|
Private Spaceflight
Private spaceflight is any spaceflight development that is not conducted by a government agency, such as NASA or ESA. During the early decades of the Space Age, the government space agencies of the Soviet Union and United States pioneered space technology in collaboration with affiliated design bureaus in the USSR and private companies in the US. They entirely funded both the development of new spaceflight technologies and the operational costs of spaceflight. Following a similar model of space technology development, the European Space Agency was formed in 1975. Arianespace, born out of ESA's independent spaceflight efforts, became the world's first commercial launch service provider in the early 1980s. Subsequently, large defense contractors began to develop and operate space launch systems, which were derived from government rockets. In the United States, the FAA has created a new certification called Commercial Astronaut, a new occupation. In the 2000s, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Missions Conducted Between 1957 And 2020
Space is a Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional continuum containing position (geometry), positions and direction (geometry), directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional Continuum (theory), continuum known as ''spacetime''. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. In the 19th and 20th centuries mathematicians began to examine geometries that are Non-Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean, in which space is conceived as ''space curvature, curved'', rather than ''flat space, flat'', as in the Euclidean space. According to Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, space around gravitational fields deviate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entrepreneur
Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value in ways that generally entail beyond the minimal amount of risk (assumed by a traditional business), and potentially involving values besides simply economic ones. An entrepreneur () is an individual who creates and/or invests in one or more businesses, bearing most of the risks and enjoying most of the rewards. The process of setting up a business is known as "entrepreneurship". The entrepreneur is commonly seen as an innovator, a source of new ideas, goods, services, and business/or procedures. More narrow definitions have described entrepreneurship as the process of designing, launching and running a new business, often similar to a small business, or (per ''Business Dictionary'') as the "capacity and willingness to develop, organize and manage a business venture along with any of its risks to make a profit". The people who create these businesses are often referred to as "entrepreneurs". In the field of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genesis II (space Habitat)
''Genesis II'' is the second experimental space habitat designed and built by the private American firm Bigelow Aerospace, launched in 2007. As the second module sent into orbit by the company, this spacecraft built on the data and experience gleaned from its previously orbited sister-ship '' Genesis I''. Like its sister-ship and other modules being designed by Bigelow Aerospace, this spacecraft was based on the NASA TransHab design, which provided increased interior volume and reduced launch diameter along with potentially reduced mass compared to traditional rigid structures. ''Genesis II'' was "retired" when its avionics systems stopped working after two and a half years, thus becoming a derelict spacecraft. As of 2024, the spacecraft remains in orbit. Spacecraft history Similar to the process endured by Bigelow for ''Genesis I'', transporting ''Genesis II'' to Russia for launch was the end result of nearly a year of regulatory processes due to restrictions imposed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genesis I
''Genesis I'' is an experimental space habitat designed and built by the private American firm Bigelow Aerospace and launched in 2006. It was the first module to be sent into orbit by the company, and tested various systems, materials and techniques related to determining the viability of long-term inflatable space structures through 2008. Such structures, including this module and others built by Bigelow Aerospace, were similar to the 1990s NASA expandable TransHab design, which aimed to provide increased interior volume at a reduced launch diameter and potentially reduced mass compared to traditional rigid structures. The on-board systems transmitted data for 2.5 years. The spacecraft remains in orbit, allowing researchers to continue to monitor the long-term viability of its expandable space structure. Spacecraft history ''Genesis I'' was launched on 12 July 2006 at 14:53:36 UTC aboard an ISC Kosmotras Dnepr launch vehicle, launched from Dombarovsky missile base near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expandable Space Habitat
Inflatable habitats or expandable habitats are pressurized tent-like structures capable of supporting life in outer space whose internal volume increases after launch. They have frequently been proposed for use in space applications to provide a greater volume of living space for a given mass. The first formal design and manufacture of an inflatable space habitat was in 1961 with a space station design produced by Goodyear (although this design was never flown). A proposal released in 1989 by Johnson Space Center's Man Systems Division outlined a diameter spherical habitat lunar outpost which was partially buried in the lunar surface. An inflatable module called TransHab (a portmanteau of ''Trans Habitation'') was proposed for the International Space Station, and later the private company Bigelow Aerospace revived the design for use in a number of potential civil and commercial applications. Construction The construction of an inflatable space habitat is determined by i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a planet, moon, asteroid, or Lagrange point. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. For most situations, orbital motion is adequately approximated by Newtonian mechanics, which explains gravity as a force obeying an inverse-square law. However, Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of spacetime, with orbits following geodesics, provides a more accurate calculation and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
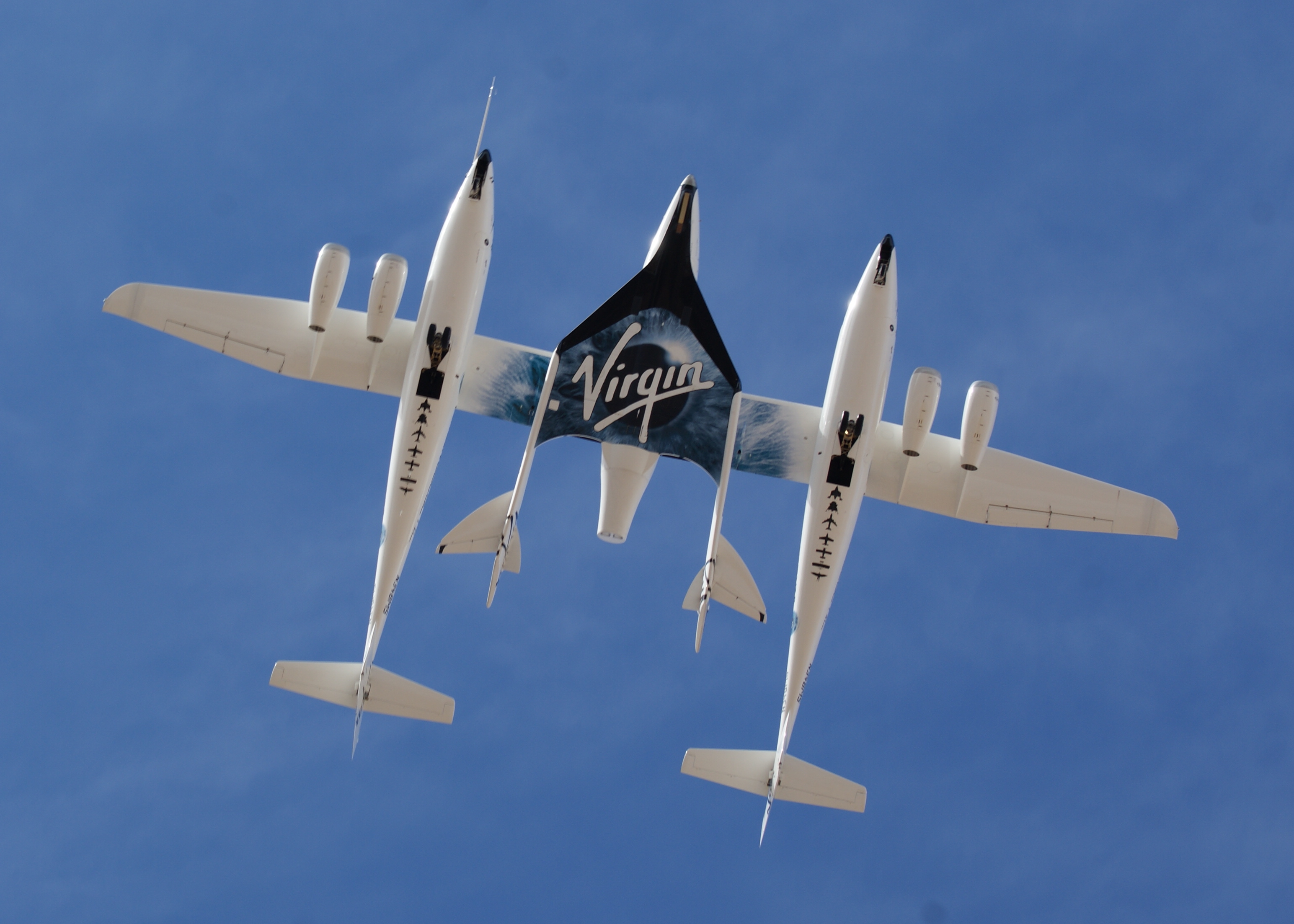
SpaceShipTwo
The Scaled Composites Model 339 SpaceShipTwo (SS2) was an air-launched suborbital spaceplane type designed for space tourism. It was manufactured by The Spaceship Company, a California-based company owned by Virgin Galactic. SpaceShipTwo was carried to its launch altitude by a Scaled Composites White Knight Two, before being released to fly on into the upper atmosphere powered by its rocket engine. It then glided back to Earth and performed a conventional runway landing. The spaceship was officially unveiled to the public on 7 December 2009 at the Mojave Air and Space Port in California. On 29 April 2013, after nearly three years of unpowered testing, the first SS2 constructed successfully performed its first powered test flight. Virgin Galactic planned to operate a fleet of five SpaceShipTwo spaceplanes in a private passenger-carrying service and took bookings for some time, with a suborbital flight carrying a ticket price of US$250,000 in 2015. The spaceplane was also u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceShipOne
SpaceShipOne is an experimental air launch, air-launched rocket-powered aircraft with sub-orbital spaceflight capability at speeds of up to / using a hybrid rocket motor. The design features a unique "Feathering (reentry), feathering" atmospheric reentry system where the rear half of the wing and the twin tail booms folds 70 degrees upward along a hinge running the length of the wing; this increases drag (physics), drag while retaining stability. SpaceShipOne completed the first human spaceflight, crewed private spaceflight in 2004. That same year, it won the US$10 million Ansari X Prize and was immediately retired from active service. Its Mother ship (aviation), mother ship was named "Scaled Composites White Knight, White Knight". Both craft were developed and flown by Mojave Aerospace Ventures, which was a joint venture between Paul Allen and Scaled Composites, Burt Rutan's aviation company. Allen provided the funding of approximately US$25 million. Rutan has indicated that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can flight, fly and gliding flight, glide as an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and function as a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceflight, Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes as of 2024 have been rocket engine, rocket-powered for takeoff and climb, but have then landed as unpowered glider (aircraft), gliders. Four examples of spaceplanes have successfully launched to orbit, Atmospheric entry, reentered Earth's atmosphere, and Landing#Aircraft, landed: the U.S. Space Shuttle, Russian Buran (spacecraft), Buran, U.S. Boeing X-37, X-37, and the Chinese Shenlong (spacecraft), Shenlong. Another, Dream Chaser, is under development in the U.S. As of 2024 all past and current orbital spaceplanes VTHL, launch vertically; some are carried as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suborbital
A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the surface of the gravitating body from which it was launched. Hence, it will not complete one orbital revolution, will not become an artificial satellite nor will it reach escape velocity. For example, the path of an object launched from Earth that reaches the Kármán line (about – above sea level), and then falls back to Earth, is considered a sub-orbital spaceflight. Some sub-orbital flights have been undertaken to test spacecraft and launch vehicles later intended for orbital spaceflight. Other vehicles are specifically designed only for sub-orbital flight; examples include crewed vehicles, such as the X-15 and SpaceShipTwo, and uncrewed ones, such as ICBMs and sounding rockets. Flights which attain sufficient velocity to go into low Earth orbit, and then de-orbit before completing their first full orbit, are not considered sub-orbital. Examples o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
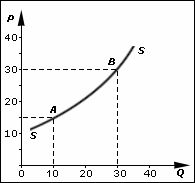
Supply (economics)
In economics, supply is the amount of a resource that firms, producers, labourers, providers of financial assets, or other economic agents are willing and able to provide to the marketplace or to an individual. Supply can be in produced goods, labour time, raw materials, or any other scarce or valuable object. Supply is often plotted graphically as a supply curve, with the price per unit on the vertical axis and quantity supplied as a function of price on the horizontal axis. This reversal of the usual position of the dependent variable and the independent variable is an unfortunate but standard convention. The supply curve can be either for an individual seller or for the market as a whole, adding up the quantity supplied by all sellers. The quantity supplied is for a particular time period (e.g., the tons of steel a firm would supply in a year), but the units and time are often omitted in theoretical presentations. In the goods market, supply is the amount of a product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |