|
Geology Of British Columbia
The geology of British Columbia is a function of its location on the leading edge of the North American continent. The mountainous physiography and the diversity of the different types and ages of rock hint at the complex geology, which is still undergoing revision despite a century of exploration and mapping. The province's most prominent geological features are its mountain ranges, including the North American Cordillera which stretches from Southern Mexico to Alaska. Terrane theory Terrane theory was first proposed by Jim Monger of the Geological Survey of Canada and Charlie Rouse in 1971 as an explanation for a set of fusulinid fossils that were found in central British Columbia. Rather than suggest that facies changes or seaways were behind this (which were common explanations at the time), the two geologists proposed that the fossils in question had been part of an assemblage of rocks that had migrated across the Pacific Ocean to their present location. This theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons. These processes include those of mountain-building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Principles of tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles can help geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth-surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
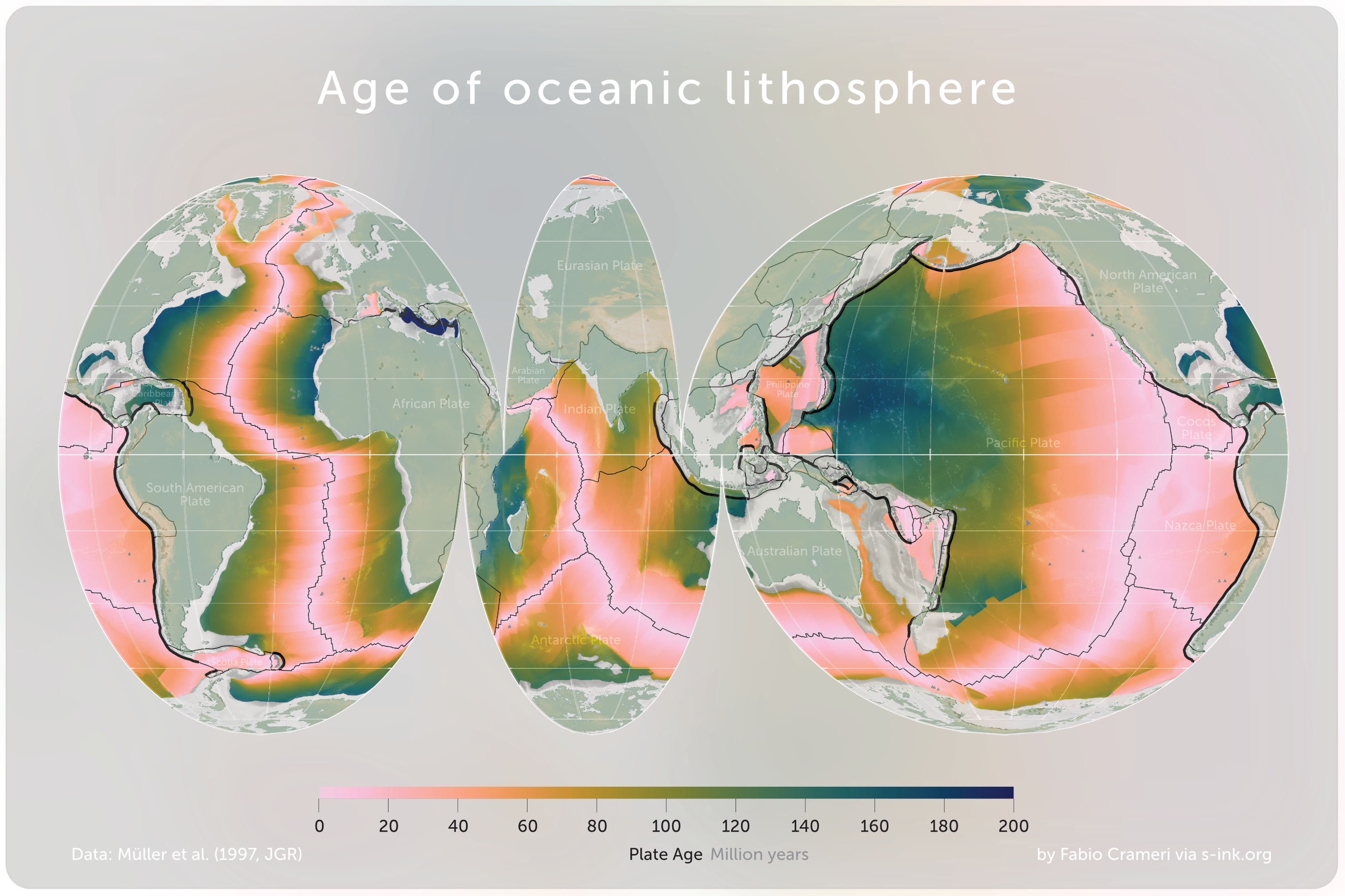
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust lies above the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Rock
Carbonate rocks are a class of sedimentary rocks composed primarily of carbonate minerals. The two major types are limestone, which is composed of calcite or aragonite (different crystal forms of CaCO3), and Dolomite (rock), dolomite rock (also known as dolostone), which is composed of Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2). They are usually Dunham classification, classified on the basis of texture and grain size. Importantly, carbonate rocks can exist as metamorphic and igneous rocks, too. When recrystallized carbonate rocks are Metamorphic rock, metamorphosed, marble is created. Rare igneous rock, igneous carbonate rocks even exist as Intrusive rock, intrusive carbonatites and, even rarer, there exists volcanic carbonate lava. Carbonate rocks are also crucial components to understanding Geological history of Earth, geologic history due to processes such as diagenesis in which carbonates undergo compositional changes based on kinetic effects. The correlation between this compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion (geology)
In geology, accretion is a process by which material is added to a tectonic plate at a subduction zone, frequently on the edge of existing continental landmasses. The added material may be sediment, volcanic arcs, seamounts, oceanic crust or other igneous features. Description Accretion involves the addition of material to a tectonic plate via subduction, the process by which one plate is forced under the other when two plates collide. The plate which is being forced down, the subducted plate, is pushed against the upper, over-riding plate. Sediment on the ocean floor of the subducting plate is often scraped off as the plate descends. This accumulated material is called an accretionary wedge (or accretionary prism), which is pushed against and attaches to the upper plate. In addition to accumulated ocean sediments, volcanic island arcs or seamounts present on the subducting plate may be amalgamated onto existing continental crust on the upper plate, increasing the contine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stitching Pluton
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and compositions, illustrated by examples like the Palisades Sill of New York and New Jersey; the Henry Mountains of Utah; the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa; Shiprock in New Mexico; the Ardnamurchan intrusion in Scotland; and the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California. Because the solid country rock into which magma intrudes is an excellent insulator, cooling of the magma is extremely slow, and intrusive igneous rock is coarse-grained (phaneritic). Intrusive igneous rocks are classified separately from extrusive igneous rocks, generally on the basis of their mineral content. The relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase, and feldspathoid is particularly important in classifying intrusive igneous rocks. Intrusions mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overlap Formation
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its distinctive geologic history, which is different from the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. There is also an older usage of the term ''terrane'', which described a series of related rock formations or an area with a preponderance of a particular rock or rock group. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane did not necessarily originate as an independent microplate, since it may not contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Fragment
Continental crustal fragments, partly synonymous with microcontinents, are pieces of continents that have broken off from main continental masses to form distinct islands that are often several hundred kilometers from their place of origin. Causes Continental fragments and microcontinent crustal compositions are very similar to those of regular continental crust. The rifting process that caused the continental fragments to form most likely impacts their layers and overall thickness along with the addition of mafic intrusions to the crust. Studies have determined that the average crustal thickness of continental fragments is approximately . The sedimentary layer of continental fragments can be up to thick and can overlay two to three crustal layers. Continental fragments have an average crustal density of which is very similar to that of typical continental crust. Strike-slip fault zones cause the fragmentation of microcontinents. The zones link the extensional zones where co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-oceanic Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Margin
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin consists of three different features: the continental rise, the continental slope, and the continental shelf. Continental margins constitute about 28% of the oceanic area. Subzones The continental shelf is the relatively shallow water area found in proximity to continents; it is the portion of the continental margin that transitions from the shore out towards to ocean. Continental shelves are believed to make up 7% of the sea floor. The width of continental shelves worldwide varies in the range of 0.03–1500 km. The continental shelf is generally flat, and ends at the shelf break, where there is a drastic increase in slope angle: The mean angle of continental shelves worldwide is 0° 07′, and typically steeper closer to the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |