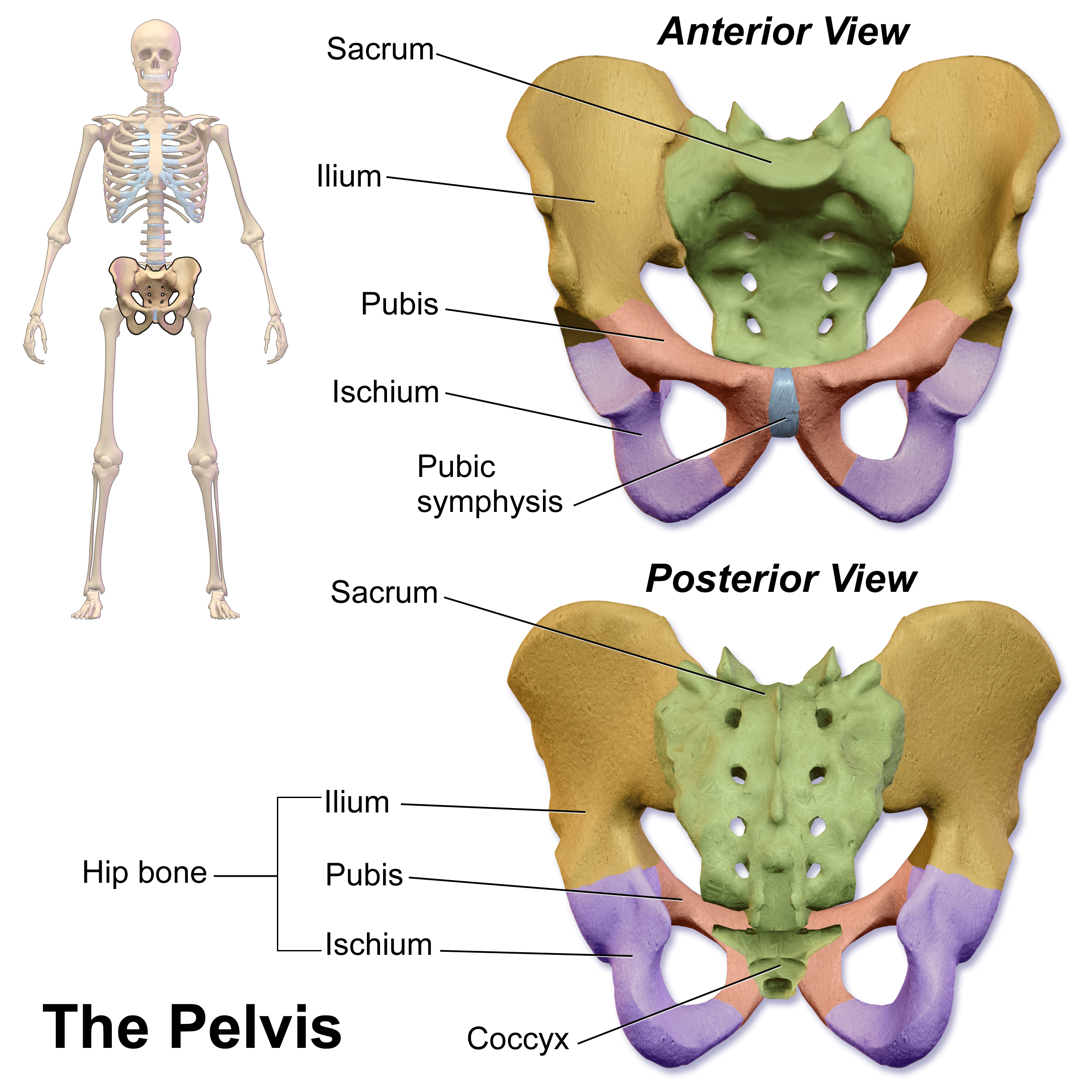
Pubic Symphysis
The pubic symphysis (: symphyses) is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is attached to the suspensory ligament of the clitoris. In most adults, it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus; : umbilici or umbilicuses; also known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord. Structure The umbilicus is used to visually separate the abdomen into quadrants. The umbilicus is a prominent Scar#Umbilical, scar on the abdomen, with its position being relatively consistent among humans. The skin around the waist at the level of the umbilicus is supplied by the tenth thoracic spinal nerve (T10 dermatome (anatomy), dermatome). The umbilicus itself typically lies at a vertical level corresponding to the junction between the L3 and L4 vertebrae, with a normal variation among people between the L3 and L5 vertebrae. Parts of the adult navel include the "umbilical cord remnant" or "umbilical tip", which is the often protruding scar left by the detachment of the umbilical cord. This is located in the center of the navel, sometimes described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphoid Process
The xiphoid process (), also referred to as the ensiform process, xiphisternum, or metasternum, constitutes a small cartilaginous process (extension) located in the inferior segment of the sternum, typically ossified in adult humans. Both the Greek-derived term ''xiphoid'' and its Latin equivalent, ''ensiform'', connote a "swordlike" or "sword-shaped" morphology. Structure The xiphoid process is anatomically situated at the level of the 9th thoracic vertebra (T9) and corresponds to the T7 dermatome. Development In neonates and young infants, particularly smaller infants, the tip of the xiphoid process may be seen as a palpable lump situated just below the sternal notch. Between the ages of 15 and 29, the xiphoid process typically undergoes fusion with the body of the sternum through a fibrous joint. Unlike the synovial articulation of major joints, this joint does not permit movement. Ossification of the xiphoid process typically occurs around the age of 40. Variation The xip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linea Alba (abdomen)
The linea alba (Latin for: white line) is a strong fibrous midline structure of the anterior abdominal wall situated between the two recti abdominis muscles (one on either side). The umbilicus (navel) is present on the linea alba through which foetal umbilical vessels pass before birth. The linea alba is formed by the union of aponeuroses (of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall) that collectively make up the rectus sheath. The linea alba attaches to the xiphoid process superiorly, and to the pubic symphysis inferiorly. It is narrow inferiorly where the two recti abdominis muscles are in contact with each other posterior to it, and broadens superior-ward from just inferior to the umbilicus. The name means ''white line'' as it is composed mostly of collagen connective tissue, which has a white appearance. In sufficiently muscular individuals, its presence can be seen on the skin, forming the depression between the left and right halves of a " six pack". Function The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a surgical incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as a celiotomy. Origins and history The first successful laparotomy was performed without anesthesia by Ephraim McDowell in 1809 in Danville, Kentucky. On July 13, 1881, George E. Goodfellow treated a miner outside Tombstone, Arizona Territory, who had been shot in the abdomen with a .32-caliber Colt revolver. Goodfellow was able to operate on the man nine days after he was shot, when he performed the first laparotomy to treat a bullet wound. Terminology The term comes from the Greek word λᾰπάρᾱ (lapara) 'the soft part of the body between the ribs and hip, flank' and the suffix ''-tomy'', from the Greek word τομή (tome) '(surgical) cut'. In diagnostic laparotomy (most often referred to as an exploratory laparotomy and abbreviated ex-lap), the nature of the disease is unknown, and laparotomy is deemed the bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |