|
Space Program Of The People's Republic Of China
The space program of the People's Republic of China is about the activities in outer space conducted and directed by the China, People's Republic of China. The roots of the Chinese space program trace back to the 1950s, when, with the help of the Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Alliance and Mutual Assistance, newly allied Soviet Union, China began development of its first ballistic missile and rocket programs in response to the perceived American (and, Sino-Soviet split, later, Soviet) threats. Driven by the successes of Soviet Sputnik 1 and American Explorer 1 satellite launches in 1957 and 1958 respectively, China would launch its first satellite, Dong Fang Hong 1 in April 1970 aboard a Long March 1 rocket, making it the fifth nation to place a satellite in orbit. China has one of the most active space programs in the world. With space launch capability provided by the Long March rocket family and four spaceports (Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, Jiuquan, Taiyuan Satelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long March 1
The Long March 1 (长征一号), also known as the Changzheng-1 (CZ-1), was the first member of China's Long March 1 (rocket family), Long March rocket family. Like the U.S.'s and the Soviet Union's first rockets, it was based on a class of ballistic missiles, namely the DF-4 class. History Development started in January 1965 as the Seventh Ministry of Machinery Industry issued a design task. The two stage liquid fueled DF-4 was modified by adding a third stage in order to make it to the desired orbit. Long March 1's second flight launched China's first satellite Dong Fang Hong 1 to space on 24 April 1970. The rocket was operational during 1970–1971. Wang Xiji was the chief designer of the rocket. Launch History See also * DF-4 - ICBM on which this rocket is based * Long March 1D - Other member of this rocket family * YF-1#Modules, YF-2A - Main propulsion module * FG-02 - Upper stage References {{Long March rockets Long March (rocket family) Vehicles intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer 1
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year (IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites, both launched by the Soviet Union during the previous year, Sputnik 1 and Sputnik 2. This began a Space Race during the Cold War between the two nations. Explorer 1 was launched on 1 February 1958 at 03:47:56 Greenwich Mean Time, GMT (or 31 January 1958 at 22:47:56 Eastern Time) atop the first Juno I booster from Cape Canaveral Launch Complex 26, LC-26A at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Cape Canaveral Missile Test Center of the Eastern Range, Atlantic Missile Range (AMR), in Florida. It was the first spacecraft to detect the Van Allen radiation belt, returning data until its batteries were exhausted after nearly four months. It remained in orbit until 1970. Explorer 1 was given Satellite Catalog Number 00004 and the Harvard designation 1958 Alpha 1, the forerunner to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Spaceflight
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be telerobotic, remotely operated from ground stations on Earth, or Autonomous robot, autonomously, without any direct human involvement. People trained for spaceflight are called astronauts (American or other), ''cosmonauts'' (Russian), or ''taikonauts'' (Chinese); and non-professionals are referred to as spaceflight participants or ''spacefarers''. The first human in space was Soviet Union, Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, who launched as part of the Soviet Union's Vostok program on Cosmonautics Day, 12 April 1961 at the beginning of the Space Race. On 5 May 1961, Alan Shepard became the first American in space, as part of Project Mercury. Humans traveled to the Moon nine times between 1968 and 1972 as part of the United States' Apollo progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
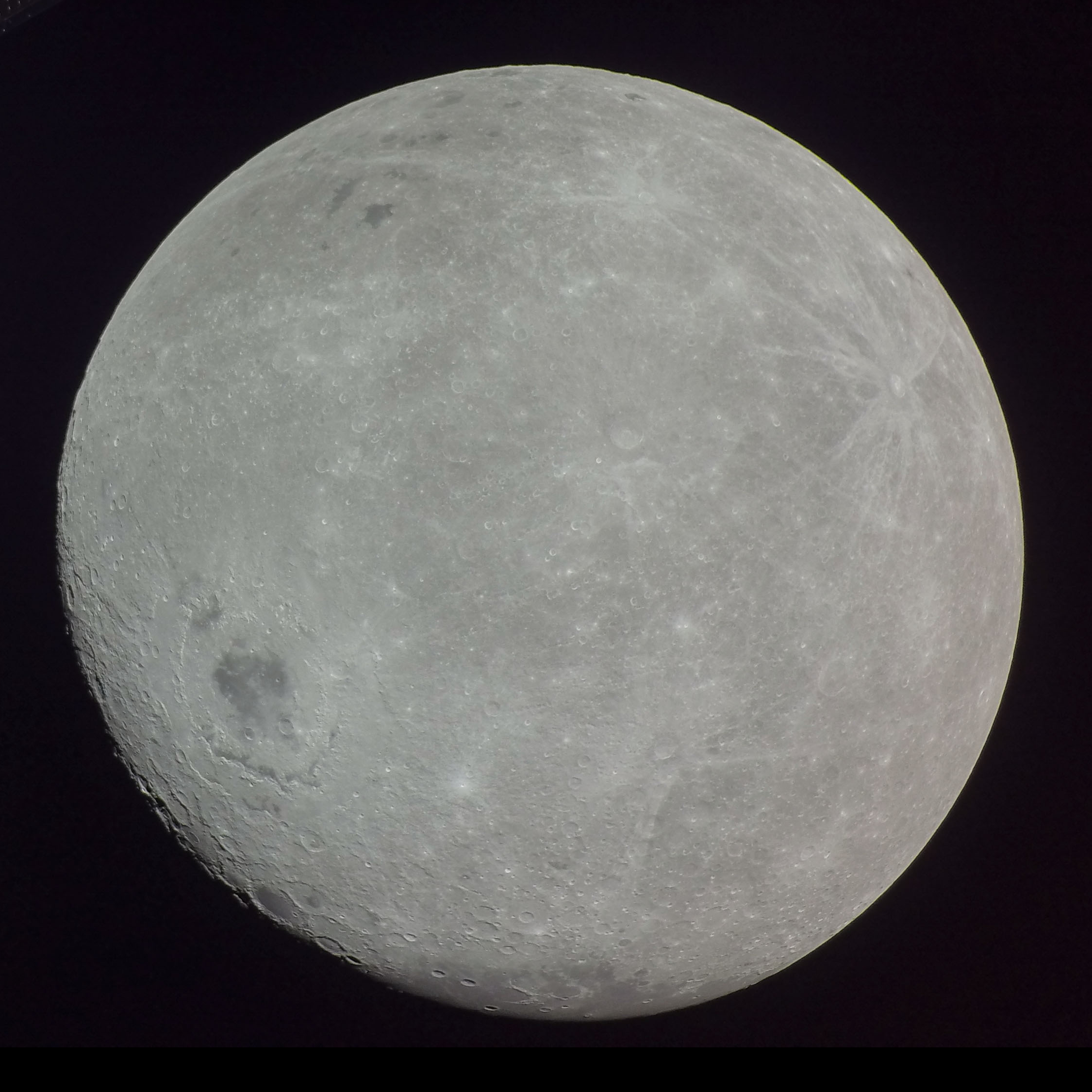
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (Lunar month#Synodic month, lunar month) of 29.5 Earth days. This is the product of Earth's gravitation having tidal forces, tidally pulled on the Moon until one part of it stopped rotating away from the near side of the Moon, near side, making always the same lunar surface face Earth. Conversley, the gravitational pull of the Moon, on Earth, is the main driver of Earth's tides. In geophysical definition of planet, geophysical terms, the Moon is a planetary-mass object or satellite planet. Its mass is 1.2% that of the Earth, and its diameter is , roughly one-quarter of Earth's (about as wide as the contiguous United States). Within the Solar System, it is the List of Solar System objects by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, peaking in number at an altitude around , while the farthest in LEO, before medium Earth orbit (MEO), have an altitude of 2,000 km, about one-third of the Earth radius, radius of Earth and near the beginning of the Van Allen radiation belt#Inner belt, inner Van Allen radiation belt. The term ''LEO region'' is used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. No human spaceflights other than the lunar missions of the Apollo program (1968-1972) have gone beyond L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Strategic And International Studies
The Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) is an American think tank based in Washington, D.C. From its founding in 1962 until 1987, it was an affiliate of Georgetown University, initially named the Center for Strategic and International Studies of Georgetown University. The center conducts policy studies and strategic analyses of political, economic and security issues throughout the world, with a focus on issues concerning international relations, trade, technology, finance, energy and geostrategy. Since its founding, CSIS "has been dedicated to finding ways to sustain American prominence and prosperity as a force for good in the world", according to its website. CSIS is officially a bipartisan think tank with scholars that represent varying points of view across the political spectrum. It is known for inviting well-known foreign policy and public service officials from the U.S. Congress and the executive branch, including those affiliated with either the Democ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Spaceflight
This is a timeline of known spaceflights, both crewed and uncrewed, sorted chronologically by launch date. Due to its large size, the timeline has been split into smaller articles, one for each year since 1951. There is a separate list for all flights that occurred before 1951. The list for the year and for its subsequent years may contain planned launches, but the statistics will only include past launches. For the purpose of these lists, a spaceflight is defined as any flight that crosses the Kármán line, the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, FAI-recognized edge of space, which is Above mean sea level, above mean sea level (AMSL). The timeline contains all the flights which have either crossed the edge of space, were intended to do so but failed, or are planned in the near future. Notable test flights of spaceflight systems may be listed even if they were not planned to reach space. Some lists are further divided into orbital launches (sending a payload into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site
The Wenchang Space Launch Site ( zh, 文昌航天发射场, links=no) is a rocket launch site located in Wenchang on the island of Hainan, in China. Formally a suborbital test center, it currently serves as China's southernmost spaceport. The site was selected for its low latitude, 19° north of the equator, allowing for larger payloads to be launched. It is capable of launching the Long March 5, the heaviest Chinese rocket. Unlike launch facilities on the mainland, Wenchang uses its seaport for deliveries. The construction of the site was complete by October 2014. The first launch took place on 25 June 2016. Due to construction delays, the initial launch of the CZ-5 booster from Wenchang, originally expected to start in 2014 was postponed and took place on 3 November 2016. The CZ-5B (maximum payload to LEO) variant was expected to be completed circa 2018 but the maiden flight took place on 5 May 2020. A CZ-5 carrier rocket was already shipped from North China's Tia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xichang Satellite Launch Center
The Xichang Satellite Launch Center (XSLC), also known as the Xichang Space Center, is a spaceport in China. It is located in (), Mianning county, approximately northwest of Xichang, Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture in Sichuan. It is operated by the People's Liberation Army Aerospace Force (formerly the People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force) and is known as the 27th Experimental Training base( MUCD: Unit 63790). The facility became operational in 1984 and is used to launch numerous civil, scientific, and military payloads annually. It is notable as the site of Sino-European space cooperation, with the launch of the first of two Double Star scientific satellites in December 2003. Chinese officials have indicated interest in conducting additional international satellite launches from XSLC. In 1996, a fatal accident occurred when the Long March 3B rocket carrying the Intelsat 708 satellite failed on its maiden launch from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center
The Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center (TSLC) also known as ''Base 25'' (), is a People's Republic of China space and defense launch facility (spaceport). It is situated in Kelan County, Xinzhou, Shanxi Province and is the second of four launch sites having been founded in March 1966 and coming into full operation in 1968. The facility was built as part of China's Third Front campaign to develop basic industry and national security in China's rugged interior in case of invasion by the Soviet Union or the United States. Taiyuan sits at an altitude of 1500 meters and its dry climate makes it an ideal launch site. The site is primarily used to launch meteorological satellites, Earth resource satellites and scientific satellites on Long March launch vehicles into Sun-synchronous orbits. TSLC is also a major launch site for intercontinental ballistic missiles and overland submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) tests. The site has a sophisticated Technical Center and Missio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |