|
Model Selection
Model selection is the task of selecting a model from among various candidates on the basis of performance criterion to choose the best one. In the context of machine learning and more generally statistical analysis, this may be the selection of a statistical model from a set of candidate models, given data. In the simplest cases, a pre-existing set of data is considered. However, the task can also involve the design of experiments such that the data collected is well-suited to the problem of model selection. Given candidate models of similar predictive or explanatory power, the simplest model is most likely to be the best choice (Occam's razor). state, "The majority of the problems in statistical inference can be considered to be problems related to statistical modeling". Relatedly, has said, "How hetranslation from subject-matter problem to statistical model is done is often the most critical part of an analysis". Model selection may also refer to the problem of selecting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , . Models can be divided into physical models (e.g. a ship model or a fashion model) and abstract models (e.g. a set of mathematical equations describing the workings of the atmosphere for the purpose of weather forecasting). Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science. In scholarly research and applied science, a model should not be confused with a theory: while a model seeks only to represent reality with the purpose of better understanding or predicting the world, a theory is more ambitious in that it claims to be an explanation of reality. Types of model ''Model'' in specific contexts As a noun, ''model'' has specific meanings in certain fields, derived from its original meaning of "structural design or layout": * Model (art), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodness Of Fit
The goodness of fit of a statistical model describes how well it fits a set of observations. Measures of goodness of fit typically summarize the discrepancy between observed values and the values expected under the model in question. Such measures can be used in statistical hypothesis testing, e.g. to test for normality of residuals, to test whether two samples are drawn from identical distributions (see Kolmogorov–Smirnov test), or whether outcome frequencies follow a specified distribution (see Pearson's chi-square test). In the analysis of variance, one of the components into which the variance is partitioned may be a lack-of-fit sum of squares. Fit of distributions In assessing whether a given distribution is suited to a data-set, the following tests and their underlying measures of fit can be used: * Bayesian information criterion * Kolmogorov–Smirnov test * Cramér–von Mises criterion * Anderson–Darling test * Berk-Jones tests * Shapiro–Wilk test * Chi-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akaike Information Criterion
The Akaike information criterion (AIC) is an estimator of prediction error and thereby relative quality of statistical models for a given set of data. Given a collection of models for the data, AIC estimates the quality of each model, relative to each of the other models. Thus, AIC provides a means for model selection. AIC is founded on information theory. When a statistical model is used to represent the process that generated the data, the representation will almost never be exact; so some information will be lost by using the model to represent the process. AIC estimates the relative amount of information lost by a given model: the less information a model loses, the higher the quality of that model. In estimating the amount of information lost by a model, AIC deals with the trade-off between the goodness of fit of the model and the simplicity of the model. In other words, AIC deals with both the risk of overfitting and the risk of underfitting. The Akaike information crite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Model Specification
In statistics, model specification is part of the process of building a statistical model: specification consists of selecting an appropriate functional form for the model and choosing which variables to include. For example, given personal income y together with years of schooling s and on-the-job experience x, we might specify a functional relationship y = f(s,x) as follows: : \ln y = \ln y_0 + \rho s + \beta_1 x + \beta_2 x^2 + \varepsilon where \varepsilon is the unexplained error term that is supposed to comprise independent and identically distributed Gaussian variables. The statistician Sir David Cox has said, "How hetranslation from subject-matter problem to statistical model is done is often the most critical part of an analysis". Specification error and bias Specification error occurs when the functional form or the choice of independent variables poorly represent relevant aspects of the true data-generating process. In particular, bias (the expected value of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploratory Data Analysis
In statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA) is an approach of data analysis, analyzing data sets to summarize their main characteristics, often using statistical graphics and other data visualization methods. A statistical model can be used or not, but primarily EDA is for seeing what the data can tell beyond the formal modeling and thereby contrasts with traditional hypothesis testing, in which a model is supposed to be selected before the data is seen. Exploratory data analysis has been promoted by John Tukey since 1970 to encourage statisticians to explore the data, and possibly formulate hypotheses that could lead to new data collection and experiments. EDA is different from Data analysis#Initial data analysis, initial data analysis (IDA), which focuses more narrowly on checking assumptions required for model fitting and hypothesis testing, and handling missing values and making transformations of variables as needed. EDA encompasses IDA. Overview Tukey defined data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Transformation (statistics)
In statistics, data transformation is the application of a deterministic mathematical function to each point in a data set—that is, each data point ''zi'' is replaced with the transformed value ''yi'' = ''f''(''zi''), where ''f'' is a function. Transforms are usually applied so that the data appear to more closely meet the assumptions of a statistical inference procedure that is to be applied, or to improve the interpretability or appearance of graphs. Nearly always, the function that is used to transform the data is invertible, and generally is continuous. The transformation is usually applied to a collection of comparable measurements. For example, if we are working with data on peoples' incomes in some currency unit, it would be common to transform each person's income value by the logarithm function. Motivation Guidance for how data should be transformed, or whether a transformation should be applied at all, should come from the particular statistical analysis to be pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robust Statistics
Robust statistics are statistics that maintain their properties even if the underlying distributional assumptions are incorrect. Robust Statistics, statistical methods have been developed for many common problems, such as estimating location parameter, location, scale parameter, scale, and regression coefficient, regression parameters. One motivation is to produce statistical methods that are not unduly affected by outliers. Another motivation is to provide methods with good performance when there are small departures from a Parametric statistics, parametric distribution. For example, robust methods work well for mixtures of two normal distributions with different standard deviations; under this model, non-robust methods like a t-test work poorly. Introduction Robust statistics seek to provide methods that emulate popular statistical methods, but are not unduly affected by outliers or other small departures from Statistical assumption, model assumptions. In statistics, classical e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
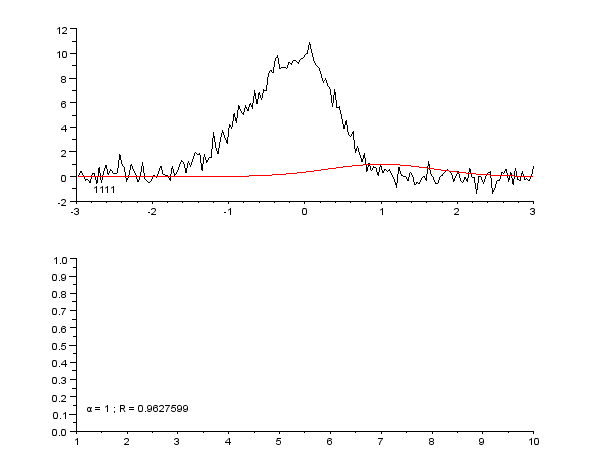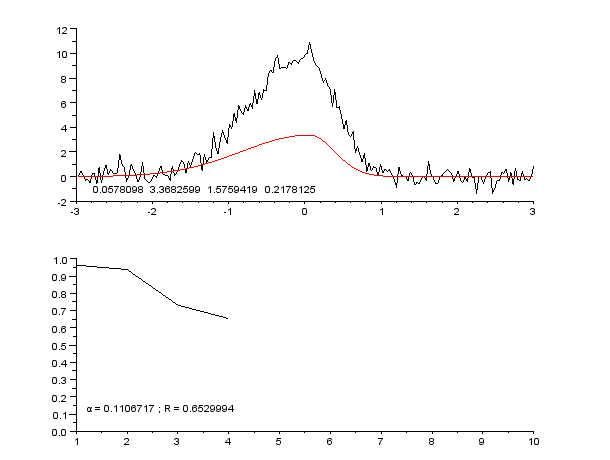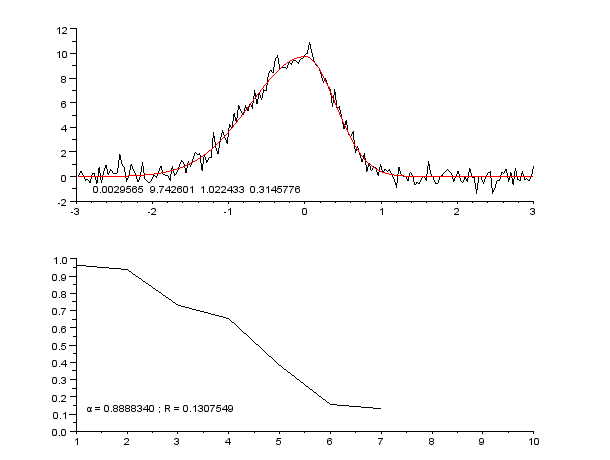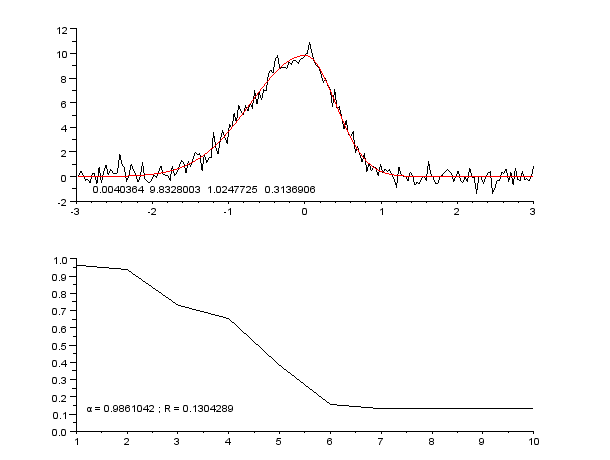
Curve Fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function is constructed that approximately fits the data. A related topic is regression analysis, which focuses more on questions of statistical inference such as how much uncertainty is present in a curve that is fitted to data observed with random errors. Fitted curves can be used as an aid for data visualization, to infer values of a function where no data are available, and to summarize the relationships among two or more variables. Extrapolation refers to the use of a fitted curve beyond the range of the observed data, and is subject to a degree of uncertainty since it may reflect the method used to construct the curve as much as it reflects the observed data. For linear-algebraic ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficiency (statistics)
In statistics, efficiency is a measure of quality of an estimator, of an experimental design, or of a hypothesis testing procedure. Essentially, a more efficient estimator needs fewer input data or observations than a less efficient one to achieve the Cramér–Rao bound. An ''efficient estimator'' is characterized by having the smallest possible variance, indicating that there is a small deviance between the estimated value and the "true" value in the L2 norm sense. The relative efficiency of two procedures is the ratio of their efficiencies, although often this concept is used where the comparison is made between a given procedure and a notional "best possible" procedure. The efficiencies and the relative efficiency of two procedures theoretically depend on the sample size available for the given procedure, but it is often possible to use the asymptotic relative efficiency (defined as the limit of the relative efficiencies as the sample size grows) as the principal comparison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. It is the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for example, the variance of a sum of uncorrelated random variables is equal to the sum of their variances. A disadvantage of the variance for practical applications is that, unlike the standard deviation, its units differ from the random variable, which is why the standard devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bias Of An Estimator
In statistics, the bias of an estimator (or bias function) is the difference between this estimator's expected value and the true value of the parameter being estimated. An estimator or decision rule with zero bias is called ''unbiased''. In statistics, "bias" is an property of an estimator. Bias is a distinct concept from consistency: consistent estimators converge in probability to the true value of the parameter, but may be biased or unbiased (see bias versus consistency for more). All else being equal, an unbiased estimator is preferable to a biased estimator, although in practice, biased estimators (with generally small bias) are frequently used. When a biased estimator is used, bounds of the bias are calculated. A biased estimator may be used for various reasons: because an unbiased estimator does not exist without further assumptions about a population; because an estimator is difficult to compute (as in unbiased estimation of standard deviation); because a biased esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
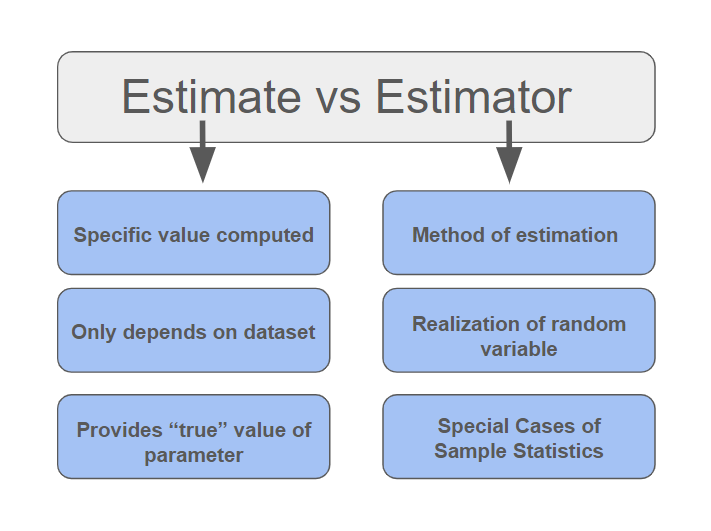
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on Sample (statistics), observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point estimator, point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |