|
Education In Saskatchewan
Education in Saskatchewan, Canada, teaches a curriculum of learning set out by the Government of Saskatchewan through the Ministry of Education. The curriculum sets out to develop skills, knowledge and understanding to improve the quality of life. On June 22, 1915, Hon. Walter Scott, Premier and Minister of Education, set out as his mandate the "purpose of procuring for the children of Saskatchewan a better education and an education of greater service and utility to meet the conditions of the chief industry in the Province, which is agriculture". Education facilitates the cultural and regional socialization of an individual through the realisation of their self-potential and latent talents. Historically, the region of Saskatchewan needed successful homesteaders so the focus was to develop a unified language for successful economic trading, and agricultural understanding to develop goods, livestock and cash crops to trade. After the mechanized advancements following the Industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elementary School
A primary school (in Ireland, India, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, South Africa, and Singapore), elementary school, or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary education of children who are 4 to 10 years of age (and in many cases, 11 years of age). Primary schooling follows preschool and precedes secondary schooling. The International Standard Classification of Education considers primary education as a single phase where programmes are typically designed to provide fundamental skills in reading, writing, and mathematics and to establish a solid foundation for learning. This is ISCED Level 1: Primary education or first stage of basic education.Annex III in the ISCED 2011 English.pdf Navigate to International St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the United States (Montana and North Dakota). Saskatchewan and neighbouring Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2025, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,250,909. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan's total area of is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs, and List of lakes in Saskatchewan, lakes. Residents live primarily in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Roughly half live in the province's largest city, Saskatoon, or the provincial capital, Regina, Saskatchewan, Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Saskatchewan, Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Estevan, Weyburn, Melfort, Saskatchewan, Melfort, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separate School
In Canada, a separate school is a type of school that has constitutional status in three provinces (Ontario, Alberta and Saskatchewan) and statutory status in the three territories (Northwest Territories, Yukon and Nunavut). In these Canadian jurisdictions, a separate school is one operated by a civil authority—a separate school board—with a mandate enshrined in the Canadian Constitution (for the three provinces) or in federal statutes (for the three territories). In these six jurisdictions a civil electorate, composed of the members of the minority faith, elects separate school trustees according to the province's or territory's local authorities election legislation. These trustees are legally accountable to their electorate and to the provincial or territorial government. No church has a constitutional, legal, or proprietary interest in a separate school. The constitutionally provided mandate of a separate school jurisdiction and of a separate school is to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislative Assembly Of Saskatchewan
The Legislative Assembly of Saskatchewan () is the legislative chamber of the Saskatchewan Legislature in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada. Bills passed by the assembly are given royal assent by the lieutenant governor of Saskatchewan, in the name of the King of Canada. The assembly meets at the Saskatchewan Legislative Building in Regina. There are 61 constituencies in the province, which elect members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs). All are single-member districts, though the cities of Regina, Saskatoon and Moose Jaw were in the past represented through multi-member districts, with members elected through block voting. The legislature has been unicameral since its establishment; there has never been a provincial upper house. The 30th Saskatchewan Legislature was elected at the 2024 Saskatchewan general election. Assemblies Party standings The party standings in the Assembly are as follows: Members *Member in BOLD CAPS is the Premier of Saskatchewan. *Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces And Territories Of Canada
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Constitution of Canada, Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully Independence, independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the List of countries and dependencies by area, world's second-largest country by area. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly called the ''British North America Acts, British North America Act, 1867''), whereas territories are federal territories whose governments a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
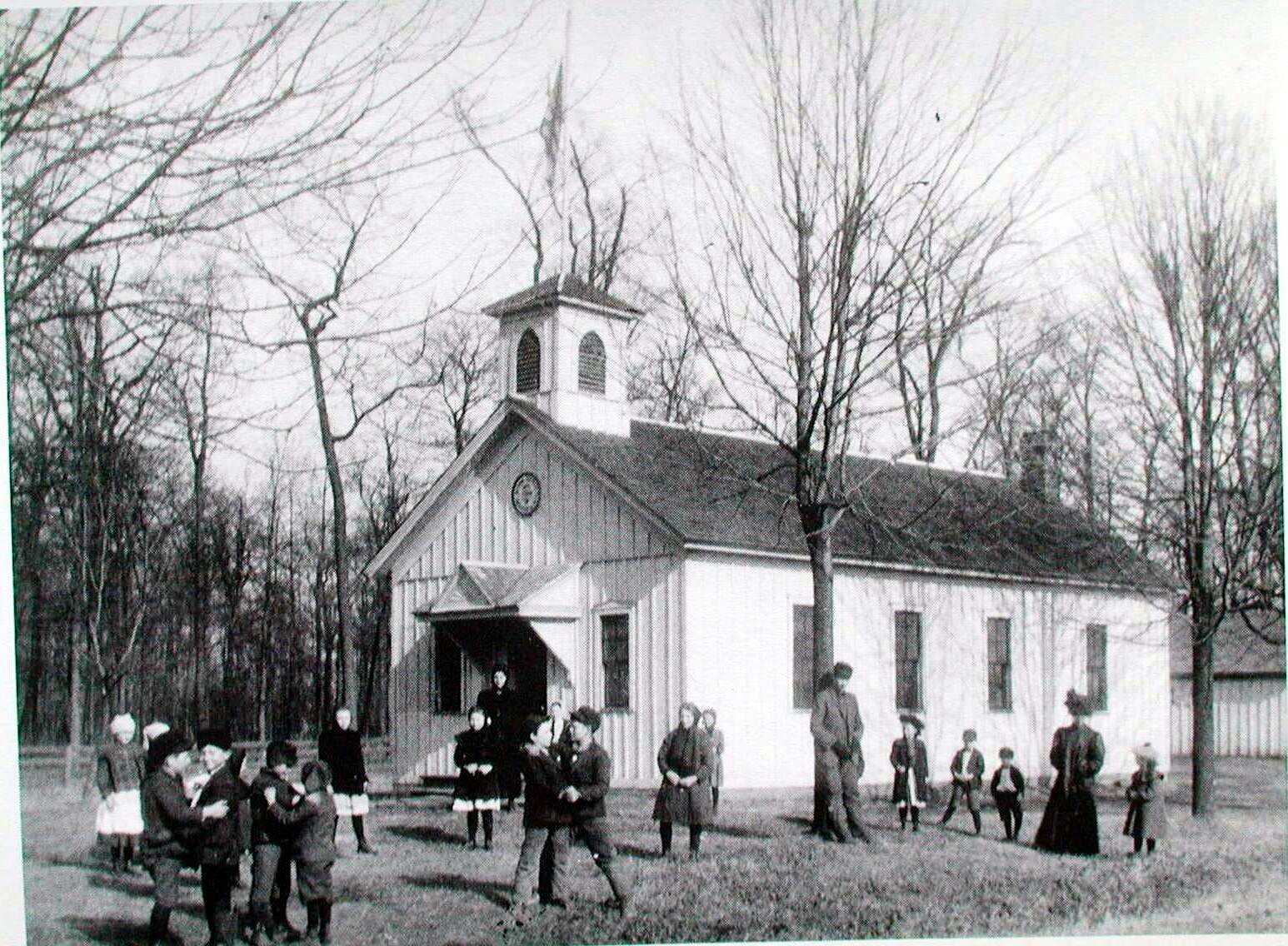
One Room School
One-room schoolhouses, or One-room schools, have been commonplace throughout rural portions of various countries, including Prussia, Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Portugal, and Spain. In most rural and small town schools, all of the students meet in a single room. There, a single teacher teaches academic basics to several grade levels of elementary-age children. Recent years have seen a revival of the format. One-room schoolhouses can also be found in developing nations and rural or remote areas undergoing colonization. In the United States, the concept of a "little red schoolhouse" is a stirring one, and historic one-room schoolhouses have widely been preserved and are celebrated as symbols of frontier values and of local and national development. When necessary, the schools were enlarged or replaced with two-room schools. More than 200 are listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. In Norway, by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
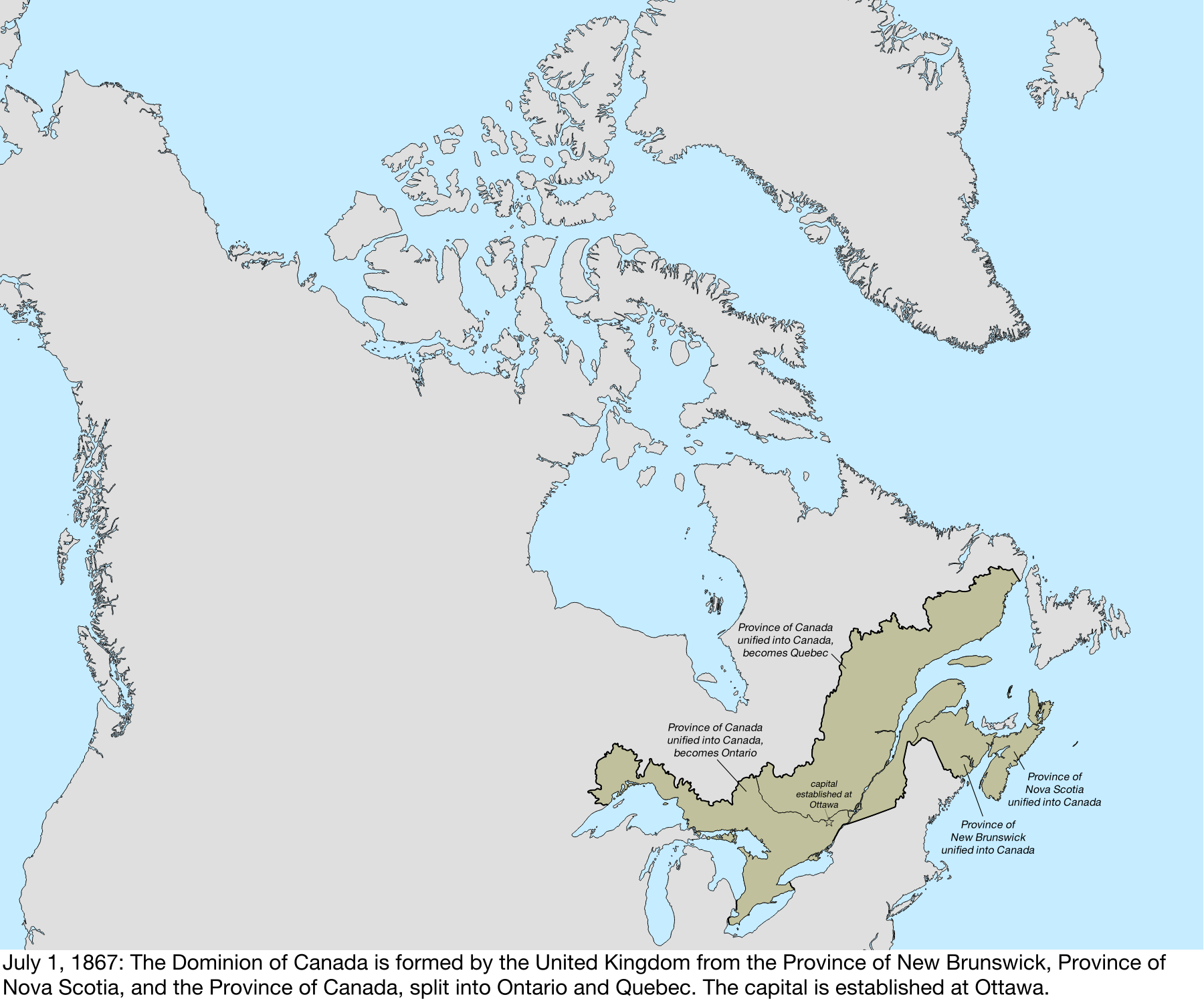
Territorial Evolution Of Canada
The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Province of Canada was immediately split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The colonies of Prince Edward Island and British Columbia joined shortly after, and Canada acquired the vast expanse of the continent controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which was eventually divided into new territories and provinces. Canada evolved into a fully sovereign state by 1982. Before being part of British North America, the constituents of Canada consisted of the former colonies of Canada and Acadia from within New France which had been ceded to Great Britain in 1763 as part of the Treaty of Paris. French Canadian nationality was maintained as one of the "two founding nations" and legally through the Quebec Act which ensured the maintenance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
College
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further education institution, or a secondary school. In most of the world, a college may be a high school or secondary school, a college of further education, a training institution that awards trade qualifications, a higher-education provider that does not have university status (often without its own degree-awarding powers), or a constituent part of a university. In the United States, a college may offer undergraduate programs – either as an independent institution or as the undergraduate program of a university – or it may be a residential college of a university or a community college, referring to (primarily public) higher education institutions that aim to provide affordable and accessible education, usually limited to two-year associate degrees. The word "college" is g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate education, undergraduate and postgraduate education, postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church, Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Secondary Education
Tertiary education (higher education, or post-secondary education) is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank defines tertiary education as including universities, colleges, and vocational schools. ''Higher education'' is taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, while vocational education beyond secondary education is known as ''further education'' in the United Kingdom, or included under the category of ''continuing education'' in the United States. Tertiary education generally culminates in the receipt of certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees. Higher education represents levels 5, 6, 7, and 8 of the 2011 version of the International Standard Classification of Education structure. Tertiary education at a nondegree level is sometimes referred to as further education or continuing education as distinct from higher education. UNESCO stated that tertiary education focuses on learning endeavors in specialize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High School
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., both levels 2 and 3 of the ISCED scale, but these can also be provided in separate schools. There may be other variations in the provision: for example, children in Australia, Hong Kong, and Spain change from the primary to secondary systems a year later at the age of 12, with the ISCED's first year of lower secondary being the last year of primary provision. In the United States, most local secondary education systems have separate middle schools and high schools. Middle schools are usually from grades 6–8 or 7–8, and high schools are typically from grades 9–12. In the United Kingdom, most state schools and privately funded schools accommodate pupils between the ages of 11 and 16 or between 11 and 18; some UK privat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |