|
Punctelia
''Punctelia'' is a genus of foliose lichens belonging to the large family Parmeliaceae. The genus, which contains about 50 species, was segregated from genus '' Parmelia'' in 1982. Characteristics that define ''Punctelia'' include the presence of hook-like to thread-like conidia (asexual spores), simple rhizines (root-like structures that attach the lichen thallus to its substrate), and point-like pseudocyphellae (tiny pores on the thallus surface that facilitate gas exchange). It is this last feature that is alluded to in the vernacular names speckled shield lichens or speckleback lichens. ''Punctelia'' lichens grow on bark, wood, and rocks. The genus has a worldwide distribution, occurring on all continents but Antarctica. Species are found in temperate to subtropical locations. ''Punctelia'' has centres of distribution in the Neotropics and Africa; about half of the known species occur in South America. The photobiont partners of ''Punctelia'' are green algae in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
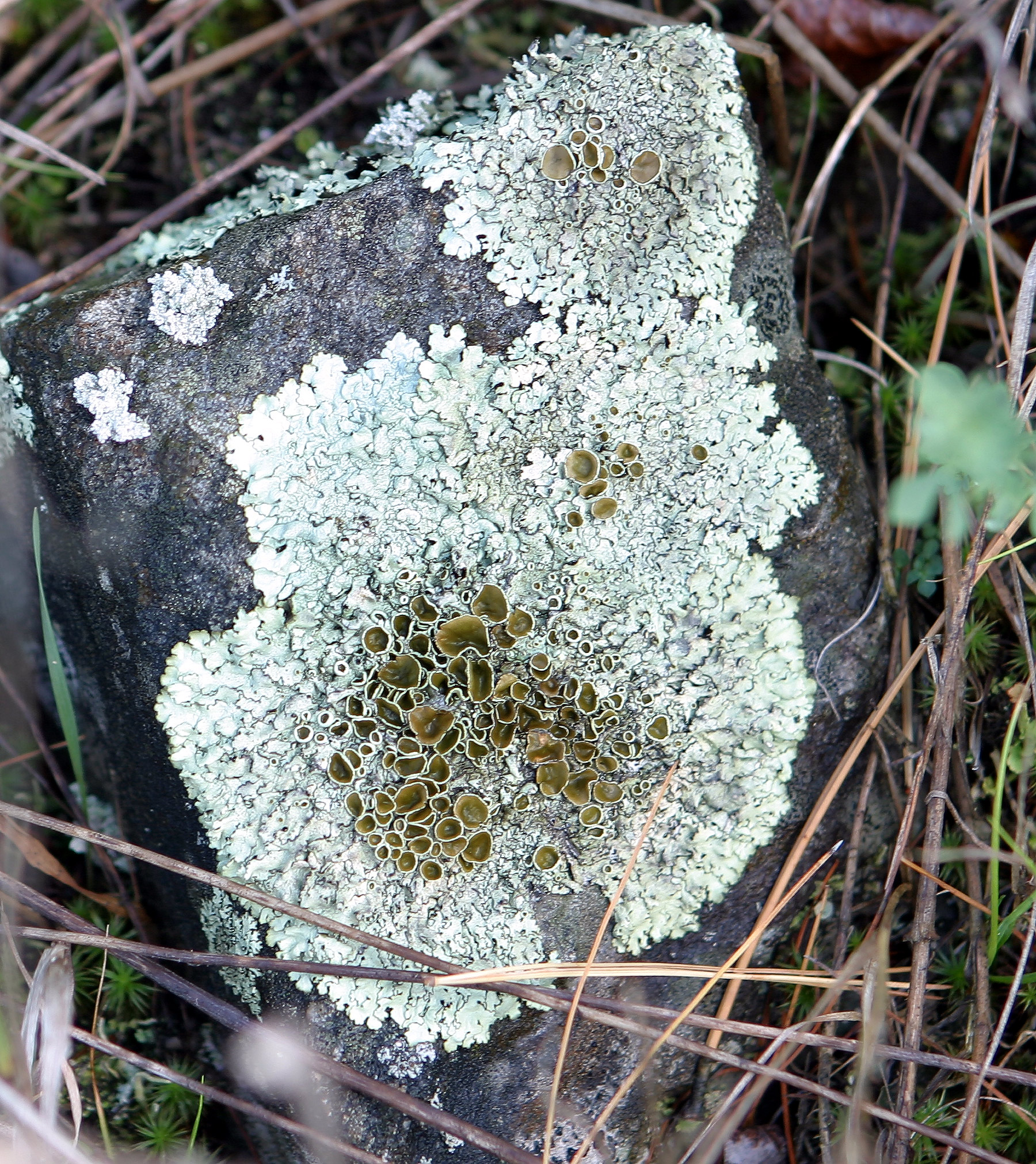
Punctelia Borreri
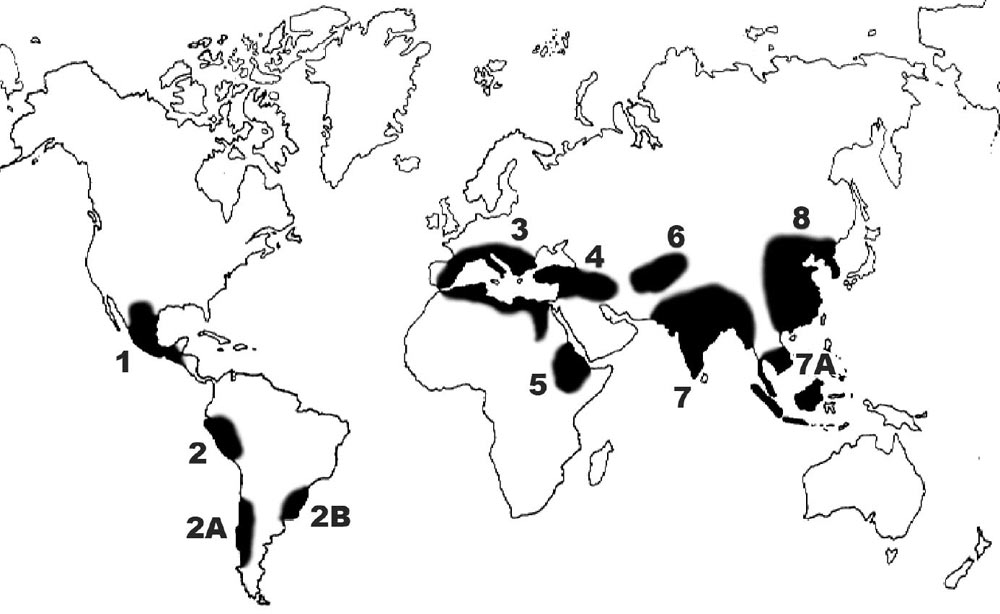
''Punctelia borreri'' is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is a common and widely distributed species, occurring in tropics, tropical, subtropics, subtropical, and temperate climate, temperate regions of Africa, Asia, Europe, North America, Oceania, and South America. The lichen typically corticolous lichen, grows on bark of deciduous trees, and less commonly saxicolous lichen, on rock. Some European countries have reported increases in the species distribution, geographic range or regional frequency of the lichen in recent decades, attributed alternatively to a reduction of atmospheric sulfur dioxide, sulphur dioxide levels or an increase in temperatures resulting from climate change. The lichen is characterised by a greenish-grey to bluish-grey upper thallus surface, a black lower surface, pseudocyphellae on the surface of the thallus (tiny pores that facilitate gas exchange), and chemically, by the presence of gyrophoric acid in the medulla (licheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parmelia Borreri
''Punctelia borreri'' is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is a common and widely distributed species, occurring in tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions of Africa, Asia, Europe, North America, Oceania, and South America. The lichen typically grows on bark of deciduous trees, and less commonly on rock. Some European countries have reported increases in the geographic range or regional frequency of the lichen in recent decades, attributed alternatively to a reduction of atmospheric sulphur dioxide levels or an increase in temperatures resulting from climate change. The lichen is characterised by a greenish-grey to bluish-grey upper thallus surface, a black lower surface, pseudocyphellae on the surface of the thallus (tiny pores that facilitate gas exchange), and chemically, by the presence of gyrophoric acid in the medulla. There are several lookalike ''Punctelia'' species, including '' P. subrudecta'', '' P. perreticulata'', and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parmeliaceae
The Parmeliaceae is a large and diverse family of Lecanoromycetes. With over 2700 species in 71 genera, it is the largest family of lichen-forming fungi. The most speciose genera in the family are the well-known groups: '' Xanthoparmelia'' ( 822 species), '' Usnea'' (355 species), '' Parmotrema'' ( 255 species), and '' Hypotrachyna'' (262 species). Nearly all members of the family have a symbiotic association with a green alga (most often ''Trebouxia'' spp., but ''Asterochloris'' spp. are known to associate with some species).Miadlikowska, J. ''et al.'' (2006). New insights into classification and evolution of the Lecanoromycetes (Pezizomycotina, Ascomycota) from phylogenetic analyses of three ribosomal RNA- and two protein-coding genes. ''Mycologia'' 98: 1088-1103. http://www.mycologia.org/cgi/reprint/98/6/1088.pdf The majority of Parmeliaceae species have a foliose, fruticose, or subfruticose growth form. The morphological diversity and complexity exhibited by this group i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parmelia (fungus)
''Parmelia'' is a genus of medium to large foliose lichen, foliose (leafy) lichens.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, It has a global distribution, extending from the ArcticSkult H (1985) A New Subspecies of ''Parmelia omphalodes'' Ascomycetes Described from the Arctic. Annales Botanici Fennici 22, 201-6. to the Antarctic continentD.C. Lindsay (1973) Notes on Antarctic lichens: IV. The genera ''Cetraria'' Hoffm., ''Hypogymnia'' (Nyl.) Nyl., ''Menegazzia'' Massal, ''Parmelia'' Ach. and ''Platismatia'' Culb. et Culb. British Antarctic Survey Bulletin 36, 105-114. but concentrated in temperate regions. There are about 40 species in ''Parmelia''. In recent decades, the once large genus ''Parmelia'' has been divided into a number of smaller genera according to thallus (tissue), thallus morphology and phylogenetic relatedness. It is a foliaceous lichen, resembling a leaf in shape. The ends of the leaf-like lobes are often squarish-tippe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trebouxia
''Trebouxia'' is a unicellular green alga. It is a photosynthetic organism that can exist in almost all habitats found in polar, tropical, and temperate regions.Erokhina, L. G., Shatilovich, A. V., Kaminskaya, O. P., & Gilichinskii, D. A. (2004). Spectral Properties of the Green Alga ''Trebouxia'', a Phycobiont of Cryptoendolithic Lichens in the Antarctic Dry Valley. Microbiology,73(4), 420-424. doi:10.1023/b:mici.0000036987.18559Lukesova, A., & Frouz, J. (2007). Soil and Freshwater Micro-Algae as a Food Source for Invertebrates in Extreme Environments. Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology Algae and Cyanobacteria in Extreme Environments,265-284. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6112-7_14Seckbach, J. (2007). Algae and cyanobacteria in extreme environments. Dordrecht: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6112-7Seckbach, J. (2002). Symbiosis: Mechanisms and model systems. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.John, D. M., Whitton, B. A., & Brook, A. J. (2002). The freshwater algal f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Origin
A Vavilov center or center of origin is a geographical area where a group of organisms, either domesticated or wild, first developed its distinctive properties. Centers of origin were first identified in 1924 by Nikolai Vavilov. Vavilov posited that the center of origin for a species or genus is the same as its ''center of diversity'', the geographic area where it has the highest genetic diversity, but this equivalence has been disputed by later scholars. Plants Locating the origin of crop plants is basic to plant breeding. This allows one to locate wild relatives, related species, and new genes (especially dominant genes, which may provide resistance to diseases). Knowledge of the origins of crop plants is important in order to avoid genetic erosion, the loss of germplasm due to the loss of ecotypes and landraces, loss of habitat (such as rainforests), and increased urbanization. Germplasm preservation is accomplished through gene banks (largely seed collections but now f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotropics
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone. Definition In biogeography, the Neotropic or Neotropical realm is one of the eight terrestrial realms. This realm includes South America, Central America, the Caribbean Islands, and southern North America. In Mexico, the Yucatán Peninsula and southern lowlands, and most of the east and west coastlines, including the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula are Neotropical. In the United States southern Florida and coastal Central Florida are considered Neotropical. The realm also includes temperate southern South America. In contrast, the Neotropical Floristic Kingdom excludes southernmost South America, which instead is placed in the Antarctic kingdom. The Neotropic is delimited by similarities in fauna or flora. Its fauna and flora are distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photobiont
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. . Lichens are the lifeform that first brought the term symbiosis (as ''Symbiotismus'') into biological context. Lichens have since been recognized as important actors in and producers which many higher trophic feeders feed on, such as reindeer, gastropods, nematodes, mites, and springtails. Lich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Algae
The green algae (: green alga) are a group of chlorophyll-containing autotrophic eukaryotes consisting of the phylum Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister group that contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants ( Embryophytes) have emerged deep within the charophytes as a sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid (spherical), and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae, many of which live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hildur Krog
Hildur Krog (22 March 1922 – 25 August 2014) was a Norwegian lichenologist and university professor who made contributions to the field of lichenology, particularly in the areas of lichen taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, chemotaxonomy, and floristics. Biography Hildur Krog was born on 22 March 1922 in Søre Simostrada, Modum, Norway. She received her early education at the landgymnas (rural high school) in Voss, Hordaland. During World War II, in late April 1940, she experienced German airstrike, air raids on Voss and fled to the mountains with her sister, where they reportedly nearly starved. In 1941, she completed her high school examination (Abitur) and began studying biology at the University of Oslo. In 1946, she returned to her studies after the Norwegian scholar Eilif Dahl, who had secured a position as a university lecturer in Oslo, came back from England. Dahl had been a member of a Norwegian resistance movement, Norwegian resistance group during the war and had been fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioindicator
A bioindicator is any species (an indicator species) or group of species whose function, population, or status can reveal the qualitative status of the environment. The most common indicator species are animals. For example, copepods and other small water crustaceans that are present in many water bodies can be monitored for changes (biochemical, physiological, or behavioural) that may indicate a problem within their ecosystem. Bioindicators can tell us about the cumulative effects of different pollutants in the ecosystem and about how long a problem may have been present, which physical and chemical testing cannot. A biological monitor or biomonitor is an organism that provides quantitative information on the quality of the environment around it. Therefore, a good biomonitor will indicate the presence of the pollutant and can also be used in an attempt to provide additional information about the amount and intensity of the exposure. A biological indicator is also the name gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles like soot and dust. It affects both outdoor air and indoor air. Natural sources of air pollution include Wildfire, wildfires, Dust storm, dust storms, and Volcanic eruption, volcanic eruptions. Indoor air pollution is often Energy poverty and cooking, caused by the use of biomass (e.g. wood) for cooking and heating. Outdoor air pollution comes from some industrial processes, the burning of Fossil fuel, fossil fuels for electricity and transport, waste management and agriculture. Many of the contributors of local air pollution, especially the burning of fossil fuels, also cause greenhouse gas emissions that cause climate change, global warming. Air pollution causes around 7 or 8 million deaths each year. It is a significant risk factor for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |