|
Demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a goods, good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. In economics "demand" for a commodity is not the same thing as "desire" for it. It refers to both the desire to purchase and the ability to pay for a commodity. Demand is always expressed in relation to a particular price and a particular time period since demand is a flow concept. Flow is any variable which is expressed per unit of time. Demand thus does not refer to a single isolated purchase, but a continuous flow of purchases. Factors influencing demand The factors that influence the decisions of household (individual consumers) to purchase a commodity are known as the determinants of demand. Some important determinants of demand are: The price of the commodity: Most important determinant of the demand for a commodity is the price of the commodity itself. Normally there is an inverse relationship between the price of the commodity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Demand
In microeconomics, the law of demand is a fundamental principle which states that there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. In other words, "conditional on ceteris paribus, all else being equal, as the price of a Goods, good increases (↑), quantity demanded will decrease (↓); conversely, as the price of a good decreases (↓), quantity demanded will increase (↑)". Alfred Marshall worded this as: "When we say that a person's demand for anything increases, we mean that he will buy more of it than he would before at the same price, and that he will buy as much of it as before at a higher price". The law of demand, however, only makes a qualitative statement in the sense that it describes the direction of change in the amount of quantity demanded but not the magnitude of change. The law of demand is represented by a graph called the demand curve, with quantity demanded on the x-axis and price on the y-axis. Demand curves are downward sloping by defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand Curve
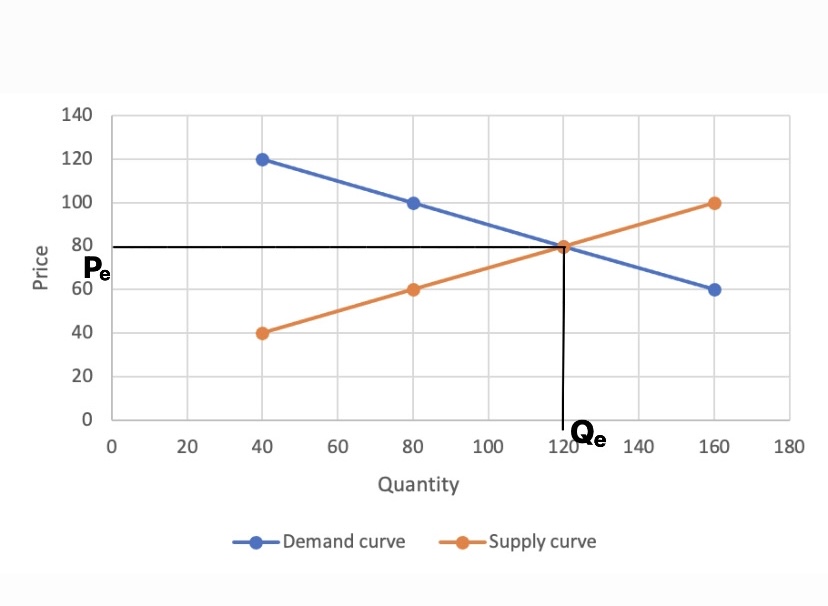
A demand curve is a graph depicting the inverse demand function, a relationship between the price of a certain commodity (the ''y''-axis) and the quantity of that commodity that is demanded at that price (the ''x''-axis). Demand curves can be used either for the price-quantity relationship for an individual consumer (an individual demand curve), or for all consumers in a particular market (a market demand curve). It is generally assumed that demand curves slope down, as shown in the adjacent image. This is because of the law of demand: for most goods, the quantity demanded falls if the price rises. Certain unusual situations do not follow this law. These include Veblen goods, Giffen goods, and speculative bubbles where buyers are attracted to a commodity if its price rises. Demand curves are used to estimate behaviour in competitive markets and are often combined with supply curves to find the equilibrium price (the price at which sellers together are willing to sell the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Demand Management
Energy demand management, also known as demand-side management (DSM) or demand-side response (DSR), is the modification of consumer energy demand, demand for energy through various methods such as financial incentives and behavioral change through education. Usually, the goal of demand-side management is to encourage the consumer to energy saving, use less energy during peak demand, peak hours, or to move the time of energy use to off-peak times such as nighttime and weekends. Peak demand management does not necessarily decrease total Domestic energy consumption, energy consumption, but could be expected to reduce the need for investments in networks and/or electricity generation, power plants for meeting peak demands. An example is the use of energy storage units to store energy during off-peak hours and discharge them during peak hours. A newer application for DSM is to aid grid operators in balancing Variable renewable energy, variable generation from wind and solar units, parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggregate Demand
In economics, aggregate demand (AD) or domestic final demand (DFD) is the total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time. It is often called effective demand, though at other times this term is distinguished. This is the demand for the gross domestic product of a country. It specifies the amount of goods and services that will be purchased at all possible price levels. Consumer spending, investment, corporate and government expenditure, and net exports make up the aggregate demand. The aggregate demand curve is plotted with real output on the horizontal axis and the price level on the vertical axis. While it is theorized to be downward sloping, the Sonnenschein–Mantel–Debreu results show that the slope of the curve cannot be mathematically derived from assumptions about individual rational behavior. Instead, the downward sloping aggregate demand curve is derived with the help of three macroeconomic assumptions about the functioning of markets: Pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand Management
Demand management is a planning methodology used to forecast, plan for and manage the demand for products and services. This can be at macro-levels as in economics and at micro-levels within individual organizations. For example, at macro-levels, a government may influence interest rates to regulate financial demand. At the micro-level, a cellular service provider may provide free night and weekend use to reduce demand during peak hours. Demand management has a defined set of processes, capabilities and recommended behaviors for companies that produce goods and services. Consumer electronics and goods companies often lead in the application of demand management practices to their demand chains; demand management outcomes are a reflection of policies and programs to influence demand as well as competition and options available to users and consumers. Effective demand management follows the concept of a "closed loop" where feedback from the results of the demand plans is fed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keynesian Economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomics, macroeconomic theories and Economic model, models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences Output (economics), economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the aggregate supply, productive capacity of the economy. It is influenced by a host of factors that sometimes behave erratically and impact production, employment, and inflation. Keynesian economists generally argue that aggregate demand is volatile and unstable and that, consequently, a market economy often experiences inefficient macroeconomic outcomes, including economic recession, recessions when demand is too low and inflation when demand is too high. Further, they argue that these economic fluctuations can be mitigated by economic policy responses coordinated between a government and their central bank. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand-led Growth
Demand-led growth is the foundation of an economic theory claiming that an increase in aggregate demand will ultimately cause an increase in total output in the long run. This is based on a hypothetical sequence of events where an increase in demand will, in effect, stimulate an increase in supply (within resource limitations). This stands in opposition to the common neo-classical theory that demand follows supply, and consequently, that supply determines growth in the long run. The demand-centric theory is built on the foundation of work by thinkers such as John Maynard Keynes, Michał Kalecki, Petrus Verdoorn, and Nicholas Kaldor; and is expanded on through research by organizations like the ILO and the Levy Economics Institute of Bard College. Within the theory of demand-led growth, there exist two schools of thought. The first claims that an increase in wage share is the impetus for growth. A study by the ILO, to illustrate, concluded that higher wage shares correlate with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derived Demand
In economics, derived demand is demand for a factor of production or intermediate good that occurs as a result of the demand for another intermediate or final good. In essence, the demand for, say, a factor of production by a firm is dependent on the demand by consumers for the product produced by the firm. The term was first introduced by Alfred Marshall in his '' Principles of Economics'' Marshall, Alfred. "Principles of Economics". London: Macmillan, 1890, pp. 381-93, 852-6. in 1890. Demand for all factors of production is considered as derived demand. This is similar to the concept of joint demand or complementary goods, the quantity consumed of one of them depending positively on the quantity of the other consumed. Example if any goods is in production process by demanding capital automatically speed of production will increase that is directly demand or derived demand. Examples Producers have a derived demand for employees. The employees themselves do not appear in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand Chain
In business, a demand chain is the understanding and management of customer demand, in contrast to a supply chain. Madhani suggests that the demand chain "comprises all the demand processes necessary to understand, create, and stimulate customer demand".Madhani, P. M.Demand Chain Management: Enhancing Customer Value Proposition ''The European Business Review'', March–April 2013, pp. 50–54. Cranfield School of Management academic Martin Christopher has suggested that "ideally the supply chain should become a demand chain", explaining that ideally all product logistics and processing should occur "in response to a known customer requirement". Concept Analysing the firm's activities as a linked chain is a tried and tested way of revealing value creation opportunities. The business economist Michael Porter of Harvard Business School pioneered a value chain approach: "the value chain disaggregates the firm into its strategically relevant activities in order to understand the costs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomists study topics such as output (economics), output/Gross domestic product, GDP (gross domestic product) and national income, unemployment (including Unemployment#Measurement, unemployment rates), price index, price indices and inflation, Consumption (economics), consumption, saving, investment (macroeconomics), investment, Energy economics, energy, international trade, and international finance. Macroeconomics and microeconomics are the two most general fields in economics. The focus of macroeconomics is often on a country (or larger entities like the whole world) and how its markets interact to produce large-scale phenomena that economists refer to as aggregate variables. In microeconomics the focus of analysis is often a single market, such as whether changes in supply or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |