|
Software-defined Radio
Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that conventionally have been implemented in analog hardware (e.g. mixers, filters, amplifiers, modulators/ demodulators, detectors, etc.) are instead implemented by means of software on a computer or embedded system. A basic SDR system may consist of a computer equipped with a sound card, or other analog-to-digital converter, preceded by some form of RF front end. Significant amounts of signal processing are handed over to the general-purpose processor, rather than being done in special-purpose hardware (electronic circuits). Such a design produces a radio which can receive and transmit widely different radio protocols (sometimes referred to as waveforms) based solely on the software used. Software radios have significant utility for the military and cell phone services, both of which must serve a wide variety of changing radio protocols in real time. In the long term, software-defined radios a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver; this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Defined Antenna
A reconfigurable antenna is an antenna (radio), antenna capable of modifying its frequency and radiation pattern dynamically, in a controlled and reversible manner. In order to provide a dynamic response, reconfigurable antennas integrate an inner mechanism (such as RF switches, varicap, varactors, actuator, mechanical actuators or tunable metamaterials, tunable materials) that enable the intentional redistribution of the RF currents over the antenna surface and produce reversible modifications of its properties. Reconfigurable antennas differ from smart antennas because the reconfiguration mechanism lies inside the antenna, rather than in an external beamforming network. The reconfiguration capability of reconfigurable antennas is used to maximize the antenna performance in a changing scenario or to satisfy changing operating requirements. Types of antenna reconfiguration Reconfigurable antennas can be classified according to the antenna parameter that is dynamically adjusted, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
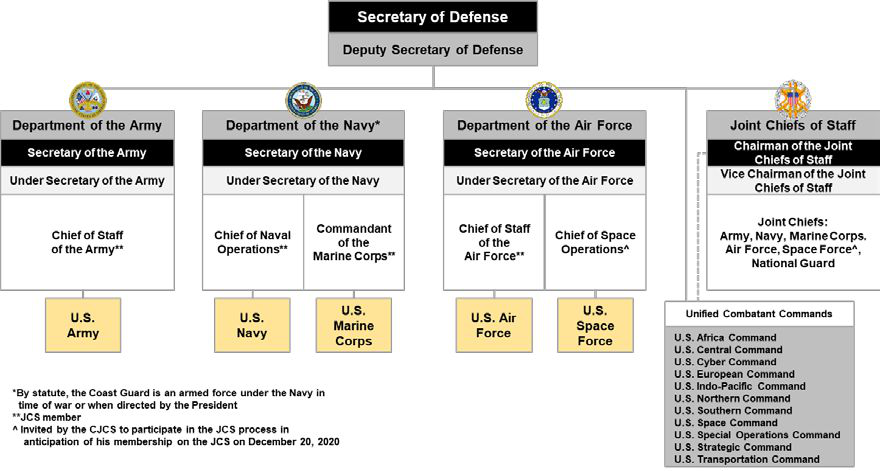
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Spectrum
''IEEE Spectrum'' is a magazine edited and published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. The first issue of ''IEEE Spectrum'' was published in January 1964 as a successor to ''Electrical Engineering''. In 2010, ''IEEE Spectrum'' was the recipient of '' Utne Reader'' magazine's Utne Independent Press Award for Science/Technology Coverage. In 2012, ''IEEE Spectrum'' was selected as the winner of the National Magazine Awards "General Excellence Among Thought Leader Magazines" category. References External links * Monthly magazines published in the United States Science and technology magazines published in the United States Engineering magazines Spectrum A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of co ... Magazines established in 1964 Magazines pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band-pass Filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects ( attenuates) frequencies outside that range. It is the inverse of a '' band-stop filter''. Description In electronics and signal processing, a filter is usually a two-port circuit or device which removes frequency components of a signal (an alternating voltage or current). A band-pass filter allows through components in a specified band of frequencies, called its ''passband'' but blocks components with frequencies above or below this band. This contrasts with a high-pass filter, which allows through components with frequencies above a specific frequency, and a low-pass filter, which allows through components with frequencies below a specific frequency. In digital signal processing, in which signals represented by digital numbers are processed by computer programs, a band-pass filter is a computer algorithm that performs the same function. The term band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Range
Dynamics (from Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' " power") or dynamic may refer to: Physics and engineering * Dynamics (mechanics), the study of forces and their effect on motion Brands and enterprises * Dynamic (record label), an Italian record label in Genoa Mathematics * Dynamical system, a concept describing a point's time dependency ** Topological dynamics, the study of dynamical systems from the viewpoint of general topology * Symbolic dynamics, a method to model dynamical systems Social science * Group dynamics, the study of social group processes especially * Population dynamics, in life sciences, the changes in the composition of a population * Psychodynamics, the study of psychological forces driving human behavior * Social dynamics, the ability of a society to react to changes * Spiral Dynamics, a social development theory Other uses * Dynamics (music), the softness or loudness of a sound or note * DTA Dynami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spurious Emission
In radio communication, a spurious emission is any component of a radiated radio frequency signal, the complete suppression of which, would not impair the integrity of the modulation type, or the information being transmitted. A radiated signal outside of a transmitter's assigned channel is an example of a spurious emission. Spurious emissions can include harmonic emissions, intermodulation Intermodulation (IM) or intermodulation distortion (IMD) is the amplitude modulation of Signal (electrical engineering), signals containing two or more different frequencies, caused by non-linear, nonlinearities or time variance in a system. ... products and frequency conversion products. See also * Interference (communication) * Radio spectrum pollution References Radio technology {{radio-comm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-noise Amplifier
A low-noise amplifier (LNA) is an electronic component that amplifies a very low-power signal without significantly degrading its signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Any electronic amplifier will increase the power of both the signal and the noise present at its input, but the amplifier will also introduce some additional noise. LNAs are designed to minimize that additional noise, by choosing special components, operating points, and circuit topologies. Minimizing additional noise must balance with other design goals such as power gain and impedance matching. LNAs are found in radio communications systems, Amateur Radio stations, medical instruments and electronic test equipment. A typical LNA may supply a power gain of 100 (20 decibels (dB)) while decreasing the SNR by less than a factor of two (a 3 dB noise figure (NF)). Although LNAs are primarily concerned with weak signals that are just above the noise floor, they must also consider the presence of larger signals tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into an electrical signal. For example, the electronic output of a microphone is a baseband signal that is analogous to the applied voice audio. In conventional analog radio broadcasting, the baseband audio signal is used to modulate an RF carrier signal of a much higher frequency. A baseband signal may have frequency components going all the way down to the DC bias, or at least it will have a high ratio bandwidth. A modulated baseband signal is called a passband signal. This occupies a higher range of frequencies and has a lower ratio and fractional bandwidth. Various uses Baseband signal A ''baseband signal'' or ''lowpass signal'' is a signal that can include frequencies that are very near zero, by comparison with its highest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency (IF) is a frequency to which a carrier wave is shifted as an intermediate step in Transmission (telecommunications), transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called heterodyning, resulting in a signal at the difference or beat frequency. Intermediate frequencies are used in Superheterodyne receiver, superheterodyne radio receivers, in which an incoming signal is shifted to an IF for Amplifier, amplification before final Detector (radio), detection is done. Conversion to an intermediate frequency is useful for several reasons. When several stages of filters are used, they can all be set to a fixed frequency, which makes them easier to build and to tune. Lower frequency transistors generally have higher gains so fewer stages are required. It's easier to make sharply selective filters at lower fixed frequencies. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
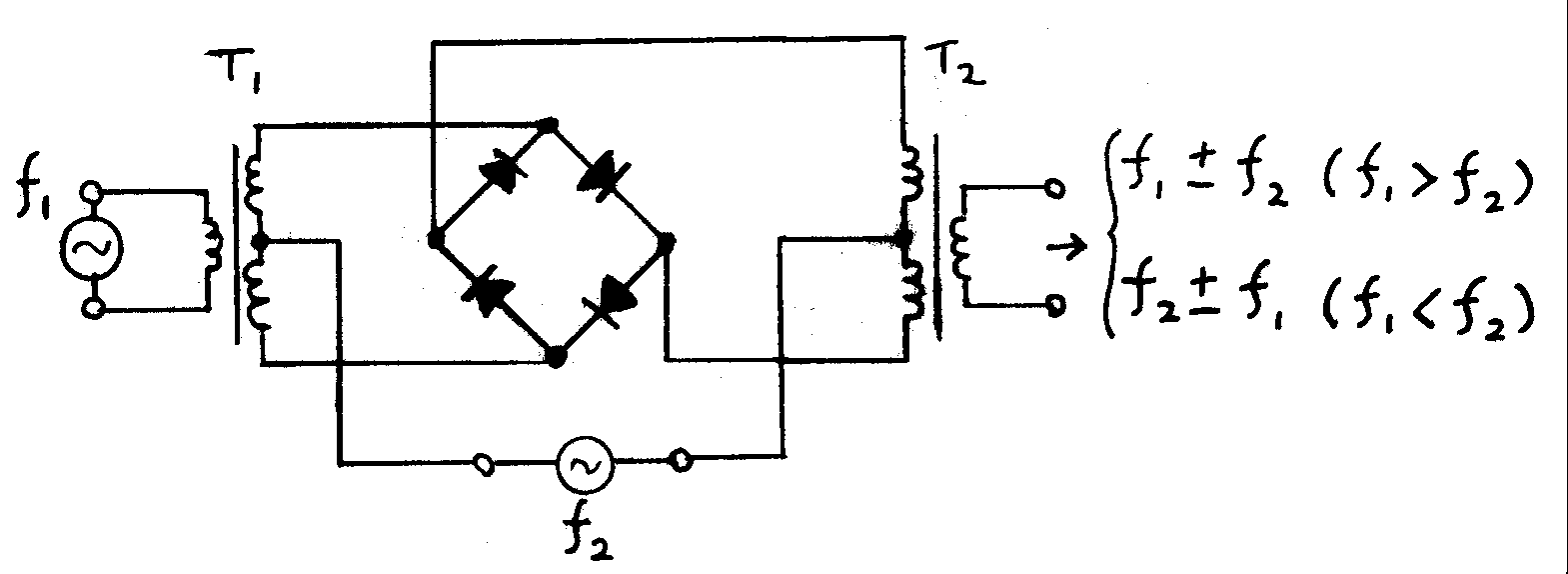
Frequency Mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer. Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulation, modulate a carrier signal in Transmitter, radio transmitters. Types The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable-frequency Oscillator
A variable frequency oscillator (VFO) in electronics is an oscillator whose frequency can be tuned (i.e., varied) over some range. It is a necessary component in any tunable radio transmitter and in receivers that work by the superheterodyne principle. The oscillator controls the frequency to which the apparatus is tuned. Purpose In a simple superheterodyne receiver, the incoming radio frequency signal (at frequency f_) from the antenna is ''mixed'' with the VFO output signal tuned to f_, producing an intermediate frequency (IF) signal that can be processed downstream to extract the modulated information. Depending on the receiver design, the IF signal frequency is chosen to be either the sum of the two frequencies at the mixer inputs ( up-conversion), f_+f_ or more commonly, the difference frequency (down-conversion), f_-f_. In addition to the desired ''IF'' signal and its unwanted image (the mixing product of opposite sign above), the mixer output will also contain the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |