|
Proportional Representation Electoral Systems
Proportionality, proportion or proportional may refer to: Mathematics * Proportionality (mathematics), the property of two variables being in a multiplicative relation to a constant * Ratio, of one quantity to another, especially of a part compared to a whole ** Fraction (mathematics) * Aspect ratio or proportions * Proportional division, a kind of fair division * Percentage, a number or ratio expressed as a fraction of 100 Science and art * Proportional fonts * Proportionally fair, a scheduling algorithm * Proportional control, a type of linear feedback control system Other uses * Proportionality (law), a legal principle * Proportionality (International Humanitarian Law), a law of war * Proportion (architecture), describes the relationships between elements of a design * Body proportions, in art, the study of relation of human body parts to each other and the whole See also * Proportional representation Proportional representation (PR) refers to any electoral system und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportionality (mathematics)
In mathematics, two sequences of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio. The ratio is called ''coefficient of proportionality'' (or ''proportionality constant'') and its reciprocal is known as ''constant of normalization'' (or ''normalizing constant''). Two sequences are inversely proportional if corresponding elements have a constant product. Two functions f(x) and g(x) are ''proportional'' if their ratio \frac is a constant function. If several pairs of variables share the same direct proportionality constant, the equation expressing the equality of these ratios is called a proportion, e.g., (for details see Ratio). Proportionality is closely related to ''linearity''. Direct proportionality Given an independent variable ''x'' and a dependent variable ''y'', ''y'' is directly proportional to ''x'' if there is a positive constant ''k'' such that: : y = kx The relation is oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio () shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ratio 4:3). Similarly, the ratio of lemons to oranges is 6:8 (or 3:4) and the ratio of oranges to the total amount of fruit is 8:14 (or 4:7). The numbers in a ratio may be quantities of any kind, such as counts of people or objects, or such as measurements of lengths, weights, time, etc. In most contexts, both numbers are restricted to be Positive integer, positive. A ratio may be specified either by giving both constituting numbers, written as "''a'' to ''b''" or "''a'':''b''", or by giving just the value of their quotient Equal quotients correspond to equal ratios. A statement expressing the equality of two ratios is called a ''proportion''. Consequently, a ratio may be considered as an ordered pair of numbers, a Fraction (mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraction (mathematics)
A fraction (from , "broken") represents a part of a whole or, more generally, any number of equal parts. When spoken in everyday English, a fraction describes how many parts of a certain size there are, for example, one-half, eight-fifths, three-quarters. A ''common'', ''vulgar'', or ''simple'' fraction (examples: and ) consists of an integer numerator, displayed above a line (or before a slash like ), and a division by zero, non-zero integer denominator, displayed below (or after) that line. If these integers are positive, then the numerator represents a number of equal parts, and the denominator indicates how many of those parts make up a unit or a whole. For example, in the fraction , the numerator 3 indicates that the fraction represents 3 equal parts, and the denominator 4 indicates that 4 parts make up a whole. The picture to the right illustrates of a cake. Fractions can be used to represent ratios and division (mathematics), division. Thus the fraction can be used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio of a geometry, geometric shape is the ratio of its sizes in different dimensions. For example, the aspect ratio of a rectangle is the ratio of its longer side to its shorter side—the ratio of width to height, when the rectangle is oriented as a "landscape format, landscape". The aspect ratio is most often expressed as two integer numbers separated by a colon (x:y), less commonly as a simple or decimal Fraction (mathematics), fraction. The values x and y do not represent actual widths and heights but, rather, the proportion between width and height. As an example, 8:5, 16:10, 1.6:1, and 1.6 are all ways of representing the same aspect ratio. In objects of more than two dimensions, such as hyperrectangles, the aspect ratio can still be defined as the ratio of the longest side to the shortest side. Applications and uses The term is most commonly used with reference to: * Graphic / image ** Aspect ratio (image), Image aspect ratio ** Display aspect ratio ** Pape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Division
A proportional division is a kind of fair division in which a resource is divided among ''n'' partners with subjective valuations, giving each partner at least 1/''n'' of the resource by his/her own subjective valuation. Proportionality was the first fairness criterion studied in the literature; hence it is sometimes called "simple fair division". It was first conceived by Steinhaus. Example Consider a land asset that has to be divided among 3 heirs: Alice and Bob who think that it's worth 3 million dollars, and George who thinks that it's worth $4.5M. In a proportional division, Alice receives a land-plot that she believes to be worth at least $1M, Bob receives a land-plot that ''he'' believes to be worth at least $1M (even though Alice may think it is worth less), and George receives a land-plot that he believes to be worth at least $1.5M. Existence A proportional division does not always exist. For example, if the resource contains several indivisible items and the number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percentage
In mathematics, a percentage () is a number or ratio expressed as a fraction (mathematics), fraction of 100. It is often Denotation, denoted using the ''percent sign'' (%), although the abbreviations ''pct.'', ''pct'', and sometimes ''pc'' are also used. A percentage is a dimensionless quantity, dimensionless number (pure number), primarily used for expressing proportions, but percent is nonetheless a unit of measurement in its orthography and usage. Examples For example, 45% (read as "forty-five percent") is equal to the fraction , or 0.45. Percentages are often used to express a proportionate part of a total. (Similarly, one can also express a number as a fraction of 1,000, using the term "per mille" or the symbol "".) Example 1 If 50% of the total number of students in the class are male, that means that 50 out of every 100 students are male. If there are 500 students, then 250 of them are male. Example 2 An increase of $0.15 on a price of $2.50 is an increase by a fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Fonts
A typeface (or font family) is a design of letters, numbers and other symbols, to be used in printing or for electronic display. Most typefaces include variations in size (e.g., 24 point), weight (e.g., light, bold), slope (e.g., italic), width (e.g., condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font. There are thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly. The art and craft of designing typefaces is called type design. Designers of typefaces are called type designers and are often employed by type foundries. In desktop publishing, type designers are sometimes also called "font developers" or "font designers" (a typographer is someone who ''uses'' typefaces to design a page layout). Every typeface is a collection of glyphs, each of which represents an individual letter, number, punctuation mark, or other symbol. The same glyph may be used for characters from different writing systems, e.g. Roman uppercase A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportionally Fair
Proportional-fair scheduling is a compromise-based scheduling algorithm. It is based upon maintaining a balance between two competing interests: Trying to maximize the total throughput of the network (wired or not) while at the same time allowing all users at least a minimal level of service. This is done by assigning each data flow a data rate or a scheduling priority (depending on the implementation) that is inversely proportional to its anticipated resource consumption. Guowang Miao, Jens Zander, Ki Won Sung, and Ben Slimane, Fundamentals of Mobile Data Networks, Cambridge University Press, , 2016. Weighted fair queuing Proportionally fair scheduling can be achieved by means of weighted fair queuing (WFQ), by setting the scheduling weights for data flow i to w_i = 1 / c_i, where the cost c_i is the amount of consumed resources per data bit. For instance: * In CDMA spread spectrum cellular networks, the cost may be the required energy per bit in the transmit power control (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
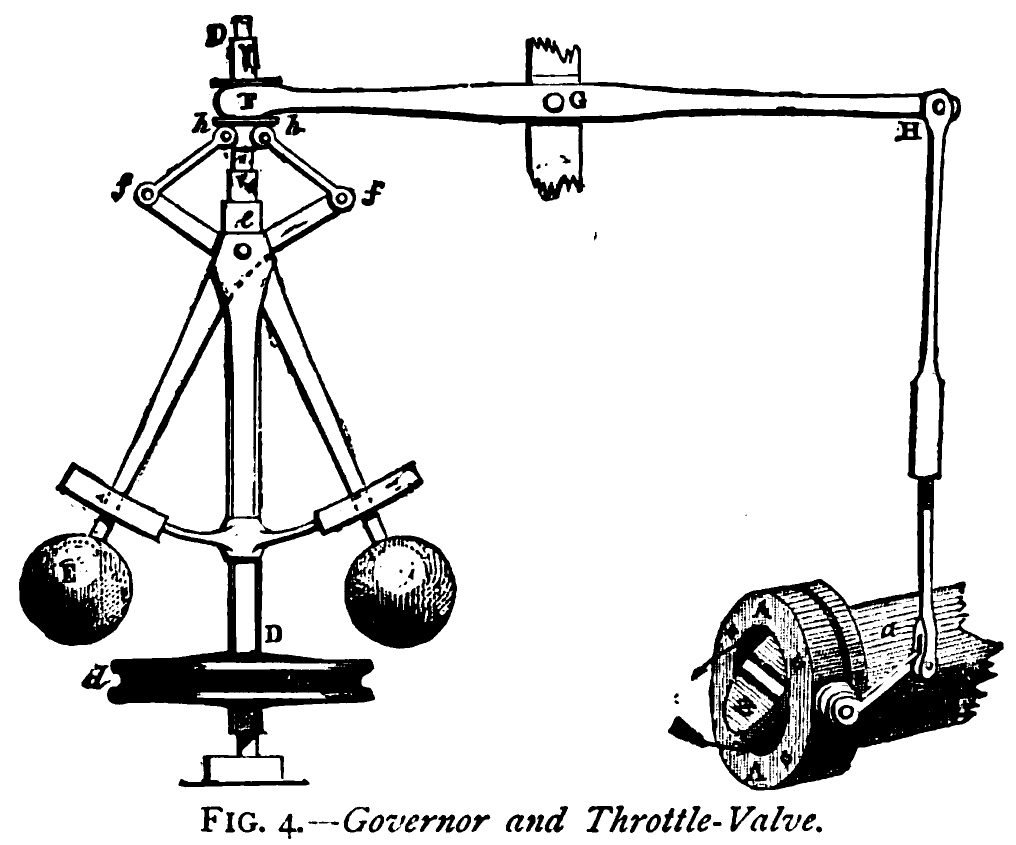
Proportional Control
Proportional control, in engineering and process control, is a type of linear feedback control system in which a correction is applied to the controlled variable, and the size of the correction is proportional to the difference between the desired value ( setpoint, SP) and the measured value ( process variable, PV). Two classic mechanical examples are the toilet bowl float proportioning valve and the fly-ball governor. The proportional control concept is more complex than an on–off control system such as a bi-metallic domestic thermostat, but simpler than a proportional–integral–derivative (PID) control system used in something like an automobile cruise control. On–off control will work where the overall system has a relatively long response time, but can result in instability if the system being controlled has a rapid response time. Proportional control overcomes this by modulating the output to the controlling device, such as a control valve at a level which avoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportionality (law)
Proportionality is a general principle in law which covers several separate (although related) concepts: *The concept of proportionality is used as a criterion of fairness and justice in statutory interpretation processes, especially in constitutional law, as a logical method intended to assist in discerning the correct balance between the restriction imposed by a corrective measure and the severity of the nature of the prohibited act. *Within criminal law, the concept is used to convey the idea that the punishment of an offender should fit the crime. *Under international humanitarian law governing the legal use of force in an armed conflict, ''proportionality'' and '' distinction'' are important factors in assessing military necessity. *Under the United Kingdom's Civil Procedure Rules, costs must be "proportionately and reasonably incurred", or "proportionate and reasonable in amount", if they are to form part of a court ruling on costs. Proportionality as a general princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportionality (International Humanitarian Law)
Proportionality is a general principle in law which covers several separate (although related) concepts: *The concept of proportionality is used as a criterion of fairness and justice in statutory interpretation processes, especially in constitutional law, as a logical method intended to assist in discerning the correct balance between the restriction imposed by a corrective measure and the severity of the nature of the prohibited act. *Within criminal law, the concept is used to convey the idea that the punishment of an offender should fit the crime. *Under international humanitarian law governing the legal use of force in an armed conflict, ''proportionality'' and '' distinction'' are important factors in assessing military necessity. *Under the United Kingdom's Civil Procedure Rules, costs must be "proportionately and reasonably incurred", or "proportionate and reasonable in amount", if they are to form part of a court ruling on costs. Proportionality as a general pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of War
The law of war is a component of international law that regulates the conditions for initiating war (''jus ad bellum'') and the conduct of hostilities (''jus in bello''). Laws of war define sovereignty and nationhood, states and territories, occupation, and other critical terms of law. Among other issues, modern laws of war address the declarations of war, acceptance of surrender and the treatment of prisoners of war, military necessity, along with ''distinction'' and ''proportionality''; and the prohibition of certain weapons that may cause unnecessary suffering. The ''law of war'' is considered distinct from other bodies of law—such as the domestic law of a particular belligerent to a conflict—which may provide additional legal limits to the conduct or justification of war. Early sources and history The first traces of a law of war come from the Babylonians. It is the Code of Hammurabi, king of Babylon, which in 1750 B.C., explains its laws imposing a code o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |