|
Prioniodinida Genera
{{Conodont-stub ...
Prioniodinida is an extinct order of conodonts, a jawless vertebrate. Families Families are: * †Bactrognathidae * † Chirognathidae * †Ellisoniidae * †Gondolellidae * † Prioniodinidae References * Sweet, W. C; P. C.J Donoghue (2001). "Conodonts: past, present, future". Journal of Paleontology 75 (6): 1174. External links * Prioniodinida at biolib.cz(retrieved 22 April 2016) Prioniodinidaat fossilworks.org (retrieved 22 April 2016) † A dagger, obelisk, or obelus is a typographical mark that usually indicates a footnote if an asterisk has already been used. The symbol is also used to indicate death (of people) or extinction (of species or languages). It is one of the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordata
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (Apomorphy and synapomorphy, synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other Taxon, taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a neural tube, hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anus, anal tail. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and inner mitochondrial membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provide molecular means to reliably distinguish chordates from all other animals. Chordates are divided into three phylum, subphyla: Vertebrata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals), whose notochor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodont
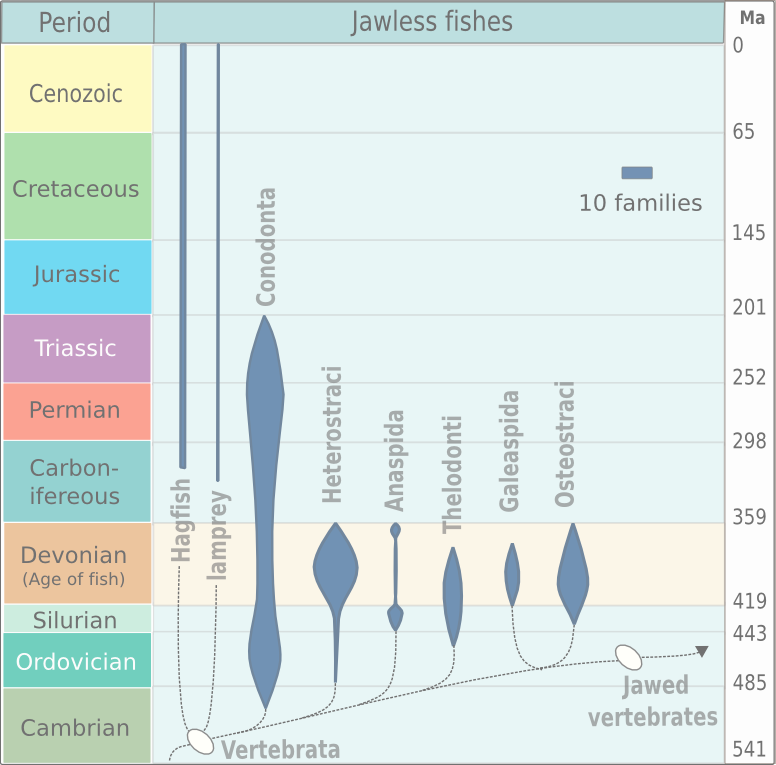
Conodonts, are an extinct group of marine jawless vertebrates belonging to the class Conodonta (from Ancient Greek κῶνος (''kōnos''), meaning " cone", and ὀδούς (''odoús''), meaning "tooth"). They are primarily known from their hard, mineralised tooth-like structures called "conodont elements" that in life were present in the oral cavity and used to process food. Rare soft tissue remains suggest that they had elongate eel-like bodies with large eyes. Conodonts were a long-lasting group with over 300 million years of existence from the Cambrian (over 500 million years ago) to the beginning of the Jurassic (around 200 million years ago). Conodont elements are highly distinctive to particular species and are widely used in biostratigraphy as indicative of particular periods of geological time. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactrognathidae
Bactrognathidae is an extinct family of conodonts in the order Prioniodinida. Genera are ''Bactrognathus'', ''Doliognathus'', and ''Staurognathus''. References External links Bactrognathidae at fossilworks.org (retrieved 22 April 2016) Conodont families Prioniodinida {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirognathidae
Chirognathidae is an extinct family of conodonts.Stratigraphical distribution of the Ordovician conodont Erraticodon Dzik in Argentina. S. Heredia, J. Carlorosi, A. Mestre and T. Soria, Journal of South American Earth Sciences, Volume 45, August 2013, Pages 224–234, Genera are '' Chirognathus'' and '' Erraticodon''. References External links Chirognathidae at biolib.cz(retrieved 30 April 2016) Prioniodinida Conodont families {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellisoniidae
Ellisoniidae is an extinct family of conodonts, a kind of primitive chordate. Genera Genera are: * †'' Ellisonia'' * †'' Foliella'' * †'' Hadrodontina'' * †'' Parapachycladina'' * †'' Parafurnishius'' * †'' Stepanovites'' References External links * Ellisoniidaeat fossilworks Fossilworks was a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was cr ....org (retrieved 22 April 2016) Conodont families Prioniodinida {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondolellidae
Gondolellidae is an extinct family of conodonts in the order Ozarkodinida Ozarkodinida is an extinct conodont order. It is part of the clade Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts". Name Ozarkodinida is named after the Ozark Mountains of Missouri Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, .... There are three subfamilies: Mullerinae, Neogondolellinae and Novispathodinae. References External links * * Ozarkodinida families {{conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prioniodinidae
Prioniodinidae is an extinct family of conodonts in the order Prioniodinida Prioniodinida is an extinct order of conodonts, a jawless vertebrate. Families Families are: * †Bactrognathidae * † Chirognathidae * † Ellisoniidae * † Gondolellidae * † Prioniodinidae References * Sweet, W. C; P. C.J Donoghue (20 .... Genera Genera are: * †'' Bryantodus'' * †'' Camptognathus'' * †'' Chirodella'' * †'' Cornuramia'' * †'' Dyminodina'' * †'' Falodus'' * †'' Guizhoudella'' * †'' Gyrognathus'' * †'' Idioprionodus'' * †'' Kamuellerella'' * †'' Lagovidina'' * †'' Ligonodina'' * †'' Metalonchodina'' * †'' Multidentodus'' * †'' Neoplectospathodus'' * †'' Oulodus'' * †'' Palmatodella'' * †'' Pluckidina'' * †'' Polygnathellus'' * †'' Prioniodella'' * †'' Prioniodina'' * †'' Prionognathodus'' * †'' Pristognathus'' * †'' Scotlandia'' * †'' Subbryantodus'' * †'' Uncadina'' * †'' Veghella'' References * Novyy ranneordovikskiy r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodont
Conodonts, are an extinct group of marine jawless vertebrates belonging to the class Conodonta (from Ancient Greek κῶνος (''kōnos''), meaning " cone", and ὀδούς (''odoús''), meaning "tooth"). They are primarily known from their hard, mineralised tooth-like structures called "conodont elements" that in life were present in the oral cavity and used to process food. Rare soft tissue remains suggest that they had elongate eel-like bodies with large eyes. Conodonts were a long-lasting group with over 300 million years of existence from the Cambrian (over 500 million years ago) to the beginning of the Jurassic (around 200 million years ago). Conodont elements are highly distinctive to particular species and are widely used in biostratigraphy as indicative of particular periods of geological time. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnatha
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfishes and lampreys) and Extinction, extinct clades (e.g. conodonts and Cephalaspidomorphi, cephalaspidomorphs, among others). They are sister taxon, sister to vertebrates with jaws known as gnathostomes, who evolution, evolved from jawless ancestors during the early Silurian by developing folding joint, articulations in the first pairs of gill arches. Sequencing, Molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as Embryology, embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that both groups of living agnathans, hagfishes and lampreys, are more closely related to each other than to Gnathostomata, jawed fish, forming the Class (biology), superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian. Living jawless fish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossilworks
Fossilworks was a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was created in 1998 by John Alroy and housed at Macquarie University Macquarie University ( ) is a Public university, public research university in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Founded in 1964 by the New South Wales Government, it was the third university to be established in the Sydney metropolitan area. .... It included many analysis and data visualization tools formerly included in the Paleobiology Database.{{cite web, title=Frequently asked questions, url=http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?page=FAQ, publisher=Fossilworks, access-date=17 December 2021, archive-date=18 May 2022, archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220518205516/http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?page=FAQ, url-status=dead Fossilworks was sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |