|
Storage Proteins
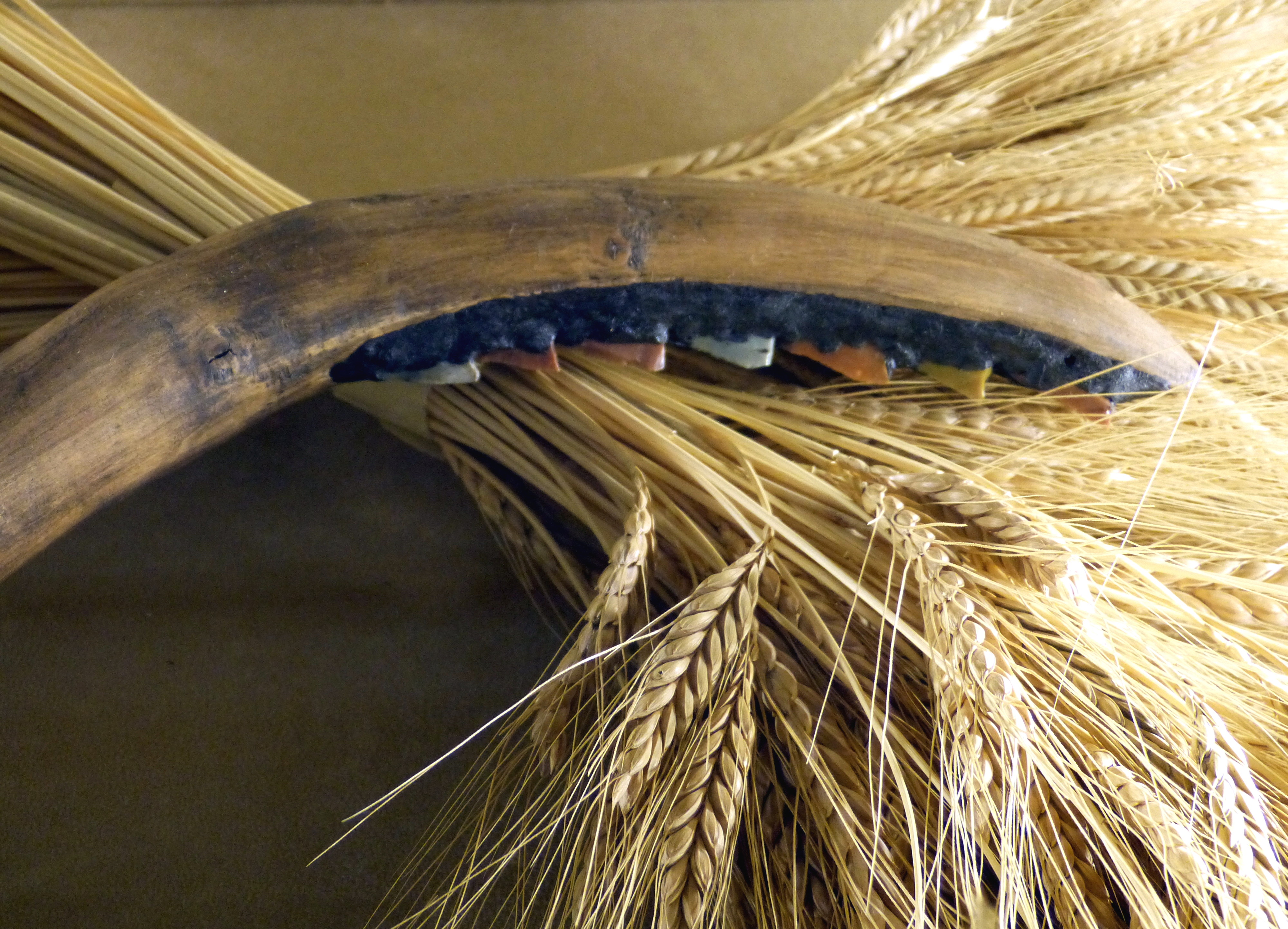
Storage proteins serve as biological reserves of metal ions and amino acids, used by organisms. They are found in plant seeds, egg whites, and milk. Ferritin is an example of a storage protein that stores iron. Iron is a component of heme, which is contained in the transport protein, hemoglobin and in cytochromes. Some storage proteins store amino acids. Storage proteins' amino acids are used in embryonic development of animals or plants. Two amino acid storage proteins in animals are casein and ovalbumin. Seeds, particularly of leguminous plants, contain high concentrations of storage proteins. Up to 25 percent of the dry weight of the seed can be composed of storage proteins. The best known storage protein in wheat is the prolamin gliadin, a component of gluten Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain Cereal, cereal grains. The term ''gluten'' usually refers to the elastic network of a wheat grain's proteins, gliadin and glutenin primarily, that forms rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ (potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− (chloride ion) and OH− (hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochromes
Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central iron (Fe) atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in the electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of binding. Four varieties are recognized by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB), cytochromes a, cytochromes b, cytochromes c and cytochrome d. Cytochrome function is linked to the reversible redox change from ferrous (Fe(II)) to the ferric (Fe(III)) oxidation state of the iron found in the heme core. In addition to the classification by the IUBMB into four cytochrome classes, several additional classifications such as cytochrome o and cytochrome P450 can be found in biochemical literature. History Cytochromes were initially described in 1884 by Charles Alexander MacMunn as respiratory pigments (myohematin or histohematin). In the 1920s, Keilin rediscovered these respiratory pigments and nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliadin
Gliadin (a type of prolamin) is a class of proteins present in wheat and several other cereals within the grass genus ''Triticum''. Gliadins, which are a component of gluten, are essential for giving bread the ability to rise properly during baking. Gliadins and glutenins are the two main components of the gluten fraction of the wheat seed. This gluten is found in products such as wheat flour. Gluten is split about evenly between the gliadins and glutenins, although there are variations found in different sources. Neither gliadins nor glutenins are water-soluble, but gliadins are soluble in 70% aqueous ethanol. There are three main types of gliadin (α, γ, and ω), to which the body is intolerant in coeliac disease, coeliac (or celiac) disease. Diagnosis of this disease has recently been improving. Gliadin can cross the intestinal epithelium. Breast milk of healthy human mothers who eat gluten, gluten-containing foods presents high levels of non-degraded gliadin. Types The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolamin
Prolamins are a group of plant storage proteins having a high proline amino acid content. They are found in plants, mainly in the seeds of cereal grains such as wheat ( gliadin), barley ( hordein), rye ( secalin), corn ( zein), sorghum ( kafirin), and oats ( avenin). They are characterised by a high glutamine and proline content, and have poor solubility in water. They solubilise best in strong alcohol (70–80%), light acid, and alkaline solutions. The prolamins of the tribe Triticeae, such as wheat gliadin, and related proteins (see Triticeae glutens) are known to trigger coeliac disease, an autoimmune condition, in genetically predisposed individuals. Maize and sorghum prolamins are sorted by molecular weight into four classes, α, β, γ and δ. Alpha- and delta- prolamins cluster in a broad phylogenetic group (Group 1). The rest cluster into Group 2. Group 1 is widely duplicated in the two plants. A database of Triticeae prolamins (glutens) is available. There does not s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, wheat species and hybrids include the most widely grown common wheat (''T. aestivum''), spelt, durum, emmer, einkorn, and Khorasan wheat, Khorasan or Kamut. The archaeological record suggests that wheat was first cultivated in the regions of the Fertile Crescent around 9600 BC. Wheat is grown on a larger area of land than any other food crop ( in 2021). World trade in wheat is greater than that of all other crops combined. In 2021, world wheat production was , making it the second most-produced cereal after maize (known as corn in North America and Australia; wheat is often called corn in countries including Britain). Since 1960, world production of wheat and other grain crops has tripled and is expected to grow further through the middle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2S Albumin
Plant lipid transfer proteins, also known as plant LTPs or PLTPs, are a group of highly- conserved proteins of about 7-9kDa found in higher plant tissues. As its name implies, lipid transfer proteins facilitate the shuttling of phospholipids and other fatty acid groups between cell membranes. LTPs are divided into two structurally related subfamilies according to their molecular masses: LTP1s (9 kDa) and LTP2s (7 kDa). Various LTPs bind a wide range of ligands, including fatty acids with a C10–C18 chain length, acyl derivatives of coenzyme A, phospho- and galactolipids, prostaglandin B2, sterols, molecules of organic solvents, and some drugs. The LTP domain is also found in seed storage proteins (including 2S albumin, gliadin, and glutelin) and bifunctional trypsin/ alpha-amylase inhibitors. These proteins share the same superhelical, disulfide-stabilised four-helix bundle containing an internal cavity. There is no sequence similarity between animal and plant LTPs. In animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabaceae
Fabaceae () or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. Article 18.5 states: "The following names, of long usage, are treated as validly published: ....Leguminosae (nom. alt.: Fabaceae; type: Faba Mill. Vicia L.; ... When the Papilionaceae are regarded as a family distinct from the remainder of the Leguminosae, the name Papilionaceae is conserved against Leguminosae." English pronunciations are as follows: , and . commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, is a large and agriculturally important family of |
Ovalbumin
Ovalbumin (abbreviated OVA) is the main protein found in egg white, making up approximately 55% of the total protein. Ovalbumin displays sequence and three-dimensional homology to the serpin superfamily, but unlike most serpins it is not a serine protease inhibitor. The function of ovalbumin is unknown, although it is presumed to be a storage protein. Research Ovalbumin is an important protein in several different areas of research, including: * general studies of protein structure and properties (because it is available in large quantities). * studies of serpin structure and function (the fact that ovalbumin does not inhibit proteases means that by comparing its structure with that of inhibitory serpins, the structural characteristics required for inhibition can be determined). * proteomics (chicken egg ovalbumin is commonly used as a molecular weight marker for calibrating electrophoresis gels). * immunology (commonly used to stimulate an allergic reaction in test subjects; e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casein
Casein ( , from Latin ''caseus'' "cheese") is a family of related phosphoproteins (CSN1S1, αS1, aS2, CSN2, β, K-casein, κ) that are commonly found in mammalian milk, comprising about 80% of the proteins in cow's milk and between 20% and 60% of the proteins in breast milk, human milk. Sheep's milk, Sheep and cow milk have a higher casein content than other types of milk with human milk having a particularly low casein content. Casein is the primary emulsifier in milk, that is, it helps in mixing oils, fats, and water in milk. Casein has a wide variety of uses, from being a major component of cheese, to use as a food additive. The most common form of casein is sodium caseinate (historically called nutrose), which is a very efficient emulsifier. Casein is secreted into milk from mammary cells in the form of colloidal casein micelles, a type of biomolecular condensate. As a food source, casein supplies amino acids, carbohydrates, and two essential elements, calcium and phosphoru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin in the blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (lungs or gills) to the other tissues of the body, where it releases the oxygen to enable aerobic respiration which powers an animal's metabolism. A healthy human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein, a chromoprotein, and a globulin. In mammals, hemoglobin makes up about 96% of a red blood cell's dry matter, dry weight (excluding water), and around 35% of the total weight (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL of O2 per gram, which increases the total blood oxygen capacity seventy-fold compared to dissolved oxygen in blood plasma alone. The mammalian hemoglobin molecule can bind and transport up to four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups (Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- (γ-) amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, Chemical polarity, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid ''Residue (chemistry)#Biochemistry, residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissue (biology), tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
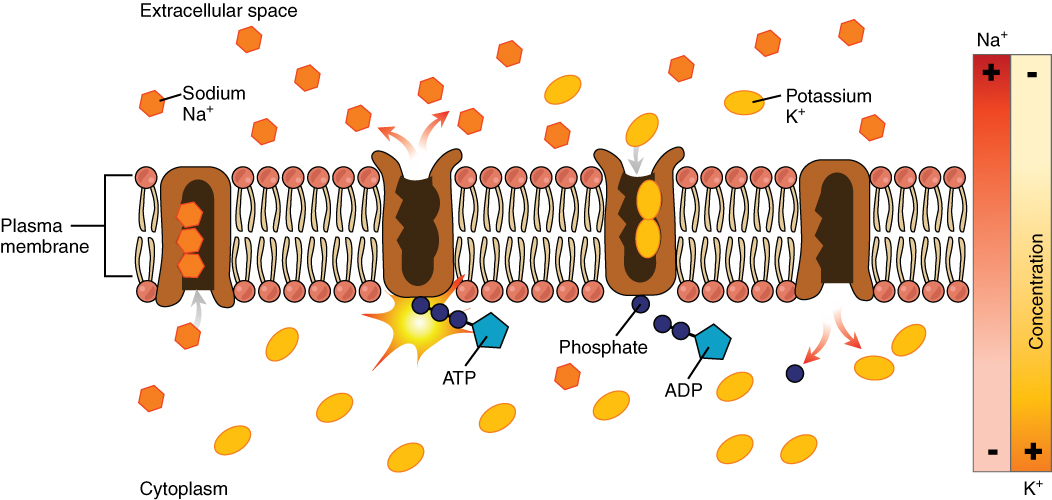
Transport Protein
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins. Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport. Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. Resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |