|
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This type of research typically involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, or field observations in order to collect data that is rich in detail and context. Qualitative research is often used to explore complex phenomena or to gain insight into people's experiences and perspectives on a particular topic. It is particularly useful when researchers want to understand the meaning that people attach to their experiences or when they want to uncover the underlying reasons for people's behavior. Qualitative methods include ethnography, grounded theory, discourse analysis, and interpretative phenomenological analysis. Qualitative research methods have been used in sociology, anthropology, political science, psychology, communication studies, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Reality
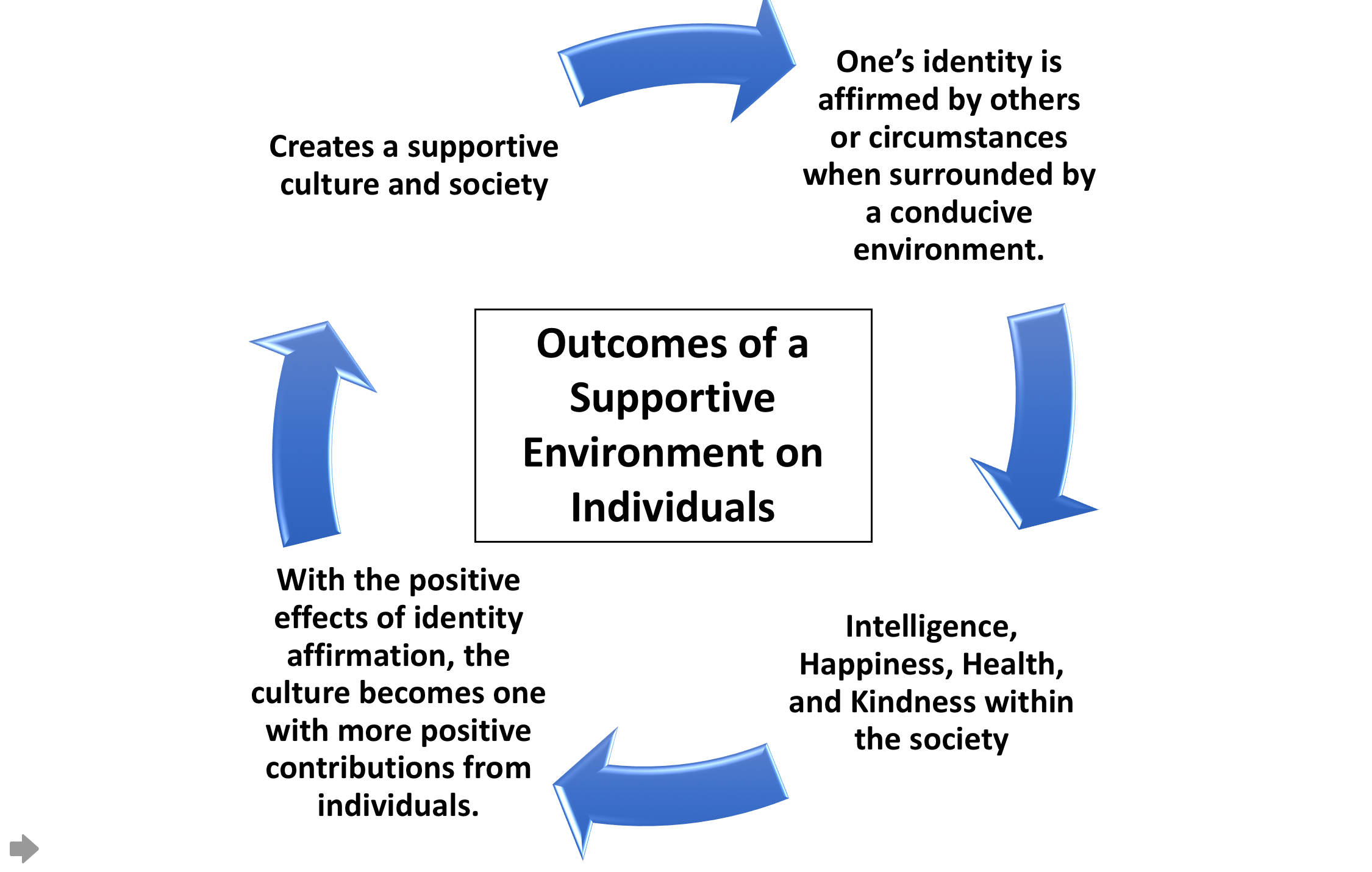
Social reality refers to a socially constructed perspective of the world, consisting of the accepted social tenets of a community involving laws and social representations. It is distinct from biological reality or individual cognitive reality, representing as it does on a subjective level created through social interaction and thereby transcending individual motives and actions. Radical constructivism would cautiously describe social reality as the product of uniformities among observers (whether or not including the current observer themselves). Schütz, Durkheim, and Spencer The problem of social reality has been treated exhaustively by philosophers in the phenomenological tradition, particularly Alfred Schütz, who used the term "social world" to designate this distinct level of reality. Within the social world, Schütz distinguished between social reality that could be experienced directly (''umwelt'') and a social reality beyond the immediate horizon, which could yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positivism
Positivism is a philosophical school that holds that all genuine knowledge is either true by definition or positivemeaning '' a posteriori'' facts derived by reason and logic from sensory experience.John J. Macionis, Linda M. Gerber, ''Sociology'', Seventh Canadian Edition, Pearson Canada. Other ways of knowing, such as intuition, introspection, or religious faith, are rejected or considered meaningless. Although the positivist approach has been a recurrent theme in the history of Western thought, modern positivism was first articulated in the early 19th century by Auguste Comte. His school of sociological positivism holds that society, like the physical world, operates according to scientific laws. After Comte, positivist schools arose in logic, psychology, economics, historiography, and other fields of thought. Generally, positivists attempted to introduce scientific methods to their respective fields. Since the turn of the 20th century, positivism, although still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter L
Peter may refer to: People * List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Peter (given name) ** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church * Peter (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) Culture * Peter (actor) (born 1952), stage name Shinnosuke Ikehata, a Japanese dancer and actor * ''Peter'' (1934 film), a film directed by Henry Koster * ''Peter'' (2021 film), a Marathi language film * "Peter" (''Fringe'' episode), an episode of the television series ''Fringe'' * ''Peter'' (novel), a 1908 book by Francis Hopkinson Smith * "Peter" (short story), an 1892 short story by Willa Cather * ''Peter'' (album), a 1972 album by Peter Yarrow * ''Peter'', a 1993 EP by Canadian band Eric's Trip * "Peter", 2024 song by Taylor Swift from '' The Tortured Poets Department: The Anthology'' Animals * Peter (Lord's cat), cat at Lord's Cricket Ground in London * Peter (chief mous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Schütz
Alfred Schutz (; born Alfred Schütz, ; 1899–1959) was an Austrian philosopher and social phenomenologist whose work bridged sociological and phenomenological traditions. Schutz is gradually being recognized as one of the 20th century's leading philosophers of social science.Walsh, George. 1997. "Introduction." In ''The Phenomenology of the Social World'', by Alfred Schütz. Illinois. He related Edmund Husserl's work to the social sciences, using it to develop the philosophical foundations of Max Weber's sociology, in his major work ''Phenomenology of the Social World''. However, much of his influence arose from the publication of his ''Collected Papers'' in the 1960s. Biography Schutz was born on 13 April 1899 in Vienna, Austria, as the only child in an upper-middle-class Jewish family. Following his graduation from high school, he was drafted into the Austrian Army where he quickly rose to the American equivalent rank of second lieutenant. His army regiment was dispatched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociology Of Knowledge
The sociology of knowledge is the study of the relationship between human thought, the social context within which it arises, and the effects that prevailing ideas have on societies. It is not a specialized area of sociology. Instead, it deals with broad fundamental questions about the extent and limits of social influences on individuals' lives and the social-cultural basis of our knowledge about the world. The sociology of knowledge has a subclass and a complement. Its subclass is sociology of scientific knowledge. Its complement is the sociology of ignorance. The sociology of knowledge was pioneered primarily by the sociologist Émile Durkheim at the beginning of the 20th century. His work deals directly with how conceptual thought, language, and logic can be influenced by the societal milieu in which they arise. The 1903 essay ''Primitive Classification'', by Durkheim and Marcel Mauss, invoked "primitive" group mythology to argue that classification systems are collective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbolic Interactionism
Symbolic interactionism is a sociological theory that develops from practical considerations and alludes to humans' particular use of shared language to create common symbols and meanings, for use in both intra- and interpersonal communication. It is particularly important in microsociology and social psychology. It is derived from the American philosophy of pragmatism and particularly from the work of George Herbert Mead, as a pragmatic method to interpret social interactions. According to Mead, symbolic interactionism is "The ongoing use of language and gestures in anticipation of how the other will react; a conversation". Symbolic interactionism is "a framework for building theory that sees society as the product of everyday interactions of individuals". In other words, it is a frame of reference to better understand how individuals interact with one another to create symbolic worlds, and in return, how these worlds shape individual behaviors. It is a framework that helps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Constructionism
Social constructionism is a term used in sociology, social ontology, and communication theory. The term can serve somewhat different functions in each field; however, the foundation of this Conceptual framework, theoretical framework suggests various facets of social reality—such as concepts, beliefs, Social norm, norms, and Value (ethics and social sciences), values—are formed through continuous interactions and negotiations among society's members, rather than Empirical research, empirical observation of Reality, physical reality. The theory of social constructionism posits that much of what individuals perceive as 'reality' is actually the outcome of a dynamic process of construction influenced by Convention (norm), social conventions and Social structure, structures. Unlike phenomena that are innately determined or biologically predetermined, these social constructs are collectively formulated, sustained, and shaped by the social environment, social contexts in which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenomenology (philosophy)
Phenomenology is a philosophical study and movement largely associated with the early 20th century that seeks to Subjectivity_and_objectivity_(philosophy), objectively investigate the nature of subjective, consciousness, conscious experience. It attempts to describe the universal features of consciousness while avoiding assumptions about the external world, aiming to describe Phenomenon, phenomena as they appear, and to explore the meaning and significance of lived experience. This approach, while philosophical, has found many applications in qualitative research across different scientific disciplines, especially in the social sciences, humanities, Phenomenology (psychology), psychology, and cognitive science, but also in fields as diverse as health sciences, Phenomenology (architecture), architecture, and Human–computer interaction, human-computer interaction, among many others. The application of phenomenology in these fields aims to gain a deeper understanding of subjectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Psychology
Cultural psychology is the study of how cultures reflect and shape their members' psychological processes.Heine, S. J. (2011). ''Cultural Psychology. ''New York: W. W. Norton & Company. It is based on the premise that the mind and culture are inseparable and mutually constitutive. The concept involves two propositions: firstly, that people are shaped by their culture, and secondly, that culture is shaped by its people.Fiske, A.; Kitayama, S.; Markus, H.R.; & Nisbett, R.E. (1998)The cultural matrix of social psychology In D. Gilbert & S. Fiske & G. Lindzey (Eds.), The Handbook of Social Psychology (4th ed., pp. 915–81). San Francisco: McGraw-Hill. Cultural psychology aims to define culture, its nature, and its function concerning psychological phenomena. Gerd Baumann argues: "Culture is not a real thing, but an abstract analytical notion. In itself, it does not cause behavior but abstracts from it. It is thus neither normative nor predictive but a heuristic means towards explaini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Psychology
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of how and why humans grow, change, and adapt across the course of their lives. Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence, adult development, aging, and the entire lifespan. Developmental psychologists aim to explain how thinking, feeling, and behaviors change throughout life. This field examines change across three major dimensions, which are physical development, cognitive development, and social emotional development. Within these three dimensions are a broad range of topics including motor skills, executive functions, moral understanding, language acquisition, social change, personality, emotional development, self-concept, and identity formation. Developmental psychology examines the influences of nature ''and'' nurture on the process of human development, as well as processes of change in context across time. Many researchers are interested in the interactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedagogy
Pedagogy (), most commonly understood as the approach to teaching, is the theory and practice of learning, and how this process influences, and is influenced by, the social, political, and psychological development of learners. Pedagogy, taken as an academic discipline, is the study of how knowledge and skills are imparted in an educational context, and it considers the interactions that take place during learning. Both the theory and practice of pedagogy vary greatly as they reflect different social, political, and cultural contexts. Pedagogy is often described as the act of teaching. The pedagogy adopted by teachers shapes their actions, judgments, and teaching strategies by taking into consideration theories of learning, understandings of students and their needs, and the backgrounds and interests of individual students. Its aims may range from furthering liberal education (the general development of human potential) to the narrower specifics of vocational education (the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 18th century. It now encompasses a wide array of additional academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, geography, history, linguistics, management, communication studies, psychology, culturology, and political science. The majority of positivist social scientists use methods resembling those used in the natural sciences as tools for understanding societies, and so define science in its stricter modern sense. Speculative social scientists, otherwise known as interpretivist scientists, by contrast, may use social critique or symbolic interpretation rather than constructing empirically falsifiable theories, and thus treat science in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |