|
Geodynamics
Geodynamics is a subfield of geophysics dealing with dynamics of the Earth. It applies physics, chemistry and mathematics to the understanding of how mantle convection leads to plate tectonics and geologic phenomena such as seafloor spreading, mountain building, volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting. It also attempts to probe the internal activity by measuring magnetic fields, gravity, and seismic waves, as well as the mineralogy of rocks and their isotopic composition. Methods of geodynamics are also applied to exploration of other planets. Overview Geodynamics is generally concerned with processes that move materials throughout the Earth. In the Earth's interior, movement happens when rocks melt or deform and flow in response to a stress field.Turcotte, D. L. and G. Schubert (2014). "Geodynamics." This deformation may be brittle, elastic, or plastic, depending on the magnitude of the stress and the material's physical properties, especially the stress relaxation time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and Physical property, properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct investigations across a wide range of scientific disciplines. The term ''geophysics'' classically refers to solid earth applications: Earth's figure of the Earth, shape; its gravitational, Earth's magnetic field, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields; its structure of the Earth, internal structure and Earth#Chemical composition, composition; its geodynamics, dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; geophysical fluid dynamics, fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; atmospheric electricity, electricity and magnetism in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle Convection
Mantle convection is the very slow creep of Earth's solid silicate mantle as convection currents carry heat from the interior to the planet's surface. Mantle convection causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface. The Earth's lithosphere rides atop the asthenosphere, and the two form the components of the upper mantle. The lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that are continuously being created or consumed at plate boundaries. Accretion occurs as mantle is added to the growing edges of a plate, associated with seafloor spreading. Upwelling beneath the spreading centers is a shallow, rising component of mantle convection and in most cases not directly linked to the global mantle upwelling. The hot material added at spreading centers cools down by conduction and convection of heat as it moves away from the spreading centers. At the consumption edges of the plate, the material has thermally contracted to become dense, and it sinks under its own weight i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
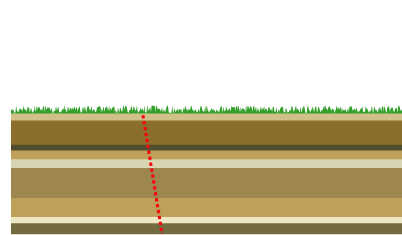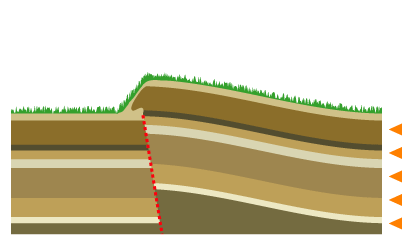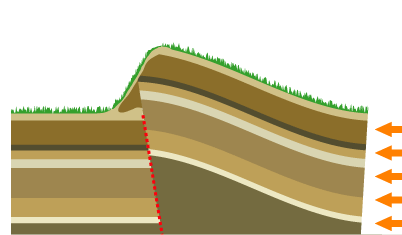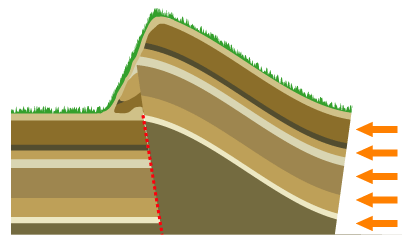
Mountain Building
Mountain formation occurs due to a variety of geological processes associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust (List of tectonic plates, tectonic plates). Fold (geology), Folding, Fault (geology), faulting, Volcano, volcanic activity, igneous intrusion and metamorphism can all be parts of the Orogeny, orogenic process of mountain building. The formation of mountains is not necessarily related to the structural geology, geological structures found on it. From the late 18th century until its replacement by plate tectonics in the 1960s, geosyncline, geosyncline theory was used to explain much mountain-building. The understanding of specific landscape features in terms of the underlying tectonics, tectonic processes is called ''geomorphology, tectonic geomorphology'', and the study of geologically young or ongoing processes is called ''neotectonics''. Types of mountains There are five main types of mountains: volcanic, fold, plateau, fault-block, and dome. A more de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by Earth science, geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust (geology), crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault (geology), fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the lithospheric mantle (or mantle lithosphere), the uppermost part of the mantle that is not convecting. The layer below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere, which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle that is able to convect. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodetic System
A geodetic datum or geodetic system (also: geodetic reference datum, geodetic reference system, or geodetic reference frame, or terrestrial reference frame) is a global datum reference or reference frame for unambiguously representing the position of locations on Earth by means of either geodetic coordinates (and related vertical coordinates) or geocentric coordinates. DatumsThe plural is not "data" in this case are crucial to any technology or technique based on spatial location, including geodesy, navigation, surveying, geographic information systems, remote sensing, and cartography. A horizontal datum is used to measure a horizontal position, across the Earth's surface, in latitude and longitude or another related coordinate system. A '' vertical datum'' is used to measure the elevation or depth relative to a standard origin, such as mean sea level (MSL). A three-dimensional datum enables the expression of both horizontal and vertical position components in a unified for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (geology)
A mantle is a layer inside a planetary body bounded below by a Planetary core, core and above by a Crust (geology), crust. Mantles are made of Rock (geology), rock or Volatile (astrogeology), ices, and are generally the largest and most massive layer of the planetary body. Mantles are characteristic of planetary bodies that have undergone planetary differentiation, differentiation by density. All Terrestrial planet, terrestrial planets (including Earth), half of the giant planets, specifically ice giants, a number of Asteroid, asteroids, and some planetary Natural satellite, moons have mantles. Examples Earth The Earth's mantle is a layer of Silicate minerals, silicate rock between the Crust (geology), crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. Its mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg is 67% the mass of the Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly solid, but in Geologic time scale, geological time it behaves as a Viscosity, visc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic waves through planetary bodies. It also includes studies of the environmental effects of earthquakes such as tsunamis; other seismic sources such as volcanoes, plate tectonics, glaciers, rivers, oceanic microseisms, and the atmosphere; and artificial processes such as explosions. Paleoseismology is a related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes. A recording of Earth's motion as a function of time, created by a seismograph is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who works in basic or applied seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Relaxation
In materials science, stress relaxation is the observed decrease in stress in response to strain generated in the structure. This is primarily due to keeping the structure in a strained condition for some finite interval of time hence causing some amount of plastic strain. This should not be confused with creep, which is a constant state of stress with an increasing amount of strain. Since relaxation relieves the state of stress, it has the effect of also relieving the equipment reactions. Thus, relaxation has the same effect as cold springing, except it occurs over a longer period of time. The amount of relaxation which takes place is a function of time, temperature and stress level, thus the actual effect it has on the system is not precisely known, but can be bounded. Stress relaxation describes how polymers relieve stress under constant strain. Because they are viscoelastic, polymers behave in a nonlinear, non-Hookean fashion.Meyers and Chawla. "Mechanical Behavior of Mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InSAR
Interferometric synthetic aperture radar, abbreviated InSAR (or deprecated IfSAR), is a radar technique used in geodesy and remote sensing. This geodetic method uses two or more synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images to generate maps of surface deformation or digital elevation, using differences in the phase of the waves returning to the satellite or aircraft. The technique can potentially measure millimetre-scale changes in deformation over spans of days to years. It has applications for geophysical monitoring of natural hazards, for example earthquakes, volcanoes and landslides, and in structural engineering, in particular monitoring of subsidence and structural stability. Technique Synthetic aperture radar Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar in which sophisticated processing of radar data is used to produce a very narrow effective beam. It can be used to form images of relatively immobile targets; moving targets can be blurred or displaced in the formed im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Core
Earth's outer core is a fluid layer about thick, composed of mostly iron and nickel that lies above Earth's solid Earth's inner core, inner core and below its Earth's mantle, mantle. The outer core begins approximately beneath Earth's surface at the Core–mantle boundary, core-mantle boundary and ends beneath Earth's surface at the inner core boundary. Properties The outer core of Earth is liquid, unlike its Earth's inner core, inner core, which is solid. Evidence for a fluid outer core includes seismology which shows that seismic wave, seismic S wave, shear-waves are not transmitted through the outer core. Although having a composition similar to Earth's solid inner core, the outer core remains liquid as there is not enough pressure to keep it in a solid state. Seismic inversions of Seismic wave#Body waves, body waves and Seismic wave#Normal modes, normal modes constrain the radius of the outer core to be 3483 km with an uncertainty of 5 km, while that of the inner core i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |