|
Rapids
Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep stream gradient, gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence. Flow, gradient, constriction, and obstacles are four factors that are needed for a rapid to be created. Physical factors Rapids are hydrology, hydrological features between a ''run'' (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a ''waterfall#Types, cascade''. Rapids are characterized by the river becoming shallower with some Rock (geology), rocks exposed above the flow surface. As flowing water splashes over and around the rocks, air bubbles become mixed in with it and portions of the surface acquire a white color, forming what is called "whitewater". Rapids occur where the stream bed, bed material is highly resistant to the erosive power of the stream in comparison with the bed downstream of the rapids. Very young streams flowing across solid rock may be rapids for much of their length. Rapids cause water aeration of the stream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitewater
Whitewater forms in the context of rapids, in particular, when a river's Stream gradient, gradient changes enough to generate so much turbulence that air is trapped within the water. This forms an unstable current that foam, froths, making the water appear opaque and white. The term "whitewater" also has a broader meaning, applying to any river or creek that has a significant number of rapids. The term is also used as an adjective describing boating on such rivers, such as whitewater canoeing or whitewater kayaking. Fast rivers Four factors, separately or in combination, can create rapids: gradient, constriction, obstruction, and flow rate. Gradient, constriction, and obstruction are streambed topography factors and are relatively consistent. Flow rate is dependent upon both seasonal variation in precipitation and snowmelt and upon release rates of upstream dams. Streambed topography Streambed topography is the primary factor in creating rapids, and is generally consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapids Of Kern River, California, USA
Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence. Flow, gradient, constriction, and obstacles are four factors that are needed for a rapid to be created. Physical factors Rapids are hydrological features between a ''run'' (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a ''cascade''. Rapids are characterized by the river becoming shallower with some rocks exposed above the flow surface. As flowing water splashes over and around the rocks, air bubbles become mixed in with it and portions of the surface acquire a white color, forming what is called "whitewater". Rapids occur where the bed material is highly resistant to the erosive power of the stream in comparison with the bed downstream of the rapids. Very young streams flowing across solid rock may be rapids for much of their length. Rapids cause water aeration of the stream or river, resulting in better water quality. For a rapid to form, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuhakoski
Kuhakoski (; literally meaning " zander rapids") is a rapids near the village of Perttula in Nurmijärvi, Finland.Kuhakoski - Suomen vesiputoukset (in Finnish) It is located in the immediate vicinity of the Numlahti Manor and the Regional Road 132, north of . At the same time, Kuhakoski is the largest in the entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storforsen
Storforsen is a waterfall on the Pite River in Swedish Norrbottens län is located approximately 38 km northwest of Älvsbyn. With an average flow of 187 m3/s, the rapids are one of the most voluminous in Europe. The rapids stretch over a distance of 5 km in which it drops 82 meters 60 of which are a single waterfall. Flow usually is highest at midsummer: 870 m3/s. During the floodyear 1995 a volume of 1200 cubic metres flowed down Storforsen each second. To prevent accidents the rocks surrounding the rapids are fenced, views being readily accessible to the public via ramps. While the rapids were used in previous years to transport logs, today its surroundings are part of a nature park, visited by 150,000 people each year. Image gallery Image:Storforsen-18.JPG Image:Storforsen Hotell från Storforsen utsiktsplats.jpg Image:Storforsen-23.JPG Image:Storforsen-28.JPG Image:Storforsen1.jpg Image:Storforsen2.jpg Image:Storforsen3.jpg Image:Storforsen in early Winter.jpg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the Canada–United States border, border between the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York (state), New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Falls, which straddles the Canada–United States border, international border of the two countries. It is also known as the Canadian Falls. The smaller American Falls and Bridal Veil Falls (Niagara Falls), Bridal Veil Falls lie within the United States. Bridal Veil Falls is separated from Horseshoe Falls by Goat Island (New York), Goat Island and from American Falls by Luna Island, with both islands situated in New York. Formed by the Niagara River, which drains Lake Erie into Lake Ontario before flowing out to the Atlantic Ocean through the St. Lawrence River, the combined falls have the List of waterfalls by flow rate, highest flow rate of any waterfall in North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
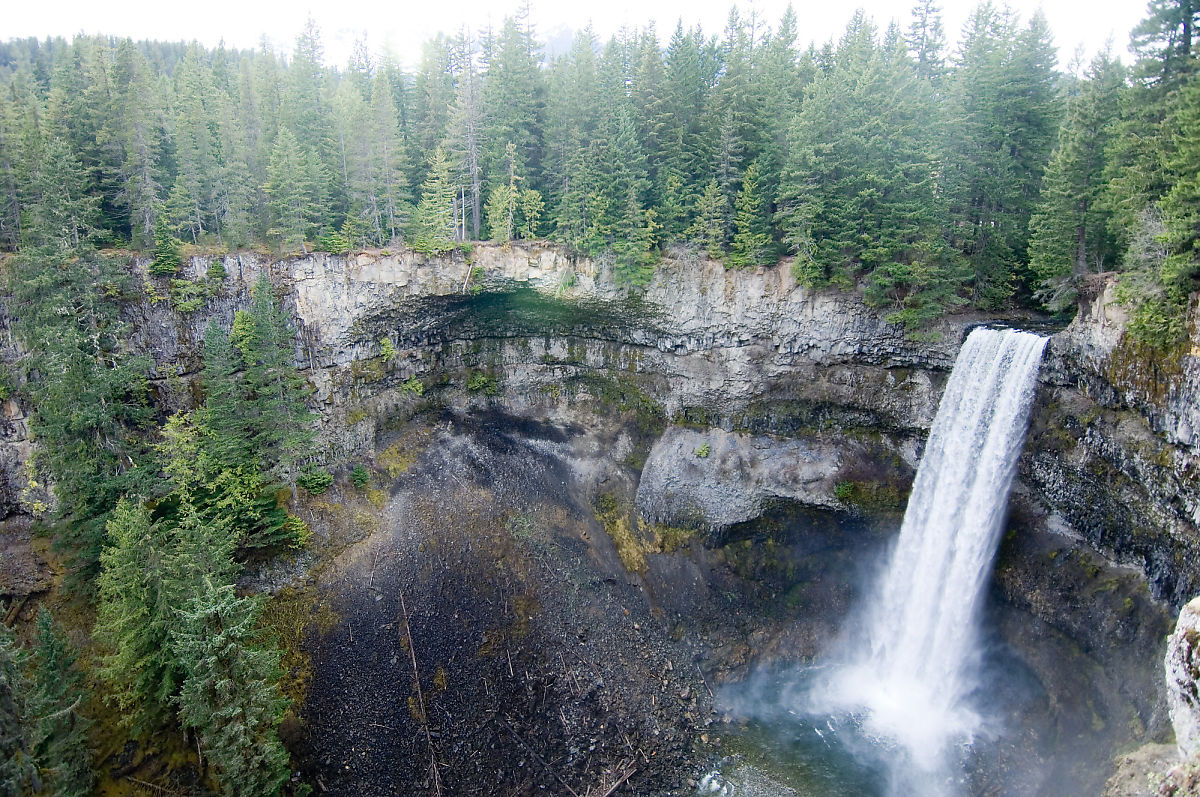
Waterfall
A waterfall is any point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop or a series of steep drops. Waterfalls also occur where meltwater drops over the edge of a tabular iceberg or ice shelf. Waterfalls can be formed in several ways, but the most common method of formation is that a river courses over a top layer of resistant bedrock before falling onto softer rock, which erodes faster, leading to an increasingly high fall. Waterfalls have been studied for their impact on species living in and around them. Humans have had a distinct relationship with waterfalls since prehistory, travelling to see them, exploring and naming them. They can present formidable barriers to navigation along rivers. Waterfalls are religious sites in many cultures. Since the 18th century, they have received increased attention as tourist destinations, sources of hydropower, andparticularly since the mid-20th centuryas subjects of research. Definition and terminology A waterfal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ume River
The Ume River (Swedish: ''Ume älv'' or ''Umeälven'') is one of the main rivers in northern Sweden. It is around long, and flows in a south-eastern direction from its source, the lake ''Överuman'' by the Norway, Norwegian border within the Scandinavian mountain range. For large parts, the European route E12, also known as Blå Vägen (Blue Route), follows its path. The river passes through Vindelfjällen Nature Reserve and Storuman, Lake Storuman and drains into the Gulf of Bothnia on Sweden's east coast at the small town of Holmsund, and adjacent to the city of Umeå. Its chief tributary is the Vindel River, which is the biggest tributary river in Sweden. The Ume and Vindel rivers meet at the village of Vännas. At the mouth of the river, where it meets the Gulf of Bothnia, lies Obbolaön (Obbola Island). The island divides the river into two streams just as it runs out into the sea. Early history People have lived in the Ume river valley for at least five thousand years. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maumee River
The Maumee River (pronounced ) (; ) is a river running in the Midwestern United States from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph River (Maumee River), St. Joseph and St. Marys River (Indiana), St. Marys rivers, where Fort Wayne, Indiana, has developed, and meanders northeastwardly for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed May 19, 2011 through an agriculture, agricultural region of glacial moraines before flowing into the Maumee Bay of Lake Erie. The city of Toledo, Ohio, Toledo is located at the mouth of the Maumee. The Maumee was designated an Ohio State Scenic River on July 18, 1974. The Maumee watershed is Ohio's breadbasket; it is two-thirds farmland, mostly corn and soybeans. It is the largest watershed of any of the rivers feeding the Great Lakes, and supplies five percent of Lake Erie's water. History Historically the river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi River (Ontario)
The Mississippi River is a tributary of the Ottawa River in Eastern Ontario, Canada, which has no relation with the Mississippi River in the United States. It is in length from its source at Mackavoy Lake, has a drainage area of , and has a mean discharge of . There are more than 250 lakes in the watershed. Communities along the river include the village of Lanark, the towns of Carleton Place, Mississippi Mills (including towns of Almonte and Pakenham), and Galetta. Here it enters the Ottawa River. Etymology The river's name is likely derived from its proximity to the nearby Kichisìpi (Ottawa River), meaning in Anicinàbemowin (the Algonquin language). The Misi-ziibi () is a minor tributary of the Kichisìpi and the largest river in the area. Alternatively, the name may originate from , Algonquian for , referring to the pictographs found on Mazinaw Lake, though this is by no means proven. According to the Algonquins of Ontario, the river's name is meaning . Descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids – liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including (the study of air and other gases in motion) and (the study of water and other liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moment (physics), moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipeline transport, pipelines, weather forecasting, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space, understanding large scale Geophysical fluid dynamics, geophysical flows involving oceans/atmosphere and Nuclear weapon design, modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country by both area and population, and is the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. Its capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.6 million, and a low population density of ; 88% of Swedes reside in urban areas. They are mostly in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden's urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Sweden has a diverse Climate of Sweden, climate owing to the length of the country, which ranges from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times around 12,000 BC. The inhabitants emerged as the Geats () and Swedes (tribe), Swedes (), who formed part of the sea-faring peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |