|
Nihilism
Nihilism (; ) is a philosophy, or family of views within philosophy, that rejects generally accepted or fundamental aspects of human existence, such as objective truth, knowledge, morality, values, or meaning. The term was popularized by Ivan Turgenev, and more specifically by his character Bazarov in the novel '' Fathers and Sons''. There have been different nihilist positions, including that human values are baseless, that life is meaningless, that knowledge is impossible, or that some set of entities do not exist or are meaningless or pointless. Pratt, Alan.Nihilism" ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy''. . Scholars of nihilism may regard it as merely a label that has been applied to various separate philosophies, or as a distinct historical concept arising out of nominalism, skepticism, and philosophical pessimism, as well as possibly out of Christianity itself. Contemporary understanding of the idea stems largely from the Nietzschean 'crisis of nihilism', from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meaning Of Life
The meaning of life, or the answer to the question: "What is the meaning of life?", pertains to the intrinsic value (ethics), significance of Life, living or existence in general. Many other related questions include: "Why are we here?", "What is life all about?", or "What is the purpose of existence?" There have been many proposed answers to these questions from many different cultural and ideological backgrounds. The search for life's meaning has produced much philosophical, scientific, theological, and metaphysics, metaphysical speculation throughout history. Different people and cultures believe different things for the answer to this question. The meaning of life can be derived from philosophical and religious contemplation of, and scientific inquiries about existence, social ties, consciousness, and happiness. Many other issues are also involved, such as linguistic meaning, symbolic meaning, ontology, value (philosophy), value, Teleology, purpose, ethics, good and evil, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fathers And Sons (novel)
''Fathers and Sons'' (russian: «Отцы и дети»; ''Otcy i deti'', ; archaic spelling Отцы и дѣти), also translated more literally as ''Fathers and Children'', is an 1862 novel by Ivan Turgenev, published in Moscow by Grachev & Co. It is one of the most acclaimed Russian novels of the 19th century. Plot Arkady Kirsanov has just graduated from the University of Petersburg. He returns with a friend, Bazarov, to his father's modest estate in an outlying province of Russia. His father, Nikolay, gladly receives the two young men at his estate, called Marino, but Nikolay's brother, Pavel, soon becomes upset by the strange new philosophy called "nihilism" which the young men, especially Bazarov, advocate. Nikolay, initially delighted to have his son return home, slowly begins to feel uneasy. A certain awkwardness develops in his regard toward his son, as Arkady's radical views, much influenced by Bazarov, make Nikolay’s own beliefs feel dated. Nikolay has always tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nietzschean
Friedrich Nietzsche (1844–1900) developed his philosophy during the late 19th century. He owed the awakening of his philosophical interest to reading Arthur Schopenhauer's ''Die Welt als Wille und Vorstellung'' ('' The World as Will and Representation'', 1819, revised 1844) and said that Schopenhauer was one of the few thinkers that he respected, dedicating to him his essay ''Schopenhauer als Erzieher'' ('' Schopenhauer as Educator''), published in 1874 as one of his '' Untimely Meditations''. Since the dawn of the 20th century, the philosophy of Nietzsche has had great intellectual and political influence around the world. Nietzsche applied himself to such topics as morality, religion, epistemology, poetry, ontology, and social criticism. Because of Nietzsche's evocative style and his often outrageous claims, his philosophy generates passionate reactions running from love to disgust. Nietzsche noted in his autobiographical '' Ecce Homo'' that his philosophy developed and evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Pratt
Alan R. Pratt (born 1953) is a Professor of Humanities at Embry–Riddle University. He is known for his research on existential nihilism and meaning of life. Books * ''Tales of Florida Fishes'', Zane Grey's West Society, 2016 (contributing editor) * ''The Critical Response to Andy Warhol'', New York: Greenwood Press, 1997 (contributing editor) * ''The Dark Side: Thoughts on the Futility of Life from the Ancient Greeks to the Present'', New York: Citadel Press, 1994 * ''Black Humor: Critical Essays'', New York: Garland Publishing, Inc., 1993 (contributing editor) See also * nihilism Nihilism (; ) is a philosophy, or family of views within philosophy, that rejects generally accepted or fundamental aspects of human existence, such as objective truth, knowledge, morality, values, or meaning. The term was popularized by I ... References External links Alan Pratt at Embry-Riddle University University of West Florida alumni Florida State University alumni Embry� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baudrillard
Jean Baudrillard ( , , ; 27 July 1929 – 6 March 2007) was a French sociologist, philosopher and poet with interest in cultural studies. He is best known for his analyses of media, contemporary culture, and technological communication, as well as his formulation of concepts such as simulation and hyperreality. Baudrillard wrote about diverse subjects, including consumerism, gender relations, critique of economy, economics, social history, art, Western foreign policy, and popular culture. Among his best known works are ''Seduction'' (1978), '' Simulacra and Simulation'' (1981), ''America'' (1986), and ''The Gulf War Did Not Take Place'' (1991). His work is frequently associated with postmodernism and specifically post-structuralism. Baudrillard: "I have nothing to do with postmodernism."MLA Brennan, Eugene. Review of Pourquoi la guerre aujourd’hui?, by Jean Baudrillard, Jacques Derrida. French Studies: A Quarterly Review, vol. 71 no. 3, 2017, p. 449-449. Project MUSE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbitrariness
Arbitrariness is the quality of being "determined by chance, whim, or impulse, and not by necessity, reason, or principle". It is also used to refer to a choice made without any specific criterion or restraint. Arbitrary decisions are not necessarily the same as random decisions. For example, during the 1973 oil crisis, Americans were allowed to purchase gasoline only on odd-numbered days if their license plate was odd, and on even-numbered days if their license plate was even. The system was well-defined and not random in its restrictions; however, since license plate numbers are completely unrelated to a person's fitness to purchase gasoline, it was still an arbitrary division of people. Similarly, schoolchildren are often organized by their surname in alphabetical order, a non-random yet an arbitrary method—at least in cases where surnames are irrelevant. Philosophy Arbitrary actions are closely related to teleology, the study of purpose. Actions lacking a ''telos'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Pessimism
Philosophical pessimism is a family of philosophical views that assign a negative value to life or existence. Philosophical pessimists commonly argue that the world contains an empirical prevalence of pains over pleasures, that existence is ontologically or metaphysically adverse to living beings, and that life is fundamentally meaningless or without purpose. Their responses to this condition, however, are widely varied and can be life-affirming. Philosophical pessimism is not a single coherent movement, but rather a loosely associated group of thinkers with similar ideas and a resemblance to each other. In ''Weltschmerz: Pessimism in German Philosophy, 1860-1900'', Frederick C. Beiser describes philosophical pessimism as "the thesis that life is not worth living, that nothingness is better than being, or that it is worse to be than not be". In a very similar way, Schopenhauer argues that it would have been better if life had not come into existence. Although adherents of philos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objective Truth
In philosophy, objectivity is the concept of truth independent from individual subjectivity (bias caused by one's perception, emotions, or imagination). A proposition is considered to have objective truth when its truth conditions are met without bias caused by the mind of a sentient being. Scientific objectivity refers to the ability to judge without partiality or external influence. Objectivity in the moral framework calls for moral codes to be assessed based on the well-being of the people in the society that follow it. Moral objectivity also calls for moral codes to be compared to one another through a set of universal facts and not through subjectivity. Objectivity of knowledge Plato considered geometry to be a condition of idealism concerned with universal truth. In '' Republic'', Socrates opposes the sophist Thrasymachus's relativistic account of justice, and argues that justice is mathematical in its conceptual structure, and that ethics was therefore a precise an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, Epistemology, knowledge, Ethics, values, Philosophy of mind, mind, and Philosophy of language, language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some sources claim the term was coined by Pythagoras ( BCE), although this theory is disputed by some. Philosophical methodology, Philosophical methods include Socratic questioning, questioning, Socratic method, critical discussion, dialectic, rational argument, and systematic presentation. in . Historically, ''philosophy'' encompassed all bodies of knowledge and a practitioner was known as a ''philosopher''."The English word "philosophy" is first attested to , meaning "knowledge, body of knowledge." "natural philosophy," which began as a discipline in ancient India and Ancient Greece, encompasses astronomy, medicine, and physics. For example, Isaac Newton, Newton's 1687 ''Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulacra And Simulation
''Simulacra and Simulation'' (french: Simulacres et Simulation) is a 1981 philosophical treatise by the philosopher and cultural theorist Jean Baudrillard, in which the author seeks to examine the relationships between reality, symbols, and society, in particular the significations and symbolism of culture and media involved in constructing an understanding of shared existence. Simulacra are copies that depict things that either had no original, or that no longer have an original. Simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Summary Definition ''Simulacra and Simulation'' is most known for its discussion of symbols, signs, and how they relate to contemporaneity (simultaneous existences). Baudrillard claims that our current society has replaced all reality and meaning with symbols and signs, and that human experience is a simulation of reality. Moreover, these simulacra are not merely mediations of reality, nor even deceptive med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
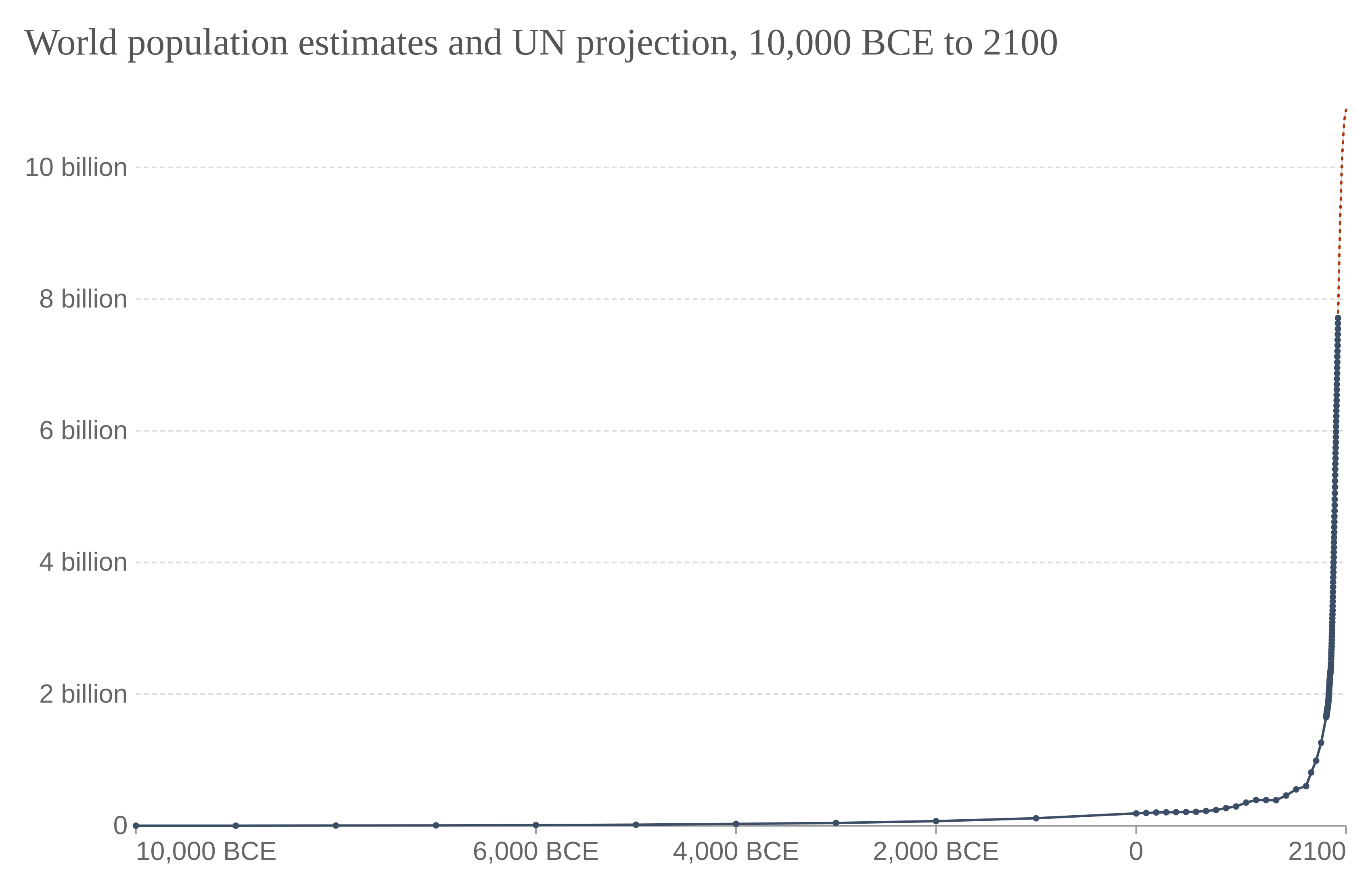
History By Period
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied through primary and secondary source documents. Humanity's written history was preceded by its prehistory, beginning with the Paleolithic ("Old Stone Age") era. This was followed by the Neolithic ("New Stone Age") era, which saw the Agricultural Revolution begin in the Middle East around 10,000 BCE. During this period, humans began the systematic husbandry of plants and animals. As agriculture advanced, most humans transitioned from a nomadic to a settled lifestyle as farmers in permanent settlements. The relative security and increased productivity provided by farming allowed communities to expand into increasingly larger units, fostered by advances in transportation. The earliest complex societies appeared in fertile river valleys. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold J
Arnold may refer to: People * Arnold (given name), a masculine given name * Arnold (surname), a German and English surname Places Australia * Arnold, Victoria, a small town in the Australian state of Victoria Canada * Arnold, Nova Scotia United Kingdom * Arnold, East Riding of Yorkshire * Arnold, Nottinghamshire United States * Arnold, California, in Calaveras County * Arnold, Carroll County, Illinois * Arnold, Morgan County, Illinois * Arnold, Iowa * Arnold, Kansas * Arnold, Maryland * Arnold, Mendocino County, California * Arnold, Michigan * Arnold, Minnesota * Arnold, Missouri * Arnold, Nebraska * Arnold, Ohio * Arnold, Pennsylvania * Arnold, Texas * Arnold, Brooke County, West Virginia * Arnold, Lewis County, West Virginia * Arnold, Wisconsin * Arnold Arboretum of Harvard University, Massachusetts * Arnold Township, Custer County, Nebraska Other uses * Arnold (automobile), a short-lived English car * Arnold of Manchester, a former English coachbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.gif)