|
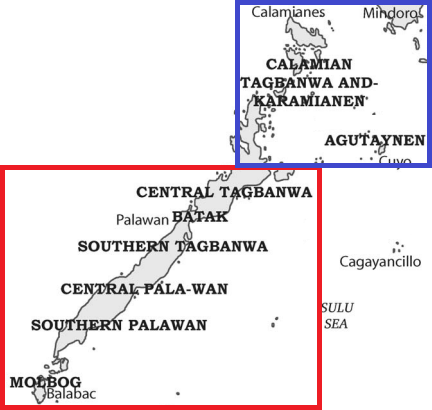
Palawanic Languages
The Palawanic languages are a subgroup in the Greater Central Philippine-family spoken on the island of Palawan and nearby islets. Languages The Palawanic languages are: * Palawano (a language cluster) ** Brooke's point Palawano ** Central Palawano ** Southwest Palawano *** Tau't Batu * Aborlan Tagbanwa * Central Tagbanwa (not to be confused with Kalamian Tagbanwa) *Batak (not to be confused with the Batak languages) Molbog Palawan, the largest province in the Philippines, is home to several indigenous ethnolinguistic groups namely, the Kagayanen, Tagbanwa, Palawano, Taaw't Bato, Molbog, and Batak tribes. They live in remote villages in the mountains and coa ... may also be in this group, closest to Palawano. Ethnologue classifies Bonggi as Palawanic. Reconstruction Proto-Palawanic has been reconstructed by Thiessen (1980). References Further reading *Zorc, R. David. (1972a). Palawano Notes'. *Zorc, R. David. (1972b). Tagbanwa (Northern) Notes'. Greater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palauan Language
Palauan () is a Malayo-Polynesian language native to the Republic of Palau, where it is one of the two official languages, alongside English. It is widely used in day-to-day life in the country. Palauan is not closely related to other Malayo-Polynesian languages and its exact classification within the branch is unclear. Classification It is a member of the Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian family of languages, and is one of only two indigenous languages in Micronesia that are not part of the Oceanic sub-branch of that family, the other being Chamorro (see , , , and ). Roger Blench (2015) argues that based on evidence from fish names, Palauan had early contact with Oceanic languages either directly or indirectly via the Yapese language. These include fish names for the sea eel, yellowfin tuna ('' Thunnus albacares''), left-eye flounder ('' Bothus mancus''), triggerfish, sailfish, barracuda ('' Sphyraena barracuda''), damsel fish ('' Abudefduf'' sp.), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooke's Point Palawano
The Palawano languages are spoken in the province of Palawan in the Philippines, by the Palawano people. Classification There are three Palawano languages: the ''Quezon Palawano'' (PLC) which is also known as ''Central Palawano''; ''Brooke's Point Palawano'' (PLW) and its dialect the ''Bugsuk Palawano'' or ''Southwest Palawano'' (PLV). The three Palawano languages share the island with several other Palawanic languages which are not part of the Palawano cluster, though they share a fair amount of vocabulary. Phonology The following overview is based on Revel-MacDonald (1979). Consonants Vowels Grammar Verb conjugations are similar to other Filipino dialects with prefixes and suffixes indicating tense, object or actor focus, as well as intention (i.e. commands). These prefixes and suffixes can be used to create various parts of speech from the same root word. For example, ''biyag'', meaning 'life', can be manipulated to mean 'to live' (''megbiyag''), 'full of food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonggi Language
Bonggi (Banggi) is an Austronesian language spoken primarily by the Bonggi people of Banggi Island, off the northern tip of Sabah, Malaysia Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre .... Orthography Vowels and diphthongs * a – , unstressed * e – * i – * o – * u – * aa – * ee – * ii – * oo – * uu – * ai – * ou – Consonants * b – , between vowels, before u * d – , before i * f – * g – , before u * h – , before i, at the end of a word * j – * k – * l – , before i * m – * n – * ng – * p – * r – * s – * t – * w – * y – At the ends of words, k, p, and t are not released. References Further reading * Northeast Sabahan languages Languages of Malaysia Endangered Austronesian lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molbog Language
Molbog is an Austronesian language spoken in the Philippines and Sabah, Malaysia. The majority of speakers are concentrated at the southernmost tip of the Philippine province of Palawan, specifically the municipalities of Bataraza and Balabac. Both municipalities are considered as bastions for environmental conservation in the province. The majority of Molbog speakers are Muslims. The classification of Molbog is controversial. Thiessen (1981) groups Molbog with the Palawanic languages, based on shared phonological and lexical innovations. This classification is supported by Smith (2017). An alternative view is taken by Lobel (2013), who puts Molbog together with Bonggi in a Molbog-Bonggi subgroup. Ethnically, the Molbog was previously a sub-group of the larger Palaw'an people, and later became as it is due to Islamic influences from the Tausug and Sama-Bajau peoples The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian people, Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batak Languages
__FORCETOC__ The Batak languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken by the Batak people in the Indonesian province of North Sumatra and surrounding areas. Internal classification The Batak languages can be divided into two main branches, Northern Batak and Southern Batak. Simalungun was long considered an intermediary, but in current classifications it is recognized as part of the Southern branch.Adelaar, K. A. (1981). "Reconstruction of Proto-Batak Phonology". In Robert A. Blust (ed.), ''Historical Linguistics in Indonesia: Part I'', 1–20. Jakarta: Universitas Katolik Indonesia Atma Jaya. Within Northern Batak, a study noted 80% cognate words between Karo and Alas, 81% with Pakpak, 76% with Simalungun & Toba, and 30% with Malay (Indonesian).The Austronesian languages of Asia and Madagascar. K. Alexander Adelaar, Nikolaus Himmelmann, p. 535 Karo and Toba Batak are mutually unintelligible. Mandailing, Toba and Angkola are related to each other and mutually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palawan Batak Language
Batak is an Austronesian language spoken by the Batak people on Palawan Island in the Philippines. It is sometimes disambiguated from the Batak languages __FORCETOC__ The Batak languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken by the Batak people in the Indonesian province of North Sumatra and surrounding areas. Internal classification The Batak languages can be divided into two mai ... as Palawan Batak. Batak is spoken in the communities of Babuyan, Maoyon, Tanabag, Langogan, Tagnipa, Caramay, and Buayan. Surrounding languages include Southern Tagbanwa, Central Tagbanwa, Kuyonon, and Agutaynen. Phonology Pronouns References Aeta languages Endangered Austronesian languages Palawanic languages Languages of Palawan {{GCPhilippine-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalamian Languages
The Kalamian languages are a small cluster of languages spoken in the Philippines: Calamian Tagbanwa and Agutaynen language, Agutaynen. Other languages called Tagbanwa, the Aborlan Tagbanwa language and Central Tagbanwa language are members of the Palawanic languages. These are among the few languages of the Philippines which continue to be written in Tagbanwa script, indigenous scripts, though mostly for poetry. Classification The Kalamian languages are a primary branch of the Philippine languages, Philippine language family, notable for reflecting Proto-Malayo-Polynesian language, Proto-Malayo-Polynesian ''*q'' as ''k'' and ''*R'' as ''l'', while reducing original ''*k'' to zero. References *Himes, Ronald S. 2007.The Kalamian microgroup of Philippine languages. ''Studies in Philippine languages and cultures'' 15:54-72. Further reading *Zorc, R. David. 1972. Agutaynon notes'. *Zorc, R. David. 1972. Kalamian notes'. See also *Tagbanwa script Calamian languages, Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Tagbanwa Language
Central Tagbanwa is spoken on Palawan Island in the Philippines. It is not mutually intelligible In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between different but related language varieties in which speakers of the different varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. Mutual intellig ... with the other languages of the Tagbanwa people. Phonology Consonants * preceding a high front vowel is usually realized as an affricate sound . * tend to shift to uvular sounds when adjacent to . Vowels * is usually a high central vowel sound, although it is occasionally moved further back to , or lowered to . * An sound is often heard when two back vowels are adjacent to one another, or as an allophone of . Grammar Pronouns The following set of pronouns are the personal pronouns found in the Central Tagbanwa language. Note: some forms are divided between full and short forms. The demonstratives are as follows. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aborlan Tagbanwa Language
Aborlan, officially the Municipality of Aborlan (), is a municipality in the province of , Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 38,736 people. Aborlan is the province's only town with an agricultural college, now called Western Philippines University. It was founded in 1910. Etymology Many stories tell about how the town got its present name: *''Abelnan'', a legendary tree of the gods; and *The English phrase "A Boar Land" that an American man shouted as he noticed the place with wild boars, thus making the place called Aboarland. History Formerly a municipal district, Aborlan became a municipality on June 28, 1949 by virtue of Executive Order No. 232. In 1951, the municipality lost the barrios of Berong and Alfonso XII when those were transferred to the newly created town of Quezon. Geography It lies in a vast plain between the Sulu Sea and the mountains, south of Puerto Princesa City. Barangays Aborlan is politically subdivided into 19 baran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Palawano
The Palawano languages are spoken in the province of Palawan in the Philippines, by the Palawano people. Classification There are three Palawano languages: the ''Quezon Palawano'' (PLC) which is also known as ''Central Palawano''; ''Brooke's Point Palawano'' (PLW) and its dialect the ''Bugsuk Palawano'' or ''Southwest Palawano'' (PLV). The three Palawano languages share the island with several other Palawanic languages which are not part of the Palawano cluster, though they share a fair amount of vocabulary. Phonology The following overview is based on Revel-MacDonald (1979). Consonants Vowels Grammar Verb conjugations are similar to other Filipino dialects with prefixes and suffixes indicating tense, object or actor focus, as well as intention (i.e. commands). These prefixes and suffixes can be used to create various parts of speech from the same root word. For example, ''biyag'', meaning 'life', can be manipulated to mean 'to live' (''megbiyag''), 'full of food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |