|
Sulfides
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families of inorganic and organic compounds, e.g. lead sulfide and dimethyl sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and bisulfide (HS−) are the conjugate acids of sulfide. Chemical properties The sulfide ion does not exist in aqueous alkaline solutions of Na2S. Instead sulfide converts to hydrosulfide: :S2− + H2O → SH− + OH− Upon treatment with an acid, sulfide salts convert to hydrogen sulfide: :S2− + H+ → SH− :SH− + H+ → H2S Oxidation of sulfide is a complicated process. Depending on the conditions, the oxidation can produce elemental sulfur, polysulfides, polythionates, sulfite, or sulfate. Metal sulfides react with halogens, forming sulfur and metal salts. :8 MgS + 8 I2 → S8 + 8 MgI2 Metal derivati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
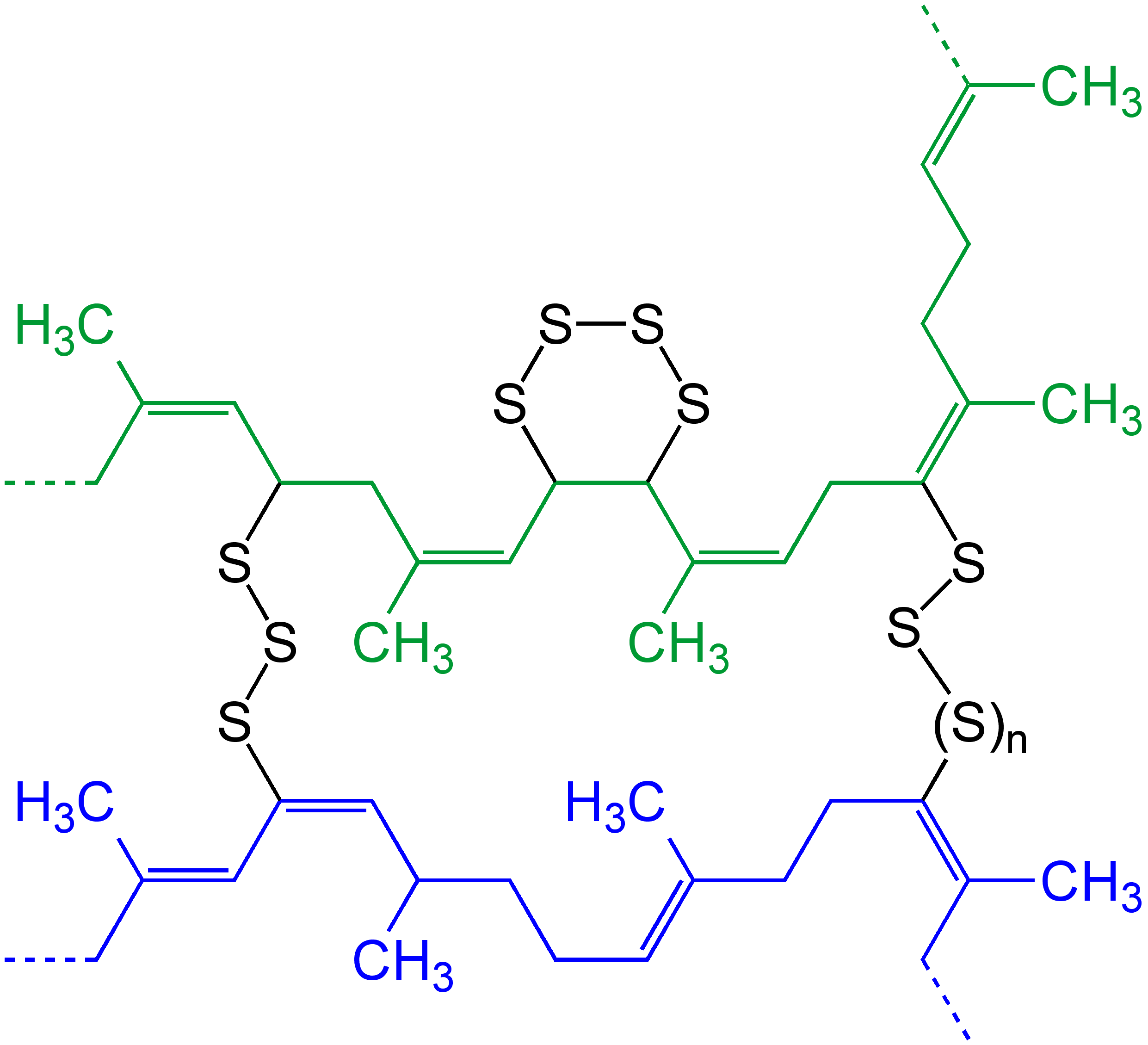
Polysulfide
Polysulfides are a class of chemical compounds derived from anionic chains of sulfur atoms. There are two main classes of polysulfides: inorganic and organic. The inorganic polysulfides have the general formula . These anions are the conjugate bases of polysulfanes . Organic polysulfides generally have the formulae , where R is an alkyl or aryl group. Polysulfide salts and complexes The alkali metal polysulfides arise by treatment of a solution of the sulfide with elemental sulfur, e.g. sodium sulfide to sodium polysulfide: In some cases, these anions have been obtained as organic salts, which are soluble in organic solvents. The energy released in the reaction of sodium and elemental sulfur is the basis of battery technology. The sodium–sulfur battery and the lithium–sulfur battery require high temperatures to maintain liquid polysulfide and -conductive membranes that are unreactive toward sodium, sulfur, and sodium sulfide. Polysulfides are ligands in coordination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of purified hydrogen sulfide in 1777. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic to humans and most other animals by inhibiting cellular respiration in a manner similar to hydrogen cyanide. When it is inhaled or its salts are ingested in high amounts, damage to organs occurs rapidly with symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to convulsions and death. Despite this, the human body produces small amounts of this sulfide and its mineral salts, and uses it as a signalling molecule. Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosulfur Compound
Organosulfur chemistry is the study of the properties and synthesis of organosulfur compounds, which are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature is abound with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is vital for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two ( cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries. Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium, and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium, and car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenide
A selenide is a chemical compound containing a selenium with oxidation number of −2. Similar to sulfide, selenides occur both as inorganic compounds and as organic derivatives, which are called organoselenium compound. Inorganic selenides The parent inorganic selenide is hydrogen selenide (H2Se). It is a colorless, malodorous, toxic gas. It dissolves in aqueous solution, to give the hydrogenselenide or biselenide ion HSe−. At higher pH, selenide forms. Solutions of hydrogen selenide and selenide are oxidized by air to give elemental selenium: : Most elements form selenides. They sometimes have salt-like properties, e.g. sodium selenide, but most exhibit covalent bonding, e.g. molybdenum diselenide. Their properties are diverse, mirroring the diverse properties of the corresponding sulfides. As indicated by the fact that only a few thousand tons of selenium are produced annually, the subset of selenium compounds called selenides find few applications. Commercially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Sulfide
Dimethyl sulfide (DMS) or methylthiomethane is an organosulfur compound with the formula . It is the simplest thioether and has a characteristic disagreeable odor. It is a flammable liquid that boils at . It is a component of the smell produced from cooking of certain vegetables (notably maize, cabbage, and beetroot) and seafoods. It is also an indication of bacterial contamination in malt production and brewing. It is a breakdown product of dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), and is also produced by the bacterial metabolism of methanethiol. Occurrence and production DMS originates primarily from DMSP, a major secondary metabolite in some marine algae. DMS is the most abundant biological sulfur compound emitted to the atmosphere. Emission occurs over the oceans by phytoplankton. DMS is also produced naturally by bacterial transformation of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) waste that is disposed of into sewers, where it can cause environmental odor problems. DMS is oxidized in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its Amphoterism, amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Lead compounds, Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
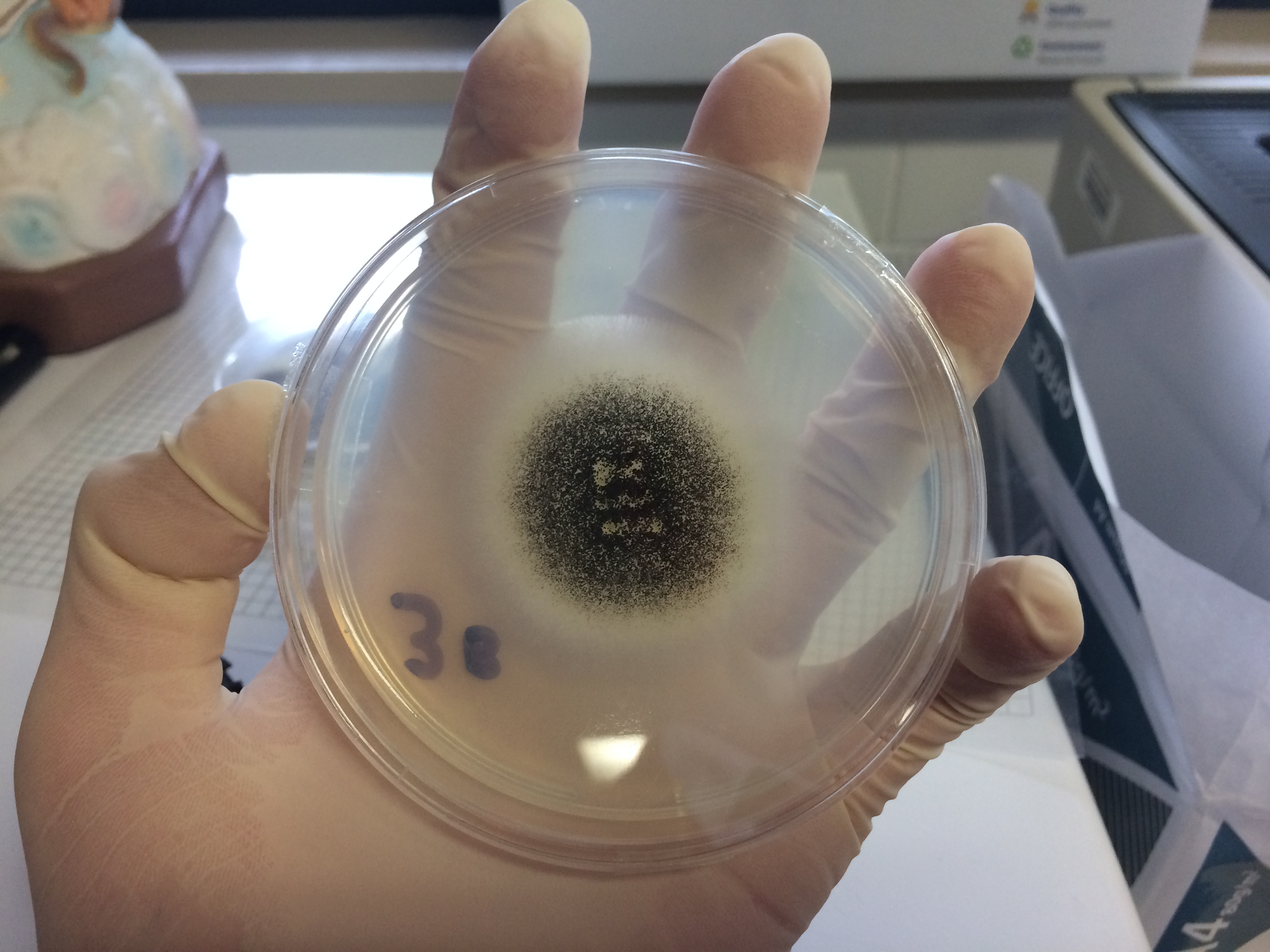
Aspergillus Niger
''Aspergillus niger'' is a mold classified within the ''Nigri'' section of the ''Aspergillus'' genus. The ''Aspergillus'' genus consists of common molds found throughout the environment within soil and water, on vegetation, in fecal matter, on decomposing matter, and suspended in the air. Species within this genus often grow quickly and can sporulate within a few days of germination. A combination of characteristics unique to ''A. niger'' makes the microbe invaluable to the production of many acids, proteins and bioactive compounds. Characteristics including extensive metabolic diversity, high production yield, secretion capability, and the ability to conduct post-translational modifications are responsible for ''A. niger's'' robust production of secondary metabolites. ''A. niger's'' capability to withstand extremely acidic conditions makes it especially important to the industrial production of citric acid. ''A. niger'' causes a disease known as "black mold" on certain fruits and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnabar
Cinnabar (; ), or cinnabarite (), also known as ''mercurblende'' is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of Mercury sulfide, mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining mercury (element), elemental mercury and is the historic source for the brilliant red or scarlet pigment termed vermilion and associated red mercury pigments. Cinnabar generally occurs as a vein-filling mineral associated with volcanic activity and Alkaline earth metal, alkaline hot springs. The mineral resembles quartz in symmetry and it exhibits birefringence. Cinnabar has a mean refractive index near 3.2, a mohs scale of mineral hardness, hardness between 2.0 and 2.5, and a specific gravity of approximately 8.1. The color and properties derive from a structure that is a hexagonal crystalline bravais lattice, lattice belonging to the trigonal crystal system, crystals that sometimes exhibit Crystal twinning, twinning. Cinnabar has been used for its color since antiquity in the Near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron transfer, Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one Substrate (chemistry), substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |