|
Deficiencies Of Intracellular Signaling Peptides And Proteins
A deficiency is generally a lack of something. It may also refer to: *A deficient number, in mathematics, a number ''n'' for which ''σ''(''n'') < 2''n'' * Angular deficiency, in geometry, the difference between a sum of angles and the corresponding sum in a Euclidean plane * , a property describing how far a given graph is from having a perfect matching *, including various types of malnutrition, as well as genetic diseases caused by deficiencies of endogenously produced proteins *A deficiency in |
Deficient Number
In number theory, a deficient number or defective number is a positive integer for which the sum of divisors of is less than . Equivalently, it is a number for which the sum of proper divisors (or aliquot sum) is less than . For example, the proper divisors of 8 are , and their sum is less than 8, so 8 is deficient. Denoting by the sum of divisors, the value is called the number's deficiency. In terms of the aliquot sum , the deficiency is . Examples The first few deficient numbers are :1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 27, 29, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 37, 38, 39, 41, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 49, 50, ... As an example, consider the number 21. Its divisors are 1, 3, 7 and 21, and their sum is 32. Because 32 is less than 42, the number 21 is deficient. Its deficiency is 2 × 21 − 32 = 10. Properties Since the aliquot sums of prime numbers equal 1, all prime numbers are deficient. More generally, all odd numbers with one or two distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Deficiency
In geometry, the angular defect or simply defect (also called deficit or deficiency) is the failure of some angles to add up to the expected amount of 360° or 180°, when such angles in the Euclidean plane would. The opposite notion is the ''excess''. Classically the defect arises in two contexts: in the Euclidean plane, angles about a point add up to 360°, while interior angles in a triangle add up to 180°. However, on a convex polyhedron, the angles of the faces meeting at a vertex add up to ''less'' than 360° (a defect), while the angles at some vertices of a nonconvex polyhedron may add up to ''more'' than 360° (an excess). Also the angles in a hyperbolic triangle add up to ''less'' than 180° (a defect), while those on a spherical triangle add up to ''more'' than 180° (an excess). In modern terms, the defect at a vertex is a discrete version of the curvature of the polyhedral surface concentrated at that point. Negative defect indicates that the vertex resembles a sadd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deficiency (graph Theory)
Deficiency is a concept in graph theory that is used to refine various theorems related to perfect matching in graphs, such as Hall's marriage theorem. This was first studied by Øystein Ore. A related property is surplus. Definition of deficiency Let be a graph, and let ''U'' be an independent set of vertices, that is, ''U'' is a subset of ''V'' in which no two vertices are connected by an edge. Let denote the set of neighbors of ''U'', which is formed by all vertices from 'V' that are connected by an edge to one or more vertices of ''U''. The deficiency of the set ''U'' is defined by: :\mathrm_G(U) := , U, - , N_G(U), Suppose ''G'' is a bipartite graph, with bipartition ''V'' = ''X'' ∪ ''Y''. The deficiency of ''G'' with respect to one of its parts (say ''X''), is the maximum deficiency of a subset of ''X'': :\mathrm(G;X) := \max_ \mathrm_G(U) Sometimes this quantity is called the critical difference of ''G''. Note that defG of the empty subset is 0, so def(''G;''X) � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deficiency (medicine)
In medicine, a deficiency is a lack or shortage of a functional entity, by less than normal or necessary supply or function. A person can have chromosomal deficiencies, mental deficiencies, nutritional deficiencies, complement deficiencies, or enzyme deficiencies. Nutritional deficiency Protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) is a condition where people consume very little in the way of energy, proteins, or both in their diets; as a result, it is common in developing nations. The two main illnesses associated with this condition are kwashiorkor, which is characterized by severe protein deficiency, and marasmus, which is total food deprivation with abnormally low amounts of protein and energy. Carbohydrates deficiency Certain human body cells, such as neurons, require high glucose concentrations. When there are insufficient carbohydrates in the diet, the breakdown of body proteins, dietary proteins, and glycerol from fats is what drives gluconeogenesis. Most gluconeogenesis occurs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the asset is built and ready for use. Construction also covers repairs and maintenance work, any works to expand, extend and improve the asset, and its eventual demolition, dismantling or wikt:decommission, decommissioning. The construction industry contributes significantly to many countries' gross domestic products (Gross domestic product, GDP). Global expenditure on construction activities was about $4 trillion in 2012. In 2022, expenditure on the construction industry exceeded $11 trillion a year, equivalent to about 13 percent of global Gross domestic product, GDP. This spending was forecasted to rise to around $14.8 trillion in 2030. The construction industry promotes economic development and brings many non-monetary benefits to many cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
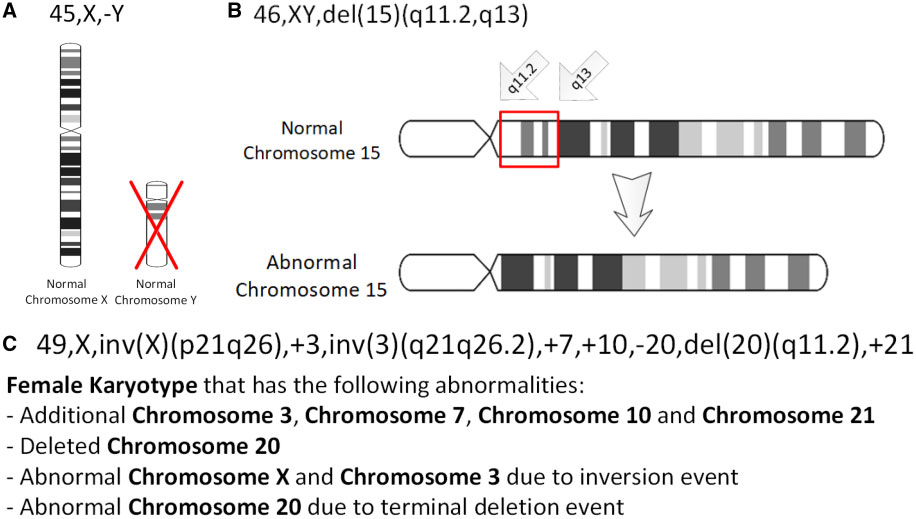
Genetic Deletion
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Some chromosomes have fragile spots where breaks occur, which result in the deletion of a part of the chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiation, or chemical reactions. When a chromosome breaks, if a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as a deletion or a deficiency. For synapsis to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop. The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single base flipping in the template DNA, followed by temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deficiency Judgment
A deficiency judgment is an unsecured money judgment against a borrower whose mortgage foreclosure sale did not produce sufficient funds to pay the underlying promissory note, or loan, in full. The availability of a deficiency judgment depends on whether the lender has a recourse or nonrecourse loan, which is largely a matter of state law. In some jurisdictions, the original loan(s) obtained to purchase property is/are non-recourse, but subsequent refinancing of a first mortgage and/or acquisition of a 2nd (3rd, etc.) are recourse loans. In short, many jurisdictions hold that the loans obtained at the acquisition of a property ("purchase-money") are non-recourse, and most, if not all, subsequent loans are recourse. States that follow the title (trust-deed) theory of mortgages typically allow non-judicial foreclosure procedures, which are fast, but do not allow deficiency judgments. States that follow the lien theory of mortgages require judiciary foreclosure procedures, but al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deficiency (statistics)
In statistics, the deficiency is a measure to compare a statistical model with another statistical model. The concept was introduced in the 1960s by the French mathematician Lucien Le Cam, who used it to prove an approximative version of the Blackwell–Sherman–Stein theorem. Closely related is the Le Cam distance, a Pseudometric space, pseudometric for the maximum deficiency between two statistical models. If the deficiency of a model \mathcal in relation to \mathcal is zero, then one says \mathcal is ''better'' or ''more informative'' or ''stronger'' than \mathcal. Introduction Le Cam defined the statistical model more abstract than a probability space with a family of probability measures. He also didn't use the term "statistical model" and instead used the term "experiment". In his publication from 1964 he introduced the statistical experiment to a parameter set \Theta as a triple (X,E,(P_\theta)_) consisting of a set X, a vector lattice E with unit I and a family of normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Model
A statistical model is a mathematical model that embodies a set of statistical assumptions concerning the generation of Sample (statistics), sample data (and similar data from a larger Statistical population, population). A statistical model represents, often in considerably idealized form, the Data generating process, data-generating process. When referring specifically to probability, probabilities, the corresponding term is probabilistic model. All Statistical hypothesis testing, statistical hypothesis tests and all Estimator, statistical estimators are derived via statistical models. More generally, statistical models are part of the foundation of statistical inference. A statistical model is usually specified as a mathematical relationship between one or more random variables and other non-random variables. As such, a statistical model is "a formal representation of a theory" (Herman J. Adèr, Herman Adèr quoting Kenneth A. Bollen, Kenneth Bollen). Introduction Informally, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangel
Mangel or Mangels may refer to: People * Mangel (surname) *Mangel, a common nickname for the Spanish given name Miguel Ángel * Mangels (surname) * Mangel (footballer), full name ''Miguel Ángel Prendes Pérez'', Spanish footballer Places * Mangel, Nigeria, a Tiv village in Benue State Fictional places * Mangel, an English town in Charlie Williams's Mangel Trilogy Other uses *Mangels-Illions Carousel, a carousel at the Columbus Zoo and Aquarium *Mangel Trilogy, three books set in the fictional town of Mangel, by Charlie Williams *Mangelwurzel Mangelwurzel or mangold wurzel (from German ''Mangel/Mangold'', "chard" and ''Wurzel'', "root"), also called mangold,Wright, Clifford A. (2001) ''Mediterranean Vegetables: a cook's ABC of vegetables and their preparation in Spain, France, Italy, ..., Mangel wurzel, a root vegetable, used as animal fodder, member of the ''Beta vulgaris'' family *Mangel, a defunct clothing store and former owner of Shoppers Fair stores See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |