|
Shoulder Medial Rotators
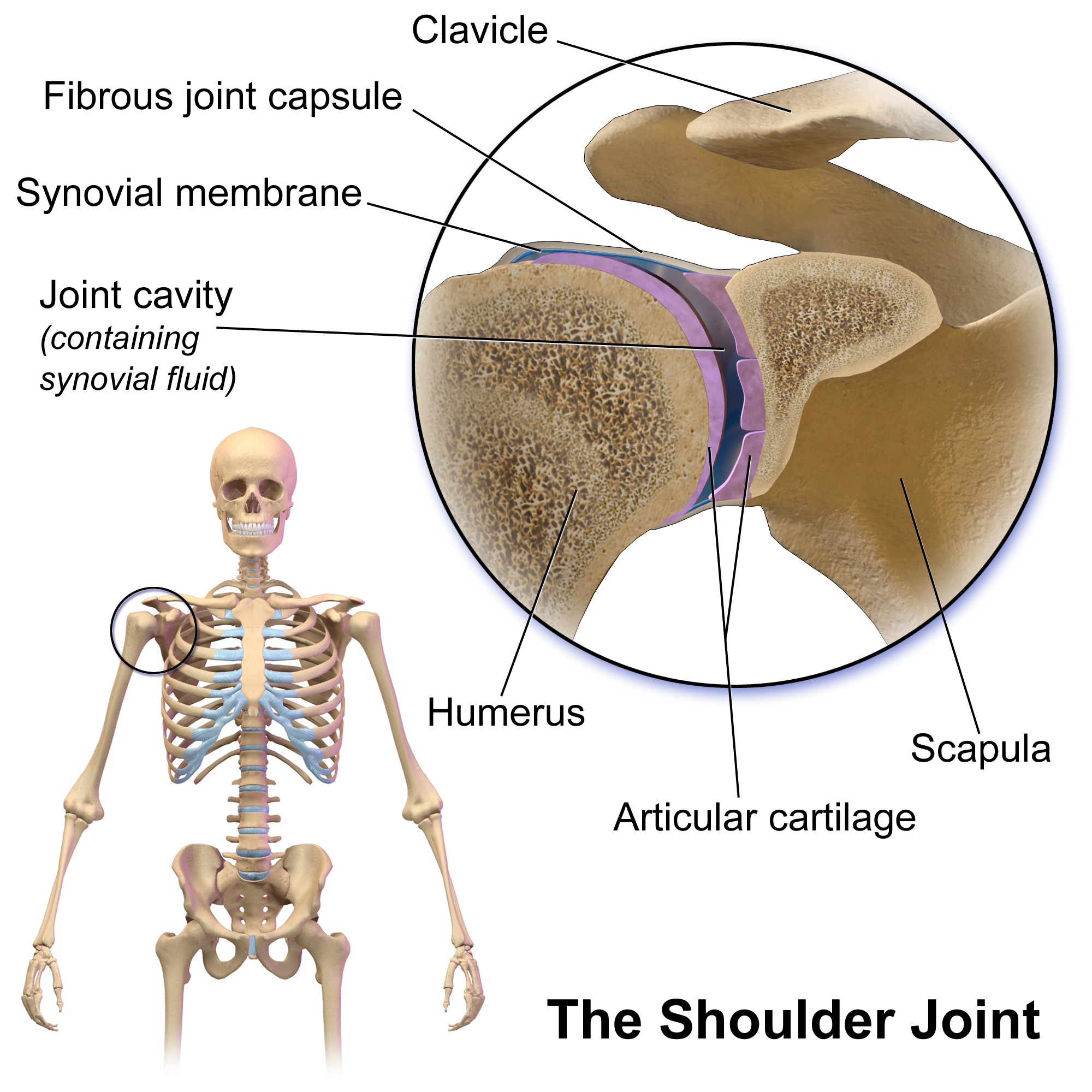
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is the major joint of the shoulder, but can more broadly include the acromioclavicular joint. In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, and the head sits in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint. The shoulder joint is the main joint of the shoulder. It is a ball and socket joint that allows the arm to rotate in a circular fashion or to hinge out and up away from the body. The joint capsule is a soft tissue envelope that encircles the glenohumeral joint and attaches to the scapula, humerus, and head of the biceps. It is lined by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from Latin ''clavicula'' 'little key' because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is Abduction (kinesiology), abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the human arm, arm to the torso, trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenohumeral Capsule
The capsule of the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint is the articular capsule of the shoulder. It completely surrounds the joint. It is attached above to the circumference of the glenoid cavity beyond the glenoidal labrum, and below to the anatomical neck of the humerus, approaching nearer to the articular cartilage above than in the rest of its extent. It is thicker above and below than elsewhere, and is so remarkably loose and lax, that it has no action in keeping the bones in contact, but allows them to be separated from each other more than 2.5 cm, an evident provision for that extreme freedom of movement which is peculiar to this articulation. It is strengthened, above, by the supraspinatus; below, by the long head of the triceps brachii; behind, by the tendons of the infraspinatus and teres minor; and in front, by the tendon of the subscapularis. Structure There are usually three openings in the capsule. * One anteriorly, below the coracoid process, establishes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Tubercle Of Humerus
The lesser tubercle of the humerus The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extrem ..., although smaller, is more prominent than the greater tubercle: it is situated in front, and is directed medially and anteriorly. The projection of the lesser tubercle is anterior from the junction that is found between the anatomical neck and the shaft of the humerus and easily identified due to the intertubercular sulcus (Bicipital groove). Above and in front it presents an impression for the insertion of the tendon of the subscapularis. Additional images File:Gray326.png, The left shoulder and acromioclavicular joints, and the proper ligaments of the scapula. File:Human arm bones diagram.svg, Human arm bones diagram References External links * * * Diagram at uwlax.edu Bones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Humeral Ligament
The transverse humeral ligament (Brodie's ligament) forms a broad band bridging the lesser and greater tubercle of the humerus. Its attachments are limited superior to the epiphysial line. By enclosing the canal of the bicipital groove (intertubercular groove), it functions to hold the long head of the biceps tendon within the bicipital groove. Studies using MRIs, cadaver dissections, and histological analysis suggest that the transverse humeral ligament may not actually be a ligament A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ..., but simply a portion of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle often mistaken for a separate ligament during dissections. References Ligaments of the upper limb {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Dislocation
A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are commonly caused by sudden Trauma (medicine), trauma to the joint like during a car accident or fall. A joint dislocation can damage the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Dislocations can occur in any major joint (shoulder, knees, hips) or minor joint (toes, fingers). The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation. The treatment for joint dislocation is usually by closed reduction (orthopedic surgery), reduction, that is, skilled manipulation to return the bones to their normal position. Only trained medical professionals should perform reductions since the manipulation can cause injury to the surrounding soft tissue, nerves, or vascular structures. Signs and Symptoms The following symptoms are common with any type of dislocation. * Intense pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blausen 0797 ShoulderJoint
Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (BMC) is the creator and owner of a library of two- and three-dimensional medical and scientific images and animations, a developer of information technology allowing access to that content, and a business focused on licensing and distributing the content. It was founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas, in 1991, and is privately held. Background Blausen Medical Communications is a privately held company founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas in 1991. BMC created and owns a library of medical and scientific images and animations, and has developed information technology tools allowing access to the library; as well, it licenses and otherwise works to distribute the content. As of this date, BMC's animation library comprised approximately 1,500 animations and over 27,000 two- and three-dimensional images designed for point-of-care patient education, which could be accessed by consumers or professional caregivers (primarily via hospital o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenoid Labrum
The glenoid labrum (glenoid ligament) is a fibrocartilaginous (but not fibrocartilage, as previously thought) structure attached around the rim of the glenoid cavity on the shoulder blade. The shoulder joint is considered a ball-and-socket joint. However, in bony terms the 'socket' (the Glenoid cavity, glenoid fossa of the scapula) is quite shallow and small, covering at most only a third of the 'ball' (the Humerus, head of the humerus). The socket is deepened by the glenoid labrum, stabilizing the shoulder joint. The labrum is triangular in section; the base is fixed to the circumference of the cavity, while the free edge is thin and sharp. It is continuous above with the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii, which gives off two muscle fascicle, fascicles to blend with the fibrous tissue of the labrum. Structure Clinical significance Injury Tearing of the labrum can occur from either Major trauma, acute trauma or repetitive shoulder motion such as in the sports of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |