|
January Uprising
The January Uprising was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at putting an end to Russian occupation of part of Poland and regaining independence. It began on 22 January 1863 and continued until the last insurgents were captured by the Russian forces in 1864. It was the longest-lasting insurgency in partitioned Poland. The conflict engaged all levels of society and arguably had profound repercussions on contemporary international relations and ultimately transformed Polish society. A confluence of factors rendered the uprising inevitable in early 1863. The Polish nobility and urban bourgeois circles longed for the semi-autonomous status they had enjoyed in Congress Poland before the previous insurgency, a generation earlier in 1830, and youth encouraged by the success of the Italian independence movement urgently desired the same outcome. Russia had been weakened by its Crimean adventure and had introduced a more liberal attitude in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish National Government (January Uprising)
The Polish National Government of 1863–64 was an underground Polish supreme authority during the January Uprising, a large scale insurrection during the Russian partition of the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It had a collegial form, resided in Warsaw and was headed by . It was intended as a temporary government, and functioned as an administrative institution with many ministries and departments. During 1863–1864 it was a real shadow government supported by the majority of Poles who even paid taxes for it, and a significant problem for the Russian secret police ( Third Section). "It organized one of the world's earliest campaigns of urban guerrilla warfare", according to Norman Davies. It became the prototype for the Polish Secret State during World War II. It was designed to be able to unite Poland Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romuald Traugutt
Romuald Traugutt (16 January 1826 – 5 August 1864) was a Polish military officer and politician who served as the last dictator of the January Uprising. Following a career in the Imperial Russian Army that included service in Hungary and Crimea, Traugutt reluctantly joined the uprising against the Russian Empire in March 1863, eventually rising to the position of the last leader of the ill-fated insurrection. Following capture by the Imperial Russian Police, he was tried and executed for his role in the Uprising. Despite the failure of the uprising, Traugutt became a Polish national hero. Following the return of Poland as a sovereign national entity he was recognized for his service, after decades of being censored by Imperial Russian authorities. Early life Traugutt was born on the , estate Grodno Governorate in the Russian Empire. Son of Ludwik and Alojza (nee Błocka). Following his mother's death when Traugutt was two, he was raised by his grandmother Justyna Błocka. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Military District (Russian Empire)
The Warsaw Military District () was a Russian military district of the Imperial Russian Army. It covered the territory of Congress Poland Congress Poland or Congress Kingdom of Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It was established w ... (without the part of Suwałki Governorate, Suwałki in Vilno Military District (Russian Empire), Vilno Military District). The Warsaw Military District was created in 1862. When World War I broke out, most of the units of the district (three out of its five infantry corps) were used to form the 2nd Army (Russian Empire), 2nd Army. Since the territory of the district was overrun by German and Austro-Hungarian armies in the course of 1915, it was dissolved, and its staff used in creating the new Minsk Military District. Composition The Warsaw Military District was an umbrella organisation for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan Bobrowski
Stefan Bobrowski (17 January 1840Sometimes given as 1841. – 12 April 1863) was a Polish politician and activist for Polish independence. He participated in the January 1863 Uprising as one of the leaders of its "Red" faction and as a member of that faction's Central National Committee (''Komitet Centralny Narodowy''), and of the Provisional National Government (''Tymczasowy Rząd Narodowy''). To rally peasants to the cause, he advocated land reform and an end to serfdom, while at the same time trying to ensure support from the ''szlachta'' (nobility). He also tried to establish links with potential revolutionaries within Russia who opposed their country's tsar. Bobrowski died in 1863 in a pistol duel with a member of the "White" faction, Count Adam Grabowski. He had agreed to the duel though he was sure to lose due to his extreme near-sightedness. Stefan Bobrowski was an uncle to English-language novelist Joseph Conrad, and a possible inspiration for the protagonist of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Muravyov-Vilensky
Count Mikhail Nikolayevich Muravyov (; 12 October 1796 in Moscow – 12 September 1866 in Saint Petersburg) was a Russian imperial statesman of the 19th century, most known for brutally putting down of Polish and Lithuanian uprisings and leading subsequent cultural and social depolonization of Northwestern Krai (today's Belarus and Lithuania). He should not be confused with his grandson, Mikhail Nikolayevich Muravyov, who served as Russian Foreign Minister between 1897 and 1900. Early years During his years at the University of Moscow, Muravyov set up the Mathematical Society, of which he would later become president. He volunteered during the Patriotic War of 1812 and was wounded at Borodino. In 1816 he became a co-founder of the first Decembrist societies, and, although he didn't actively participate in the movement after 1820, he was briefly apprehended by the police after their failed uprising in December 1825. By some sources he was cooperating with the investigation buyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm Rembert Von Berg
Friedrich Wilhelm Rembert Graf von Berg (; ; – ) was a Russian nobleman, statesman, diplomat and general of Baltic German descent. Berg was a count of the Austrian Empire and Grand Duchy of Finland. He was also the fifth last person to be promoted to the rank of general-field marshal in the history of the Russian Empire. He served as the governor-general of Finland from 1854 to 1861 and as the last viceroy of the Kingdom of Poland from 1863 to 1874. Berg was most notable for his role as the viceroy of Finland and Poland. He led Russian military efforts during the Åland War, a minor theater of the Crimean War, and also played a crucial role in suppressing the 1863 January Uprising by Congress Poland; during the uprising, the Poles carried out numerous unsuccessful assassination attempts on him, which led martial law to be consequently declared in Poland. Berg also held responsible for improving the economy and industry of Finland and Poland during his time as viceroy. As a Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander II Of Russia
Alexander II ( rus, Алекса́ндр II Никола́евич, Aleksándr II Nikoláyevich, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ftɐˈroj nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ; 29 April 181813 March 1881) was Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Finland from 2 March 1855 until Assassination of Alexander II of Russia, his assassination in 1881. Alexander's most significant reform as emperor was the emancipation reform of 1861, emancipation of Serfdom in Russia, Russia's serfs in 1861, for which he is known as Alexander the Liberator ( rus, Алекса́ндр Освободи́тель, r=Aleksándr Osvobodítel, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ɐsvəbɐˈdʲitʲɪlʲ). The tsar was responsible for other Liberalism, liberal reforms, including reorganizing the judicial system, setting up elected local judges, abolishing corporal punishment, promoting local self-government through the ''zemstvo'' system, imposing universal military service, ending some privileges of the nobility, and promot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Nationalism
Polish nationalism () is a nationalism which asserts that the Polish people are a nation and which affirms the cultural unity of Poles. British historian of Poland Norman Davies defines nationalism as "a doctrine ... to create a nation by arousing people's awareness of their nationality, and to mobilize their feelings into a vehicle for political action." The nationalism of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth – a polity which existed ''de facto'' from 1386, and officially from 1569, until the Commonwealth's 1795 Third Partition – incorporating Poles, Lithuanians, East Slavs, and smaller minorities. was multi-ethnic and multi-confessional, though the Commonwealth's dominant social classes became extensively Polonized and Roman Catholicism was regarded as the dominant religion. The nationalist ideology which arose soon after the Partitions was initially free of any kind of "ethnic nationalism". It was a Romantic movement which sought the restoration of a Polish sovereign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land And Liberty (Russia)
Land and Liberty (; also sometimes translated Land and Freedom) was a Russian clandestine revolutionary organization in the period 1861–1864, and was re-established as a political party A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular area's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific political ideology, ... in the period 1876–1879. It was a central organ of the ''Narodnik'' movement. The first composition (1861–1864) The inspirers of the society were Alexander Herzen and Nikolay Chernyshevsky. The participants set as their goal the preparation of a peasant revolution, their policy documents created under the influence of the ideas of Herzen and Ogarev, the latter of which had coined the term "Land and Liberty" in one of his articles. The first Executive Committee of the organization included 6 of its organizers (Nikolai Obruchev, Sergey Ryma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
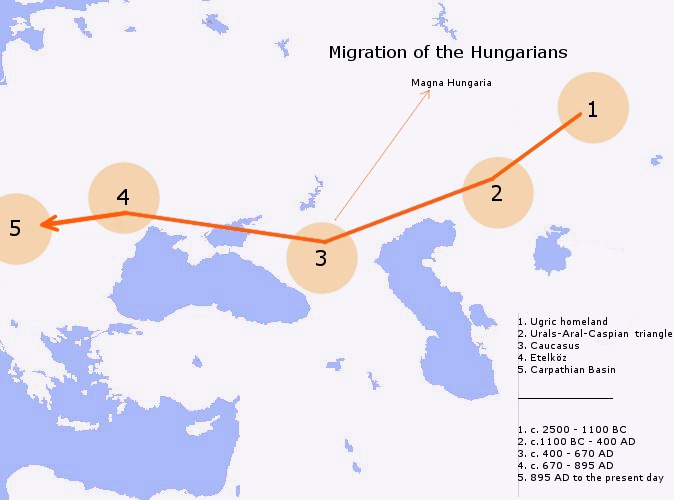
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs modern British citizenship and nationality, which can be acquired, for instance, by descent from British nationals. When used in a historical context, "British" or "Britons" can refer to the Ancient Britons, the Celtic-speaking inhabitants of Great Britain during the Iron Age, whose descendants formed the major part of the modern Welsh people, Cornish people, Bretons and considerable proportions of English people. It also refers to those British subjects born in parts of the former British Empire that are now independent countries who settled in the United Kingdom prior to 1973. Though early assertions of being British date from the Late Middle Ages, the Union of the Crowns in 1603 and the creation of the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707 triggered a sense of British national identit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French People
French people () are a nation primarily located in Western Europe that share a common Culture of France, French culture, History of France, history, and French language, language, identified with the country of France. The French people, especially the native speakers of langues d'oïl from northern and central France, are primarily descended from Roman people, Romans (or Gallo-Romans, western European Celts, Celtic and Italic peoples), Gauls (including the Belgae), as well as Germanic peoples such as the Franks, the Visigoths, the Suebi and the Burgundians who settled in Gaul from east of the Rhine after the fall of the Roman Empire, as well as various later waves of lower-level irregular migration that have continued to the present day. The Norsemen also settled in Normandy in the 10th century and contributed significantly to the ancestry of the Normans. Furthermore, regional ethnic minorities also exist within France that have distinct lineages, languages and cultures such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |