|
GNOME Core Applications
The GNOME Core Applications (also known as Apps for GNOME) are a software suite of software applications that are packaged as part of the standard free and open-source GNOME desktop environment. GNOME Core Applications have a consistent look and feel to the GNOME desktop, utilize the Adwaita (design language), Adwaita design language and tightly integrate with the GNOME desktop. GNOME Core Applications are developed and maintained through GNOME's official GitLab instance. A comprehensive list of these applications is available at Configuration * Settings – main interface to configure various aspects of GNOME. Diverse panels represent graphical front-ends to configure the NetworkManager, NetworkManager daemon and other daemons. Communication * Calls - initiating and answering Telephone call, phone calls and Voice over IP, VoIP calls (mainly utilized on Linux for mobile devices#Smartphones, Linux phones) * Contacts – the contacts book app Files * Document Scanner (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The GNOME Project
GNOME Project is a community behind the GNOME desktop environment and the software platform upon which it is based. It consists of all the software developers, artists, writers, translators, other contributors, and active users of GNOME. The GNOME Foundation used to recognize GNOME as part of GNU; however, in 2021, the staff of the Foundation declared that GNOME is not a GNU Project. GNOME Foundation In August 2000, the GNOME Foundation was set up to deal with administrative tasks and press interest, and to act as a contact point for companies interested in developing GNOME software. While not directly involved in technical decisions, the Foundation does coordinate releases and decide which projects will be part of GNOME. Membership is open to anyone who has made a non-trivial contribution to the project. Members of the Foundation elect a board of directors every November, and candidates for the positions must be members themselves. Programs and events The GNOME Project holds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux For Mobile Devices
Linux for mobile devices, sometimes referred to as mobile Linux, is the usage of Linux-based operating systems on portable devices, whose primary or only Human interface device (HID) is a touchscreen. It mainly comprises smartphones and tablet computers, but also some mobile phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs) portable media players that come with a touchscreen separately. Mobile Linux is a relatively recent addition to the Linux range of use, with Google's Android operating system pioneering the concept. While UBPorts tried to follow suit with Ubuntu Touch, a wider development of free Linux operating systems specifically for mobile devices was only really spurred in the latter 2010s, when various smaller companies started projects to develop open source phones. Lists Operating systems This is a list of Linux distros directly targeted towards use with mobile phones, being offered preconfigured with the mobile-oriented software listed below. There are both phone produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Usage
CPU time (or process time) is the amount of time that a central processing unit (CPU) was used for processing instructions of a computer program or operating system. CPU time is measured in clock ticks or seconds. Sometimes it is useful to convert CPU time into a percentage of the CPU capacity, giving the CPU usage. Measuring CPU time for two functionally identical programs that process identical inputs can indicate which program is faster, but it is a common misunderstanding that CPU time can be used to compare ''algorithms''. Comparing programs by their CPU time compares specific ''implementations'' of algorithms. (It is possible to have both efficient and inefficient implementations of the same algorithm.) Algorithms are more commonly compared using measures of time complexity and space complexity. Typically, the CPU time used by a program is measured by the operating system, which schedules all of the work of the CPU. Modern multitasking operating systems run hundred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNOME System Monitor
The GNOME Core Applications (also known as Apps for GNOME) are a software suite of software applications that are packaged as part of the standard free and open-source GNOME desktop environment. GNOME Core Applications have a consistent look and feel to the GNOME desktop, utilize the Adwaita design language and tightly integrate with the GNOME desktop. GNOME Core Applications are developed and maintained through GNOME's official GitLab instance. A comprehensive list of these applications is available at Configuration * Settings – main interface to configure various aspects of GNOME. Diverse panels represent graphical front-ends to configure the NetworkManager daemon and other daemons. Communication * Calls - initiating and answering phone calls and VoIP calls (mainly utilized on Linux phones) * Contacts – the contacts book app Files * Document Scanner (SimpleScan) - the scanner application * Image Viewer (Loupe) – the image viewer * Evince & Papers (Document ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatpak
Flatpak is a utility for software deployment and package management for Linux. It provides a sandbox environment in which users can run application software in (partial) isolation from the rest of the system. Flatpak was known as xdg-app until 2016. Features Applications using Flatpak need permissions to access resources such as Bluetooth, sound (with PulseAudio), network, and files. These permissions are configured by the maintainer of the Flatpak and can be added or removed by users on their system. Another key feature of Flatpak allows application developers to directly provide updates to users without going through Linux distributions, and without having to package and test the application separately for each distribution. Because Flatpak runs in a sandbox (which provides a separate, ABI-stable version of common system libraries), it uses more space on the system than common native packages. However, OSTree, a technology underlying Flatpak, deduplicates matching fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
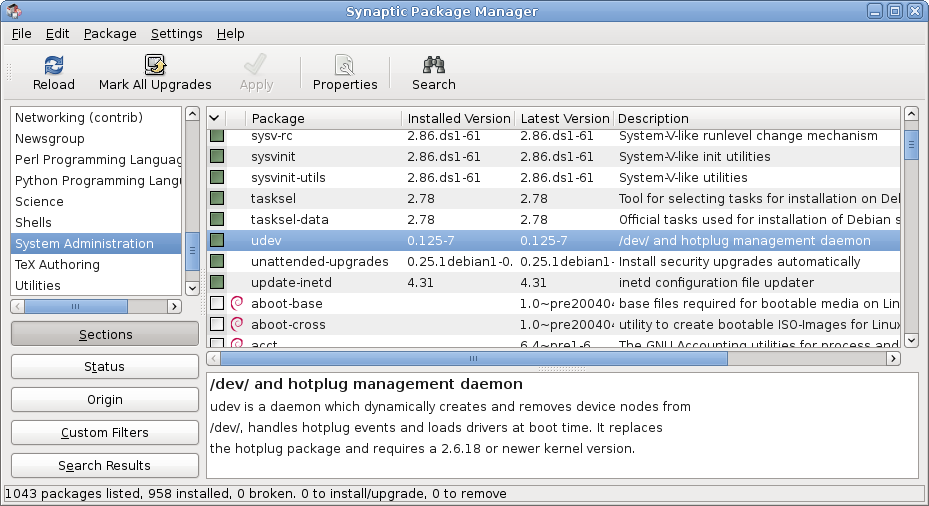
Package Manager
A package manager or package management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNOME Software
GNOME Software is a utility for installing applications and updates on Linux. It is part of the GNOME Core Applications, and was introduced in GNOME 3.10. It is the GNOME front-end to the PackageKit, in turn a front-end to several package management systems, which include systems based on both RPM and DEB. The program is used to add and manage software repositories as well as Ubuntu Ubuntu ( ) is a Linux distribution based on Debian and composed primarily of free and open-source software. Developed by the British company Canonical (company), Canonical and a community of contributors under a Meritocracy, meritocratic gover ... Personal Package Archives (PPA). Ubuntu replaced its previous Ubuntu Software Center program with GNOME Software starting with Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, and re-branded it as "Ubuntu Software". It also supports fwupd for servicing of system firmware. GNOME Software supports automatic updates for Flatpak applications, but not for system packages or upd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yelp (software)
Yelp, also known as the GNOME Help Browser is the default help viewer for GNOME that allows users to access help documentation. Yelp follows the freedesktop.org help system specification and reads mallard, DocBook, man pages, info, and HTML documents. HTML is available by using XSLT to render XML documents into HTML. Yelp has a search feature as well as a toolbar at the top for navigation through previously viewed documentation. Yelp can be accessed by typing either into GNOME Shell, after pressing within GNOME, or within a terminal using the format. The command can also be used to access Yelp. Although Yelp is not required for GNOME to function, it is required to view GNOME's help documentation. Ubuntu also uses yelp to provide a customized help interface for its software. A format string vulnerability in GNOME versions 2.19.90 and 2.24 allowed arbitrary code execution In computer security, arbitrary code execution (ACE) is an attacker's ability to run any commands or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Usage Analyzer
Disk Usage Analyzer is a graphical disk space analyzer, disk usage analyzer for GNOME. It was part of GNOME Core Applications, but was split off for GNOME 3.4. It was originally named Baobab after the ''Adansonia'' tree. The software gives the user a menu-driven, graphical representation of what is on a disk drive. The interface allows for selection of specific parts of filesystem being scanned so a single folder, the entire filesystem, and even remote folders and filesystems can be scanned. The graphical representation can be switched between a ring chart and a treemap chart so the presentation can be tailored to the specific content being scanned. In 2012, Disk Usage Analyzer was rewritten in Vala (programming language), Vala. Future At the GNOME Users And Developers European Conference (GUADEC) in 2013, a plan to merge the Disk Usage Analyzer with gnome-system-monitor to a new program called Usage was presented.https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/SystemMonitor/MergeWithUsage SystemM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |