|
Meat Industry
The meat industry are the people and companies engaged in modern industrialized livestock agriculture for the production, packing, preservation and marketing of meat (in contrast to dairy products, wool, etc.). In economics, the meat industry is a fusion of primary (agriculture) and secondary (industry) activity and hard to characterize strictly in terms of either one alone. The greater part of the meat industry is the meat packing industry – the segment that handles the slaughtering, processing, packaging, and distribution of animals such as poultry, cattle, pigs, sheep and other livestock. A great portion of the ever-growing meat branch in the food industry involves intensive animal farming in which livestock are kept almost entirely indoors or in restricted outdoor settings like pens. Many aspects of the raising of animals for meat have become industrialized, even many practices more associated with smaller family farms, e.g. gourmet foods such as foie gras. The producti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrialization
Industrialisation (British English, UK) American and British English spelling differences, or industrialization (American English, US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive reorganisation of an economy for the purpose of manufacturing. Industrialisation is associated with increase of Pollution, polluting industries heavily dependent on fossil fuels. With the increasing focus on sustainable development and green industrial policy practices, industrialisation increasingly includes Leapfrogging, technological leapfrogging, with direct investment in more advanced, cleaner technologies. The reorganisation of the economy has many unintended consequences both economically and socially. As industrial workers' incomes rise, markets for consumer goods and services of all kinds tend to expand and provide a further stimulus to industrial investment and economic growth. Moreo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worldwatch Institute
The Worldwatch Institute was a globally focused environmental research organization based in Washington, D.C., founded by Lester R. Brown. Worldwatch was named as one of the top ten sustainable development research organizations by Globescan Survey of Sustainability Experts. Brown left to found the Earth Policy Institute in 2000. The institute terminated in 2017, after publication of its last '' State of the World Report''. Worldwatch.org was unreachable from mid 2019. Mission The mission of the Institute read: "Through research and outreach that inspire action, the Worldwatch Institute works to accelerate the transition to a sustainable world that meets human needs. The Institute's top mission objectives are universal access to renewable energy and nutritious food, expansion of environmentally sound jobs and development, transformation of cultures from consumerism to sustainability, and an early end to population growth through healthy and intentional childbearing." The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feed Conversion Efficiency
In animal husbandry, feed conversion ratio (FCR) or feed conversion rate is a ratio or rate measuring of the efficiency with which the bodies of livestock convert animal feed into the desired output. For dairy cows, for example, the output is milk, whereas in animals raised for meat (such as beef cows,Dan Shike, University of IllinoiBeef Cattle Feed Efficiency/ref> pigs, chickens, and fish) the output is the flesh, that is, the body mass gained by the animal, represented either in the final mass of the animal or the mass of the dressed output. FCR is the mass of the input divided by the output (thus mass of feed per mass of milk or meat). In some sectors, feed efficiency, which is the output divided by the input (i.e. the inverse of FCR), is used. These concepts are also closely related to efficiency of conversion of ingested foods (ECI). Background Feed conversion ratio (FCR) is the ratio of inputs to outputs; it is the inverse of "feed efficiency" which is the ratio of output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
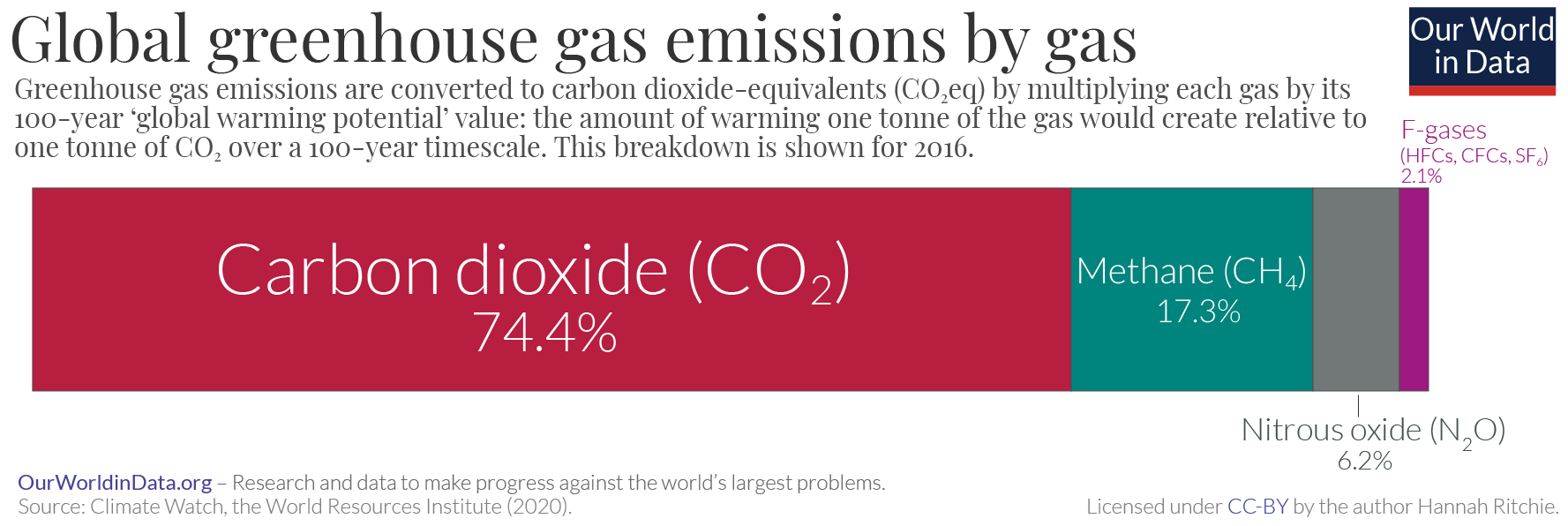
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Water pollution results when contaminants mix with these water bodies. Contaminants can come from one of four main sources. These are sewage discharges, industrial activities, agricultural activities, and urban runoff including stormwater. Water pollution may affect either surface water or groundwater pollution, groundwater. This form of pollution can lead to many problems. One is the environmental degradation, degradation of aquatic ecosystems. Another is spreading Waterborne diseases, water-borne diseases when people use polluted water for drinking or irrigation. Water pollution also reduces the ecosystem services such as drinking water provided by the Water resources, water resource. Sources of water pollution are either p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Use
Land use is an umbrella term to describe what happens on a parcel of land. It concerns the benefits derived from using the land, and also the land management actions that humans carry out there. The following categories are used for land use: forest land, cropland ( agricultural land), grassland, wetlands, settlements and other lands. The way humans use land, and how land use is changing, has many impacts on the environment. Effects of land use choices and changes by humans include, for example, urban sprawl, soil erosion, soil degradation, land degradation and desertification. Land use and land management practices have a major impact on natural resources including water, soil, nutrients, plants and animals. ''Land use change'' is "the change from one land-use category to another". Land-use change, together with use of fossil fuels, are the major anthropogenic sources of carbon dioxide, a dominant greenhouse gas. Human activity is the most significant cause of land c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livestock Industry
Livestock are the domesticated animals that are raised in an agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals which are raised for consumption, and sometimes used to refer solely to farmed ruminants, such as cattle, sheep, and goats. The breeding, maintenance, slaughter and general subjugation of livestock called ''animal husbandry'', is a part of modern agriculture and has been practiced in many cultures since humanity's transition to farming from hunter-gatherer lifestyles. Animal husbandry practices have varied widely across cultures and periods. It continues to play a major economic and cultural role in numerous communities. Livestock farming practices have largely shifted to intensive animal farming. Intensive animal farming increases the yield of the various commercial outputs, but also negatively impacts animal welfare, the envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply Chain
A supply chain is a complex logistics system that consists of facilities that convert raw materials into finished products and distribute them to end consumers or end customers, while supply chain management deals with the flow of goods in distribution channels within the supply chain in the most efficient manner. In sophisticated supply chain systems, used products may re-enter the supply chain at any point where residual value is recyclable. Supply chains link value chains. Suppliers in a supply chain are often ranked by "tier", with first-tier suppliers supplying directly to the client, second-tier suppliers supplying to the first tier, and so on. The phrase "supply chain" may have been first published in a 1905 article in ''The Independent (New York City), The Independent'' which briefly mentions the difficulty of "keeping a supply chain with India unbroken" during the British expedition to Tibet. Overview A typical supply chain can be divided into two stages namely, produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Integration
In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration, also referred to as vertical consolidation, is an arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each member of the supply chain produces a different Product (business), product or (market-specific) service, and the products combine to satisfy a common need. It contrasts with horizontal integration, wherein a company produces several items that are related to one another. Vertical integration has also described management styles that bring large portions of the supply chain not only under a common ownership but also into one corporation (as in the 1920s when the Ford River Rouge complex began making much of its own steel rather than buying it from suppliers). Vertical integration can be desirable because it secures supplies needed by the firm to produce its product and the market needed to sell the product, but it can become undesirable wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foie Gras
; (, ) is a specialty food product made of the liver of a Domestic duck, duck or Domestic goose, goose. According to French law, ''foie gras'' is defined as the liver of a duck or goose fattened by ''gavage'' (force feeding). ''Foie gras'' is a delicacy in French cuisine. Its flavour is rich, buttery, and delicate, unlike an ordinary duck or goose liver. It is sold whole or is prepared as mousse, parfait, or pâté, and may also be served as an accompaniment to another food item, such as steak. French law states, "''Foie gras'' belongs to the protected cultural and gastronomical heritage of France." The technique of ''gavage'' dates as far back as 2500 BC, when the ancient Egyptians began confining Anatidae, anatid birds to be forcedly fed to be fattened as a food source. Today, France is by far the largest producer and consumer of ''foie gras'', though there are producers and markets worldwide, particularly in other European nations, the United States, and China. Foie gras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gourmet
Gourmet (, ) is a cultural idea associated with the culinary arts of fine food and drink, or haute cuisine, which is characterized by their high level of refined and elaborate food preparation techniques and displays of balanced meals that have an aesthetically pleasing presentation of several contrasting, often quite rich courses. Historically the ingredients used in the meal tended to be rare for the region, which could also be impacted by the local state and religious customs. The term and the related characteristics are typically used to describe people with more discerning palates and enthusiasm. Gourmet food is more frequently provided with small servings and in more upscale and posh fine dining establishments that cater to a more affluent and exclusive client base. When it comes to cooking gourmet dishes, there are also frequent cross-cultural interactions that introduce new, exotic, and expensive ingredients, materials, and traditions with more refined, complex, formal, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Farm
A family farm is generally understood to be a farm owned and/or operated by a family. It is sometimes considered to be an Estate (land), estate passed down by inheritance. Although a recurring conceptual model, conceptual and archetype, archetypal distinction is that of a family farm as a smallholding versus corporate farming as large-scale agribusiness, that notion does not accurately describe the realities of farm ownership in many countries. Family farm businesses can take many forms, from smallholder farms to larger farms operated under intensive farming practices. In various countries, most farm families have structured their farm businesses as corporations (such as limited liability company, limited liability companies) or trust (business), trusts, for liability, tax, and business purposes. Thus, the idea of a family farm as a unitary concept or definition does not easily translate across languages, cultures, or centuries, as there are substantial differences in agricultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |