|
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of Node (networking), nodes. In addition, a personal area network (PAN) is also in nature a type of Decentralized computing, decentralized peer-to-peer network typically between two devices. Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage, or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client–server model in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided. While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the Internet file sharing system Napster, originally released in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decentralized Computing
Decentralized computing is the allocation of resources, both hardware and software, to each individual workstation, or office location. In contrast, centralized computing exists when the majority of functions are carried out or obtained from a remote centralized location. Decentralized computing is a trend in modern-day business environments. This is the opposite of centralized computing, which was prevalent during the early days of computers. A decentralized computer system has many benefits over a conventional centralized network. Desktop computers have advanced so rapidly, that their potential performance far exceeds the requirements of most business applications. This results in most desktop computers remaining idle (in relation to their full potential). A decentralized system can use the potential of these systems to maximize efficiency. However, it is debatable whether these networks increase overall effectiveness. All computers have to be updated individually with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Application
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different computer network, networked computers. The components of a distributed system communicate and coordinate their actions by message passing, passing messages to one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining Concurrency (computer science), concurrency of components, overcoming the clock synchronization, lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from service-oriented architecture, SOA-based systems to microservices to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer, peer-to-peer applications. Distributed systems cost significantly more than monolithic architectures, primarily due to increased needs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Sharing
File sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digital media, such as computer programs, multimedia (audio, images and video), documents or electronic books. Common methods of storage, transmission and dispersion include removable media, centralized servers on computer networks, Internet-based hyperlinked documents, and the use of distributed peer-to-peer networking. File sharing technologies, such as BitTorrent, are integral to modern media piracy, as well as the sharing of scientific data and other free content. History Files were first exchanged on removable media. Computers were able to access remote files using filesystem mounting, bulletin board systems (1978), Usenet (1979), and FTP servers (1970's). Internet Relay Chat (1988) and Hotline (1997) enabled users to communicate remotely through chat and to exchange files. The mp3 encoding, which was standardized in 1991 and substantially reduced the size of audio files, grew to widespread use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napster
Napster was an American proprietary peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing application primarily associated with digital audio file distribution. Founded by Shawn Fanning and Sean Parker, the platform originally launched on June 1, 1999. Audio shared on the service was typically encoded in the MP3 format. As the software became popular, the company encountered legal difficulties over copyright infringement. Napster ceased operations in 2001 after losing multiple lawsuits and filed for bankruptcy in June 2002. The P2P model employed by Napster involved a centralized database that indexed a complete list of all songs being shared from connected clients. While effective, the service could not function without the central database, which was hosted by Napster and eventually forced to shut down. Following Napster's demise, alternative decentralized methods of P2P file-sharing emerged, including LimeWire, Gnutella, Freenet, FastTrack, I2P, and BitTorrent. Napster's assets were event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miracast
Miracast is a Wireless, wireless communications standard created by the Wi-Fi Alliance which is designed to transmit video and sound from devices (such as laptops or smartphones) to display receivers (such as TVs, monitors, or projectors). It uses Wi-Fi Direct to create an Wireless ad hoc network, ad hoc encrypted wireless connection and can roughly be described as "HDMI over Wi-Fi", replacing cables in favor of wireless.On Wifi-Display, Democratic Republics and Miracles Patrick Herrmann, on the development of Miraclecast, 2014-02-17. Miracast is utilised in many devices and is used or branded under various names by different manufacturers, including Smart View (by Samsung), SmartShare (by LG), screen mirroring (by Sony), Cast (in Windows 11) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BitTorrent
BitTorrent is a Protocol (computing), communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a Decentralised system, decentralized manner. The protocol is developed and maintained by Rainberry, Inc., and was first released in 2001. To send or receive files, users use a Comparison of BitTorrent clients, BitTorrent client on their Internet-connected computer, which are available for a variety of computing platforms and Comparison of BitTorrent clients#Operating system support, operating systems, including BitTorrent (software), an official client. BitTorrent trackers provide a list of files available for transfer and allow the client to find peer users, known as "seeds", who may transfer the files. BitTorrent downloading is considered to be faster than HTTP ("direct downloading") and File Transfer Protocol, FTP due to the lack of a central server that could limit bandwidth. BitTorrent is one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Request For Comments
A Request for Comments (RFC) is a publication in a series from the principal technical development and standards-setting bodies for the Internet, most prominently the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). An RFC is authored by individuals or groups of engineers and computer scientists in the form of a memorandum describing methods, behaviors, research, or innovations applicable to the working of the Internet and Internet-connected systems. It is submitted either for peer review or to convey new concepts, information, or, occasionally, engineering humor. The IETF adopts some of the proposals published as RFCs as Internet Standards. However, many RFCs are informational or experimental in nature and are not standards. The RFC system was invented by Steve Crocker in 1969 to help record unofficial notes on the development of ARPANET. RFCs have since become official documents of Internet specifications, communications protocols, procedures, and events. According to Crocker, the docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
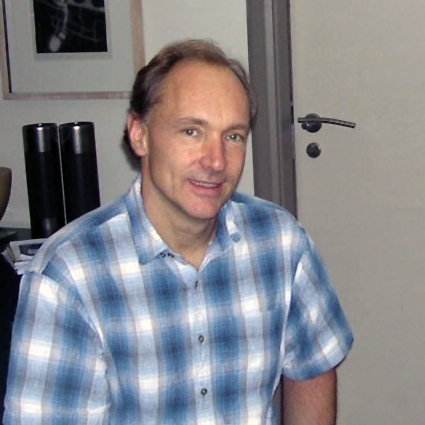
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web, the HTML markup language, the URL system, and HTTP. He is a professorial research fellow at the University of Oxford and a professor emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Berners-Lee proposed an information management system on 12 March 1989 and implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and Server (computing), server via the Internet in mid-November. He devised and implemented the first Web browser and Web server and helped foster the Web's subsequent development. He is the founder and emeritus director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which oversees the continued development of the Web. He co-founded (with Rosemary Leith) the World Wide Web Foundation. In April 2009, he was elected as Foreign Associate of the National Academy of Sciences. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the data distribution, distribution of sound, audio audiovisual content to dispersed audiences via a electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a :wikt:one-to-many, one-to-many model. Broadcasting began with AM radio, which came into popular use around 1920 with the spread of vacuum tube radio transmitters and radio receiver, receivers. Before this, most implementations of electronic communication (early radio, telephone, and telegraph) were wikt:one-to-one, one-to-one, with the message intended for a single recipient. The term ''broadcasting'' evolved from its use as the agricultural method of sowing seeds in a field by casting them broadly about. It was later adopted for describing the widespread distribution of information by printed materials or by telegraph. Examples applying it to "one-to-many" radio transmissions of an individual station to multiple listeners appeared as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the HTTP, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). The Web was invented by English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee while at CERN in 1989 and opened to the public in 1993. It was conceived as a "universal linked information system". Documents and other media content are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |