|
Pupils Of Iannis Xenakis
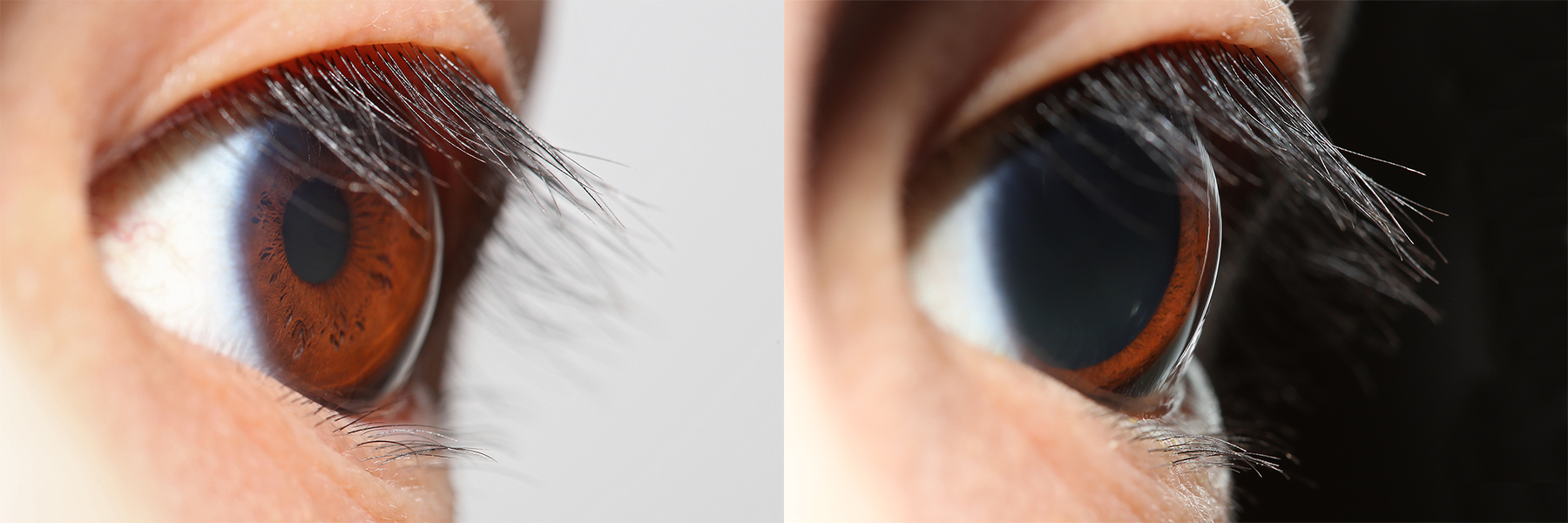
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. (1990) ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company. It appears black because light rays entering the pupil are either absorbed by the tissues inside the eye directly, or absorbed after diffuse reflections within the eye that mostly miss exiting the narrow pupil. The size of the pupil is controlled by the iris, and varies depending on many factors, the most significant being the amount of light in the environment. The term "pupil" was coined by Gerard of Cremona. In humans, the pupil is circular, but its shape varies between species; some cats, reptiles, and foxes have vertical slit pupils, goats and sheep have horizontally oriented pupils, and some catfish have annular types. In optical terms, the anatomical pupil is the eye's aperture and the iris is the aperture stop. The image of the pupil as seen from outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plural
In many languages, a plural (sometimes list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated as pl., pl, , or ), is one of the values of the grammatical number, grammatical category of number. The plural of a noun typically denotes a quantity greater than the default quantity represented by that noun. This default quantity is most commonly one (a form that represents this default quantity of one is said to be of ''singular'' number). Therefore, plurals most typically denote two or more of something, although they may also denote fractional, zero or negative amounts. An example of a plural is the English word ''boys'', which corresponds to the singular ''boy''. Words of other types, such as verbs, adjectives and pronouns, also frequently have distinct plural forms, which are used in agreement (linguistics), agreement with the number of their associated nouns. Some languages also have a dual (grammatical number), dual (denoting exactly two of something) or other systems of number categories. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture Stop
In optics, the aperture of an optical system (including a system consisting of a single lens) is the hole or opening that primarily limits light propagated through the system. More specifically, the entrance pupil as the front side image of the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of ray (optics), rays that comes to a focus (optics), focus in the image plane. An optical system typically has many structures that limit ray bundles (ray bundles are also known as ''pencils'' of light). These structures may be the edge of a lens (optics), lens or mirror, or a ring or other fixture that holds an optical element in place or may be a special element such as a diaphragm (optics), diaphragm placed in the optical path to limit the light admitted by the system. In general, these structures are called stops, and the aperture stop is the stop that primarily determines the cone of rays that an optical system accepts (see entrance pupil). As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body's unconscious actions. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed-and-breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion, and defecation. Its action is described as being complementary to that of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for stimulating activities associated with the fight-or-flight response. Nerve fibres of the parasympathetic nervous system arise from the central nervous system. Specific nerves include several cranial nerves, specifically the oculomotor nerve, facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, and vagus nerve. Three spinal nerves in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oculomotor Nerve
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation (ability to focus on near objects as in reading). The oculomotor nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves IV and VI also participate in control of eye movement. Structure The oculomotor nerve originates from the third nerve nucleus at the level of the superior colliculus in the midbrain. The third nerve nucleus is located ventral to the cerebral aqueduct, on the pre-aqueductal grey matter. The fibers from the two third nerve nuclei located laterally on either side of the cerebral aqueduct then pass through the red nucleus. From the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal Ganglion Cell
A retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptor cell, photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: Bipolar cell of the retina, bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and making it so that ganglion cells can observe a small dot moving a small distance. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit image-forming and non-image forming visual information from the retina in the form of action potential to several regions in the thalamus, hypothalamus, and mesencephalon, or midbrain. Retinal ganglion cells vary significantly in terms of their size, connections, and responses to visual stimulation but they all share the defining property of having a long axon that extends into the brain. These axons form the optic ner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanopsin
Melanopsin is a type of photopigment belonging to a larger family of light-sensitive retinylidene protein, retinal proteins called opsins and encoded by the gene ''Opn4''. In the mammalian retina, there are two additional categories of opsins, both involved in the formation of visual images: rhodopsin and photopsin (types I, II, and III) in the Rod cell, rod and Cone cell, cone photoreceptor cells, respectively. In humans, melanopsin is found in intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs). It is also found in the iris of mice and primates. Melanopsin is also found in rats, amphioxus, and other chordates. ipRGCs are photoreceptor cells which are particularly sensitive to the absorption of short-wavelength (blue) visible light and communicate information directly to the area of the brain called the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), also known as the central "body clock", in mammals. Melanopsin plays an important non-image-forming role in the Entrainment (chronobiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |