|
Federalism In Australia
Federalism was adopted, as a constitutional principle, in Australia on 1 January 1901 – the date upon which the six self-governing Australian Colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia federated, formally constituting the Commonwealth of Australia. It remains a federation of those six "original States" under the Constitution of Australia. Australia is the sixth oldest surviving federation in the world after the United States (1789), Mexico (1824), Switzerland (1848), Canada (1867), and Brazil (1891). Relatively few changes have been made in terms of the formal (written) constitution since Australian federation occurred; in practice, however, the way the federal system functions has changed enormously. The most significant respect in which it has changed is in the degree to which the Commonwealth government has assumed a position of dominance. Federation Instigated by Henry Parkes' Tenterfield Oration of 24 Octo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Australia
The Constitution of Australia (or Australian Constitution) is a written constitution, constitutional document that is Constitution, supreme law in Australia. It establishes Australia as a Federation of Australia, federation under a constitutional monarchy and outlines the structure and powers of the Australian government's three constituent parts, the Government of Australia, executive, Parliament of Australia, legislature, and Judiciary of Australia, judiciary. The constitution was drafted between 1891 and 1898, through a series of Constitutional Convention (Australia), conventions conducted by representatives of the six self-governing British colonies in Australia. The final draft was then approved in a 1898–1900 Australian constitutional referendums, set of referendums from 1898 to 1900. The British government objected to some elements of the final draft, but a slightly modified form was enacted as section 9 of the ''Commonwealth of Australia Constitution Act 1900'', an Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Parkes
Sir Henry Parkes, (27 May 1815 – 27 April 1896) was a colonial Australian politician and longest non-consecutive Premier of the Colony of New South Wales, the present-day state of New South Wales in the Commonwealth of Australia. He has been referred to as the "Father of Federation" due to his early promotion for the federation of the six colonies of Australia, as an early critic of British convict transportation and as a proponent for the expansion of the Australian continental rail network. Parkes delivered his famous Tenterfield Oration in 1889, which yielded a federal conference in 1890 and a Constitutional Convention in 1891, the first of a series of meetings that led to the federation of Australia. He died in 1896, five years before this process was completed. He was described during his lifetime by ''The Times'' as "the most commanding figure in Australian politics". Alfred Deakin described Sir Henry Parkes as having flaws but nonetheless being "a large-brai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of Australia
The states and territories are federated state, federated administrative divisions in Australia, ruled by regional governments that constitute the second level of governance between the Australian Government, federal government and local government in Australia, local governments. States are self-governance, self-governing polity, polities with incomplete sovereignty (having ceded some sovereign rights to federation) and have their own state constitution (Australia), constitutions, legislatures, ministry (government department), departments, and certain civil authority, civil authorities (e.g. Judiciary of Australia#State and territory courts and tribunals, judiciary and state police#Australia, law enforcement) that administer and deliver most public policy, public policies and programs. Territories can be autonomous administrative division, autonomous and administer local policies and programs much like the states in practice, but are still constitutionally and financially su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Court Of Australia (6769096715)
The High Court of Australia is Australia's apex court. It exercises original and appellate jurisdiction on matters specified within Australia's Constitution. The High Court was established following passage of the ''Judiciary Act 1903''. It derives its authority from Chapter III of the Australian Constitution, which vests it responsibility for the judicial power of the Commonwealth. Important legal instruments pertaining to the High Court include the ''Judiciary Act 1903'' and the ''High Court of Australia Act 1979''.. Its bench is composed of seven justices, including a Chief Justice, currently Susan Kiefel. Justices of the High Court are appointed by the Governor-General on the advice of the Prime Minister and are appointed permanently until their mandatory retirement at age 70, unless they retire earlier. The court has resided in Canberra since 1980, following the construction of a purpose-built High Court Building, located in the Parliamentary Triangle and overlooki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Court Of Australia
The High Court of Australia is Australia's apex court. It exercises original and appellate jurisdiction on matters specified within Australia's Constitution. The High Court was established following passage of the ''Judiciary Act 1903''. It derives its authority from Chapter III of the Australian Constitution, which vests it responsibility for the judicial power of the Commonwealth. Important legal instruments pertaining to the High Court include the ''Judiciary Act 1903'' and the ''High Court of Australia Act 1979''.. Its bench is composed of seven justices, including a Chief Justice, currently Susan Kiefel. Justices of the High Court are appointed by the Governor-General on the advice of the Prime Minister and are appointed permanently until their mandatory retirement at age 70, unless they retire earlier. The court has resided in Canberra since 1980, following the construction of a purpose-built High Court Building, located in the Parliamentary Triangle and overlooking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Senate
The Senate is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of Australia, the lower house being the House of Representatives. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Chapter I of the Constitution of Australia. There are a total of 76 senators: 12 are elected from each of the six Australian states regardless of population and 2 from each of the two autonomous internal Australian territories (the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory). Senators are popularly elected under the single transferable vote system of proportional representation. Unlike upper houses in other Westminster-style parliamentary systems, the Senate is vested with significant powers, including the capacity to reject all bills, including budget and appropriation bills, initiated by the government in the House of Representatives, making it a distinctive hybrid of British Westminster system, Westminster bicameralism and American-style bicameralism. As a result of propor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicameralism
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single group. , about 40% of world's national legislatures are bicameral, and about 60% are unicameral. Often, the members of the two chambers are elected or selected by different methods, which vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. This can often lead to the two chambers having very different compositions of members. Enactment of primary legislation often requires a concurrent majority—the approval of a majority of members in each of the chambers of the legislature. When this is the case, the legislature may be called an example of perfect bicameralism. However, in many parliamentary and semi-presidential systems, the house to which the executive is responsible (e.g. House of Commons of UK and National Assembly of France) can overrule the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federalism In The United States
Federalism in the United States is the constitutional division of power between U.S. state governments and the federal government of the United States. Since the founding of the country, and particularly with the end of the American Civil War, power shifted away from the states and toward the national government. The progression of federalism includes dual, cooperative, and new federalism. Early federalism Federalism is a form of political organization that seeks to distinguish states and unites them, which assigns different types of decision-making power at different levels to allow a degree of political independence in an overarching structure. Federalism was a political solution for the problems with the Articles of Confederation which gave little practical authority to the federal government. For example, the Articles allowed the Continental Congress the power to sign treaties and declare war, but it could not raise taxes to pay for an army and all major decisions requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
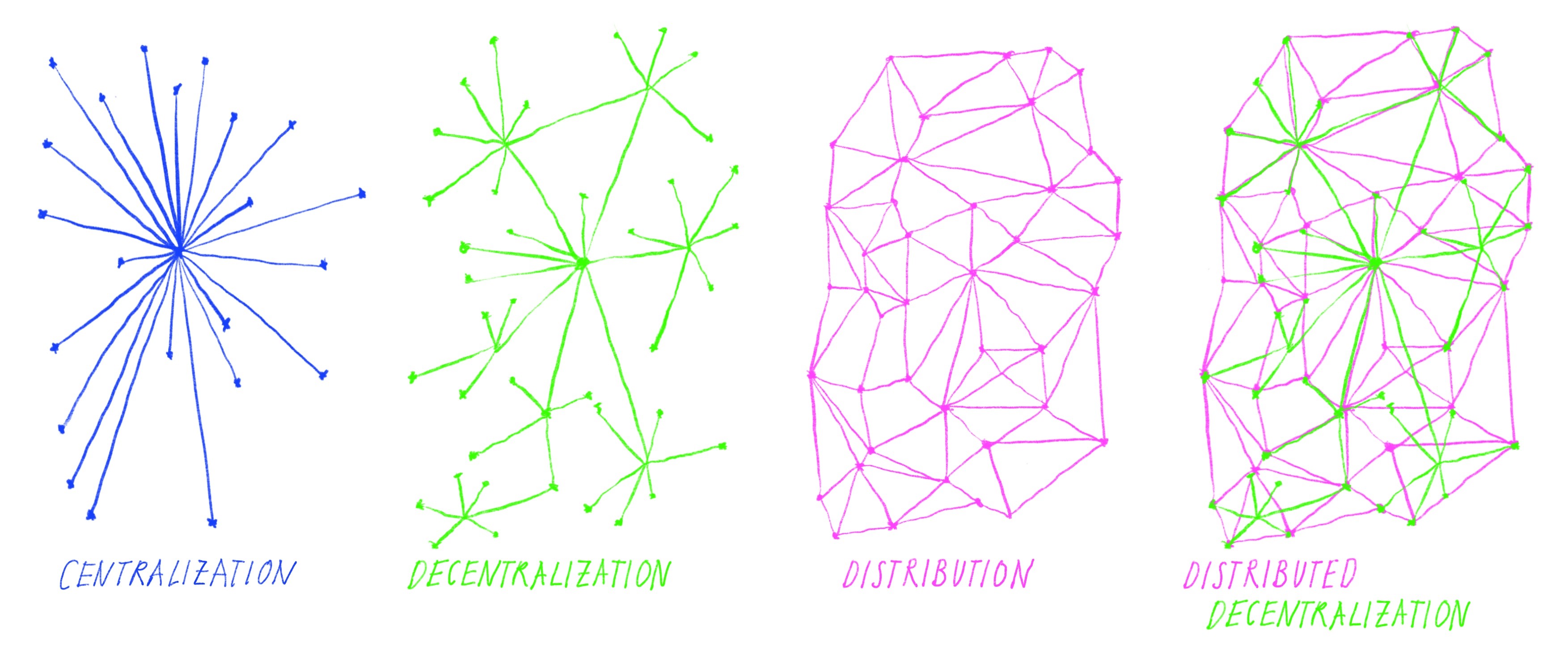
Centralised
Centralisation or centralization (see spelling differences) is the process by which the activities of an organisation, particularly those regarding planning and decision-making, framing strategy and policies become concentrated within a particular geographical location group. This moves the important decision-making and planning powers within the center of the organisation. The term has a variety of meanings in several fields. In political science, centralisation refers to the concentration of a government's power—both geographically and politically—into a centralised government. An antonym of ''centralisation'' is ''decentralisation''. Centralisation in politics History of the centralisation of authority ''Centralisation of authority'' is the systematic and consistent concentration of authority at a central point or in a person within the organization. This idea was first introduced in the Qin Dynasty of China. The Qin government was highly bureaucratic and was administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Identity
National identity is a person's identity or sense of belonging to one or more states or to one or more nation, nations. It is the sense of "a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, and language". National identity may refer to the subjective feeling one shares with a group of people about a nation, regardless of one's legal citizenship status. National identity is viewed in psychological terms as "an awareness of difference", a "feeling and recognition of 'we' and 'they'". National identity also includes the general population and diaspora of Multi-ethnic state, multi-ethnic states and societies that have a shared sense of common identity identical to that of a nation while being made up of several component ethnic groups. Hyphenated ethnicity, Hyphenated ethnicities are an example of the confluence of multiple ethnic and national identities within a single person or entity. As a collective phenomenon, national identity can arise as a direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment Capital
In economics, capital goods or capital are "those durable produced goods that are in turn used as productive inputs for further production" of goods and services. At the macroeconomic level, "the nation's capital stock includes buildings, equipment, software, and inventories during a given year." A typical example is the machinery used in factories. Capital can be increased by the use of the factors of production, which however excludes certain durable goods like homes and personal automobiles that are not used in the production of saleable goods and services. Adam Smith defined capital as "that part of man's stock which he expects to afford him revenue". In economic models, capital is an input in the production function. The total physical capital at any given moment in time is referred to as the capital stock (not to be confused with the capital stock of a business entity). Capital goods, real capital, or capital assets are already-produced, durable goods or any non-fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and policy that taxes foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. '' Protective tariffs'' are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import quotas and export quotas and other non-tariff barriers to trade. Tariffs can be fixed (a constant sum per unit of imported goods or a percentage of the price) or variable (the amount varies according to the price). Taxing imports means people are less likely to buy them as they become more expensive. The intention is that they buy local products instead, boosting their country's economy. Tariffs therefore provide an incentive to develop production and replace imports with domestic products. Tariffs are meant to reduce pressure from foreign competition and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.png)