|
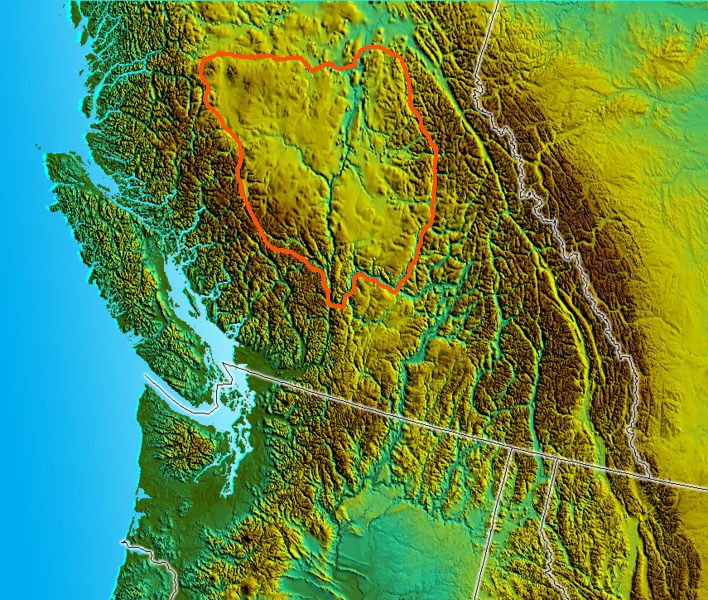
Omineca Country
The Omineca Country, also called the Omineca District or the Omineca, is a historical geographic region of the Northern Interior of British Columbia, roughly defined by the basin of the Omineca River but including areas to the south which allowed access to the region during the Omineca Gold Rush of the 1860s. The term Omineca District also refers to the Omineca Mining District which referred to the same area but was a government administrative division. Today the name loosely refers to the region northwest of Prince George and north of Hwy 16 (the Yellowhead Highway) and occurs in the names of such entities as electoral districts, e.g. Prince George-Omineca. See also *Cariboo *Chilcotin District The Chilcotin () region of British Columbia is usually known simply as "the Chilcotin", and also in speech commonly as "the Chilcotin Country" or simply Chilcotin. It is a plateau and mountain region in British Columbia on the inland lee of the C ... * Lost Creek * Peace River Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia Interior
The British Columbia Interior, popularly referred to as the BC Interior or simply the Interior, is a geographic region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. While the exact boundaries are variously defined, the British Columbia Interior is generally defined to include the 14 regional districts that do not have coastline along the Pacific Ocean or Salish Sea, and are not part of the Lower Mainland. Other boundaries may exclude parts of or even entire regional districts, or expand the definition to include the regional districts of Fraser Valley, Squamish–Lillooet, and Kitimat–Stikine. Home to just under 1 million people, the British Columbia Interior's 14 regional districts contain many cities, towns, airports, and associated regional, provincial, and national parks connected by the province's highway and railway network. The region is known for the complexity of its landforms, the result of millions of years of tectonic plate movements. The ecology of the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omineca River
Omineca River is a river of the North American boreal forest, in northern British Columbia, Canada. It flows into Williston Lake, and is part of the Peace River basin. Before the creation of Williston Lake, the Omineca was a tributary of the Finlay River. According to Father Adrien-Gabriel Morice the name is derived from a Sekani word meaning 'lake-like or sluggish river'. Tributaries * Ominicetla Creek * Germansen River * Osilinka River * Mesilinka River See also *List of rivers of British Columbia The following is a partial list of rivers of British Columbia, organized by drainage basin, watershed. Some large creeks are included either because of size or historical importance (See Alphabetical List of British Columbia rivers ). Also includ ... References * Rivers of British Columbia Omineca Country Cassiar Land District {{BritishColumbiaInterior-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omineca Gold Rush
The Omineca Gold Rush was a gold rush in British Columbia, Canada, in the Omineca Country, Omineca region of the Northern Interior of the province. Gold was first discovered there in 1861, but the rush did not begin until late in 1869 with the discovery at Vital Creek. There were several routes to the goldfields: two were from Fort St. James, one of which was a water route through the Stuart River (Canada), Stuart and Tachie River, Tachie Rivers to Trembleur Lake to Takla Lake and the other was overland, called the Baldy Mountain route. A third route came in overland from Hazelton, British Columbia, Hazelton on the Skeena River and a fourth route used the Fraser River and crossed over the Giscome Portage to Summit Lake Provincial Park, Summit Lake, through McLeod Lake, and up the Finlay River to the Omineca River. 1860s Toy's Bar The first recorded gold discovery in the Omineca district was made by William Cust (miner), William Cust and Edward Carey (businessman), Edward Carey in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omineca Mining District
The Omineca Country, also called the Omineca District or the Omineca, is a historical geographic region of the Northern Interior of British Columbia, roughly defined by the basin of the Omineca River but including areas to the south which allowed access to the region during the Omineca Gold Rush of the 1860s. The term Omineca District also refers to the Omineca Mining District which referred to the same area but was a government administrative division. Today the name loosely refers to the region northwest of Prince George and north of Hwy 16 (the Yellowhead Highway) and occurs in the names of such entities as electoral districts, e.g. Prince George-Omineca. See also *Cariboo *Chilcotin District * Lost Creek *Peace River Block * Slate Creek *Stikine Country The Stikine Country , also referred to as the Stikine District or simply "the Stikine", is one of the historical geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia, located inland from the central Alaska Panha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince George, British Columbia
Prince George is a city in British Columbia, Canada, situated at the confluence of the Fraser River, Fraser and Nechako River, Nechako rivers. The city itself has a population of 76,708; the metro census agglomeration has a population of 89,490. It is often called the province's "northern capital". because it serves as a centre for higher education, health care, government services, arts and entertainment, sports, and support for major industries such as forest products and mining. History The origins of Prince George can be traced to the North West Company fur trading post of Fort George, which was established in 1807 by Simon Fraser (explorer), Simon Fraser and named in honour of George III, King George III.Runnalls, F.E. A History of Prince George. 1946 The post was centred in the centuries-old homeland of the Lheidli T'enneh Band, Lheidli T'enneh First Nations in Canada, First Nation, whose name means "people of the confluence of the two rivers." The Lheidli T'enneh name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia Highway 16
Highway 16 is a highway in British Columbia, Canada. It is an important section of the Yellowhead Highway, a part of the Trans-Canada Highway that runs across Western Canada. The highway closely follows the path of the northern B.C. alignment of the Canadian National Railway (CN). The number "16" was first given to the highway in 1941, and originally, the route that the highway took was more to the north of today's highway, and it was not as long as it is now. Highway 16 originally ran from New Hazelton east to Aleza Lake. In 1948, Highway 16's western end was moved from New Hazelton to the coastal city of Prince Rupert, and in 1953, the highway was re-aligned to end at Prince George. In 1969, further alignment east into Yellowhead Pass was opened to traffic after being constructed up through 1968 and raised to all-weather standards in 1969. Highway 16's alignment on Haida Gwaii was commissioned in 1983 and is connected to the mainland segment via BC Ferries route #11. A seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowhead Highway
The Yellowhead Highway () is a major interprovincial highway in Western Canada that runs from Winnipeg west to Graham Island off the coast of British Columbia via Saskatoon and Edmonton. It stretches across the four western provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba and is part of the Trans-Canada Highway system and the larger National Highway System, but should not be confused with the more southerly, originally-designated Trans-Canada Highway. The highway was officially opened in 1970. Beginning in 1990, the green and white Trans-Canada logo is used to designate the roadway. The highway is named for the Yellowhead Pass, the route chosen to cross the Canadian Rockies. The pass and the highway are named after a fur trader and explorer named Pierre Bostonais. He had yellow streaks in his hair, and was nicknamed " Tête Jaune" (Yellowhead). Almost the entire length of the highway is numbered as 16, except for the section in Manitoba that is concurrent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince George-Omineca
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". In a related sense, now not commonly used, all more or less sovereign rulers over a state, including kings, were "princes" in the language of international politics. They normally had another title, for example king or duke. Many of these were Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, ), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cariboo
The Cariboo is an intermontane region of British Columbia, Canada, centered on a plateau stretching from Fraser Canyon to the Cariboo Mountains. The name is a reference to the Caribou (North America), caribou that were once abundant in the region. The Cariboo was the first region of the interior north of the lower Fraser River and its canyon to be settled by non-indigenous people, and played an important part in the early history of the colony and province. The boundaries of the Cariboo proper in its historical sense are debatable, but its original meaning was the region north of the forks of the Quesnel River and the low mountainous basins between the mouth of that river on the Fraser at the city of Quesnel and the northward end of the Cariboo Mountains, an area that is mostly in the Quesnel Highland and focused on several now-famous gold-bearing creeks near the head of the Willow River (British Columbia), Willow River. The richest of them all, Williams Creek (British Columbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilcotin District
The Chilcotin () region of British Columbia is usually known simply as "the Chilcotin", and also in speech commonly as "the Chilcotin Country" or simply Chilcotin. It is a plateau and mountain region in British Columbia on the inland lee of the Coast Mountains on the west side of the Fraser River. Chilcotin is also the name of the river draining that region. In the Chilcotin language, language of the Tsilhqot'in people, their name and the name of the river means "those of the red ochre river" (its tributary the Chilko River means "red ochre river"). The proper name of the Chilcotin Country, or Tsilhqotʼin territory, in their language is Tŝilhqotʼin Nen. The Chilcotin district is often viewed as an extension of the Cariboo region, east of that river, although it has a distinct identity from the Cariboo District. It is, nonetheless, part of the Cariboo Regional District which is a municipal-level body governing some aspects of infrastructure and land-used planning. The vast maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Creek (British Columbia)
Lost Creek is a creek located in the Omineca Country region of British Columbia British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that .... The creek flows into the Manson River from the south and was discovered in 1871. Lost Creek has been mined by Europeans and Chinese miners. References External links * Rivers of British Columbia Cassiar Land District {{BritishColumbia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace River Block
The Peace River Block is a area of land in northeastern British Columbia, in the Peace River Country. In exchange for building a rail line across Canada to British Columbia, the Canadian Pacific Railway was given the Railway Belt, of land on each side of the railway. To compensate the CPR for alienated or non-arable land in the strip, the province allowed the Government of Canada to take control of 3,500,000 acres within British Columbia, northeast of the Rocky Mountains. This arrangement passed the provincial Legislature on December 19, 1883, and passed the Parliament of Canada on March 21, 1884, as the ''Settlement Act''. All the land northeast of the Rocky Mountains became a provincial reserve pending the government of Canada's decision on what land to select, which prevented homesteading and land claims. After several surveys of the land, the government took possession of the Peace River Block in 1907. The land the government chose was an approximately square-shaped block o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |