|
Crown Of Thorns (woodworking)
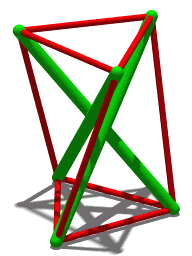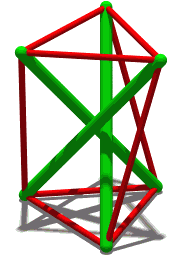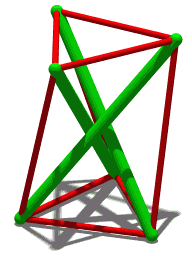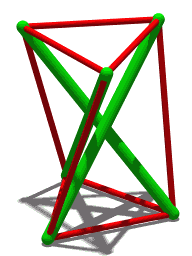
The Crown of Thorns (puzzle work) is a woodworking technique of tramp art using interlocking wooden pieces that are notched to intersect at right angles forming joints and self-supporting objects, objects that have a "prickly" and transparent quality. Common examples include wreath-shaped picture frames that look similar to Jesus' "crown of thorns". Larger-scale crowns may use the principles of tensegrity structures, where the wooden sticks provide rigidity and separate cables in tension carry the forces that hold them together. See also *Burr puzzle - similar structures meant as puzzles to assemble *sailor work *interlocking woodwork References External links Whittled Whimseys website with information about making a crown-of-thorns wreaths. {{DEFAULTSORT:Crown Of Thorns (Woodworking) Joinery Woodworking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodworking
Woodworking is the skill of making items from wood, and includes cabinet making (cabinetry and furniture), wood carving, joinery, carpentry, and woodturning. History Along with stone, clay and animal parts, wood was one of the first materials worked by early humans. Microwear analysis of the Mousterian stone tools used by the Neanderthals show that many were used to work wood. The development of civilization was closely tied to the development of increasingly greater degrees of skill in working these materials. Among early finds of wooden tools are the worked sticks from Kalambo Falls, Clacton-on-Sea and Lehringen. The spears from Schöningen (Germany) provide some of the first examples of wooden hunting gear. Flint tools were used for carving. Since Neolithic times, carved wooden vessels are known, for example, from the Linear Pottery culture wells at Kückhofen and Eythra. Examples of Bronze Age wood-carving include tree trunks worked into coffins from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tramp Art
Tramp art is a style of woodworking which emerged in America in the latter half of the 19th century. Some of tramp art's defining characteristics include chip or notch carving, the reclamation of cheap or available wood such as that from cigar boxes and shipping crates, the use of simple tools such as penknives, and the layering of materials into geometric shapes through glue or nails. One technique used in tramp art is Crown of Thorns joinery. History Although widespread use of wooden cigar boxes in the 1850s sparked involvement in tramp art, it was most prevalent during the Great Depression. Tramp art was made around the world but it prospered in the United States. Examples can be found in every state. The most common forms were the box and the frame and although there were no rules or patterns to lend commonality in the artists’ work there were objects made in every conceivable shape and size including full sized furniture and objects of whimsy. Tramp art was an art form mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of Thorns
According to the New Testament, a woven crown of thorns ( or grc, ἀκάνθινος στέφανος, akanthinos stephanos, label=none) was placed on the head of Jesus during the events leading up to his crucifixion. It was one of the instruments of the Passion, employed by Jesus' captors both to cause him pain and to mock his claim of authority. It is mentioned in the gospels of Matthew (Matthew 27:29), Mark (Mark 15:17) and John (John 19:2, 19:5), and is often alluded to by the early Church Fathers, such as Clement of Alexandria, Origen and others, along with being referenced in the apocryphal Gospel of Peter. Since at least around the year 400 AD, a relic believed by many to be the crown of thorns has been venerated. In 1238, the Latin Emperor Baldwin II of Constantinople yielded the relic to French King Louis IX. It was kept in the Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris until 15 April 2019, when it was rescued from a fire and moved to the Louvre Museum. As a reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensegrity
Tensegrity, tensional integrity or floating compression is a structural principle based on a system of isolated components under compression inside a network of continuous tension, and arranged in such a way that the compressed members (usually bars or struts) do not touch each other while the prestressed tensioned members (usually cables or tendons) delineate the system spatially. The term was coined by Buckminster Fuller in the 1960s as a portmanteau of "tensional integrity". The other denomination of tensegrity, ''floating compression'', was used mainly by the constructivist artist Kenneth Snelson. Concept Tensegrity structures are based on the combination of a few simple design patterns: * members loaded in either pure compression or pure tension, which means that the structure will only fail if the cables yield or the rods buckle. This enables the material properties and cross-sectional geometry of each member to be optimized to the particular load it carries. * pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burr Puzzle
A burr puzzle is an interlocking puzzle consisting of notched sticks, combined to make one three-dimensional, usually symmetrical unit. These puzzles are traditionally made of wood, but versions made of plastic or metal can also be found. Quality burr puzzles are usually precision-made for easy sliding and accurate fitting of the pieces. In recent years the definition of "burr" is expanding, as puzzle designers use this name for puzzles not necessarily of stick-based pieces. History The term "burr" is first mentioned in a 1928 book by Edwin Wyatt, but the text implies that it was commonly used before. The term is attributed to the finished shape of many of these puzzles, resembling a seed burr. The origin of burr puzzles is unknown. The first known record appears in a 1698 engraving used as a title page of Chambers's Cyclopaedia. Later records can be found in German catalogs from the late 18th century and early 19th century. There are claims of the burr being a Chinese inventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailor Work
A sailor, seaman, mariner, or seafarer is a person who works aboard a watercraft as part of its crew, and may work in any one of a number of different fields that are related to the operation and maintenance of a ship. The profession of the sailor is old, and the term ''sailor'' has its etymological roots in a time when sailing ships were the main mode of transport at sea, but it now refers to the personnel of all watercraft regardless of the mode of transport, and encompasses people who operate ships professionally, be it for a military navy or civilian merchant navy, as a sport or recreationally. In a navy, there may be further distinctions: ''sailor'' may refer to any member of the navy even if they are based on land; while ''seaman'' may refer to a specific enlisted rank. Professional mariners Seafarers hold a variety of professions and ranks, each of which carries unique responsibilities which are integral to the successful operation of an ocean-going vessel. A ship's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlocking Woodwork
In railway signalling, an interlocking is an arrangement of signal apparatus that prevents conflicting movements through an arrangement of tracks such as junctions or crossings. The signalling appliances and tracks are sometimes collectively referred to as an ''interlocking plant''. An interlocking is designed so that it is impossible to display a signal to proceed unless the route to be used is proven safe. Interlocking is a safety measure designed to prevent signals and points/switches from being changed in an improper sequence. For example interlocking would prevent a signal from being changed to indicate a diverging route, unless the corresponding points/switches had been changed first. In North America, the official railroad definition of interlocking is: "''An arrangement of signals and signal appliances so interconnected that their movements must succeed each other in proper sequence''". Configuration and use A minimal interlocking consists of signals, but usually i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joinery
Joinery is a part of woodworking that involves joining pieces of wood, engineered lumber, or synthetic substitutes (such as laminate), to produce more complex items. Some woodworking joints employ mechanical fasteners, bindings, or adhesives, while others use only wood elements (such as dowels or plain mortise and tenon fittings). The characteristics of wooden joints - strength, flexibility, toughness, appearance, etc. - derive from the properties of the materials involved and the purpose of the joint. Therefore, different joinery techniques are used to meet differing requirements. For example, the joinery used to construct a house can be different from that used to make cabinetry or furniture, although some concepts overlap. While a form of carpentry elsewhere, in British English usage it is distinguished from it, which is considered to be a form of structural timber work. History Many traditional wood joinery techniques use the distinctive material properties of wood, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |