|
Pleura
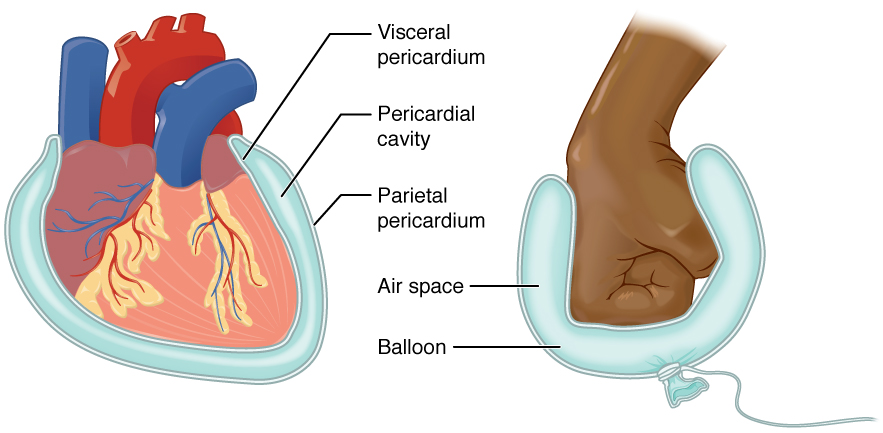
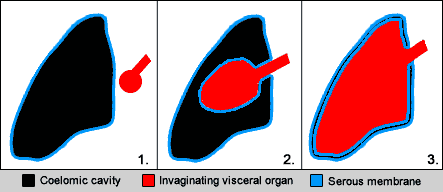
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the mediastinum, the inside surfaces of the surrounding chest walls and the diaphragm. Although wrapped onto itself resulting in an apparent double layer, each lung is surrounded by a single, continuous pleural membrane. The portion of the pleura that covers the surface of each lung is often called the visceral pleura. This can lead to some confusion, as the lung is not the only visceral organ covered by the pleura. The pleura typically dips between the lobes of the lung as ''fissures'', and is formed by the invagination of lung buds into each thoracic sac during embryonic development. The portion of the pleura seen as the outer layer covers the chest wall, the diaphragm and the mediastinum and is often also misleadingly called the parieta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleural Cavity
The pleural cavity, or pleural space (or sometimes intrapleural space), is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication between the membranes, and also to create a pressure gradient. The serous membrane that covers the surface of the lung is the visceral pleura and is separated from the outer membrane, the parietal pleura, by just the film of pleural fluid in the pleural cavity. The visceral pleura follows the fissures of the lung and the root of the lung structures. The parietal pleura is attached to the mediastinum, the upper surface of the diaphragm, and to the inside of the ribcage. Structure In humans, the left and right lungs are completely separated by the mediastinum, and there is no communication between their pleural cavities. Therefore, in cases of a unilateral pneumothorax, the contralateral lung will remain functioning n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleural Fluid
The pleural cavity, or pleural space (or sometimes intrapleural space), is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication between the membranes, and also to create a pressure gradient. The serous membrane that covers the surface of the lung is the visceral pleura and is separated from the outer membrane, the parietal pleura, by just the film of pleural fluid in the pleural cavity. The visceral pleura follows the fissures of the lung and the root of the lung structures. The parietal pleura is attached to the mediastinum, the upper surface of the diaphragm, and to the inside of the ribcage. Structure In humans, the left and right lungs are completely separated by the mediastinum, and there is no communication between their pleural cavities. Therefore, in cases of a unilateral pneumothorax, the contralateral lung will remain functioning normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes Animal communication#Auditory, vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory System
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In terrestrial animal, land animals, the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles, these are called pulmonary alveolus, alveoli, and in birds, they are known as Bird anatomy#Respiratory system, atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchus, bronchi. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Ligament
The root of the lung is a group of structures that emerge at the hilum of each lung, just above the middle of the mediastinal surface and behind the cardiac impression of the lung. It is nearer to the back (posterior border) than the front (anterior border). The root of the lung is connected by the structures that form it to the heart and the trachea. The rib cage is separated from the lung by a two-layered membranous coating, the pleura. The hilum is the large triangular depression where the connection between the parietal pleura (covering the rib cage) and the visceral pleura (covering the lung) is made, and this marks the meeting point between the mediastinum and the pleural cavities. Location The root of the right lung lies behind the superior vena cava and part of the right atrium, and below the azygos vein. That of the left lung passes beneath the aortic arch and in front of the descending aorta; the phrenic nerve, pericardiacophrenic artery and vein, and the anterio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serosa
The serous membrane (or serosa) is a smooth epithelial membrane of mesothelium lining the contents and inner walls of body cavities, which secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding movements between opposing surfaces. The serous membrane that covers internal organs (viscera) is called ''visceral'', while the one that covers the cavity wall is called ''parietal''. For instance the parietal peritoneum is attached to the abdominal wall and the pelvic walls. The visceral peritoneum is wrapped around the visceral organs. For the heart, the layers of the serous membrane are called parietal and visceral pericardium. For the lungs they are called parietal and visceral pleura. The visceral serosa of the uterus is called the perimetrium. The potential space between two opposing serosal surfaces is mostly empty except for the small amount of serous fluid. The Latin anatomical name is tunica serosa. Serous membranes line and enclose several body cavities, also known as s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serous Membrane
The serous membrane (or serosa) is a smooth epithelial membrane of mesothelium lining the contents and inner walls of body cavity, body cavities, which secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding (motion), sliding movements between opposing surfaces. The serous membrane that covers Viscera, internal organs (viscera) is called ''visceral'', while the one that covers the cavity wall is called ''parietal''. For instance the peritoneum, parietal peritoneum is attached to the abdominal wall and the pelvic walls. The peritoneum, visceral peritoneum is wrapped around the visceral organs. For the heart, the layers of the serous membrane are called parietal and visceral pericardium. For the lungs they are called parietal and visceral pleura. The visceral serosa of the uterus is called the perimetrium. The potential space between two opposing serosal surfaces is mostly empty except for the small amount of serous fluid. The Latin anatomical name is Tunica (biology)#Anatomy usages, tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the vagus nerve, vagus, phrenic nerve, phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pulmonary pleurae, pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the Spine (anatomy), spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercostal Nerve
The intercostal nerves are part of the somatic nervous system, and arise from the anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11. The intercostal nerves are distributed chiefly to the thoracic pleura and abdominal peritoneum, and differ from the anterior rami of the other spinal nerves in that each pursues an independent course without plexus formation. The first two nerves supply fibers to the upper limb and thorax; the next four distribute to the walls of the thorax; the lower five supply the walls of the thorax and abdomen. The 7th intercostal nerve ends at the xyphoid process of the sternum. The 10th intercostal nerve terminates at the navel. The 12th ( subcostal) thoracic is distributed to the walls of the abdomen and groin. Each of these fibers contains around 1300 axons. Unlike the nerves from the autonomic nervous system that innervate the visceral pleura of the thoracic cavity, the intercostal nerves arise from the somatic nervous system. This enables th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprapleural Membrane
The suprapleural membrane, eponymously known as Sibson's fascia, is a structure described in human anatomy. It is named for Francis Sibson. Anatomy It refers to a thickening of connective tissue that covers the apex of each human lung. It is an extension of the endothoracic fascia that exists between the parietal pleura and the thoracic cage. Sibson muscular part is originated from scalenus minimus muscle. Fascial part is originated from Endothoracic Fascia. It attaches to the internal border of the first rib and the transverse processes of vertebra Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ... C7. It extends approximately an inch more superiorly than the superior thoracic aperture, because the lungs themselves extend higher than the top of the ribcage. Clinical significanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |