|
Council Of Ten
The Council of Ten (; ), or simply the Ten, was from 1310 to 1797 one of the major governing bodies of the Republic of Venice. Elections took place annually and the Council of Ten had the power to impose punishments upon Venetian nobility, patricians. The Council of Ten had a broad jurisdictional mandate over matters of National security, state security. The Council of Ten and the Full College constituted the inner circle of oligarchical patricians who effectively ruled the Republic of Venice. Origins The Council of Ten was created in 1310 by Doge Pietro Gradenigo.David Chambers & Brian Pullan with Jennifer Fletcher (eds.). ''Venice: A Documentary History, 1450-1630'' (2001, reprinted 2004). University of Toronto Press/Renaissance Society of America. p. 55. Originally created as a temporary body to investigate the Tiepolo conspiracy, plot of Bajamonte Tiepolo and Marco Querini, the powers of the Council were made formally permanent in 1455.Edward Muir (1981). ''Civic Ritual in Ren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Hayez 010
Francesco, the Italian language, Italian (and original) version of the personal name "Francis (given name), Francis", is one of the List of most popular given names, most common given name among males in Italy. Notable persons with that name include: People with the given name Francesco * Francesco I (other), several people * Francesco Barbaro (other), several people * Francesco Bernardi (other), several people *Francesco di Giorgio Martini (1439-1501), Italian architect, engineer and painter *Francesco Zurolo (first half of the 15th century–1480), Italian feudal lord, baron and italian leader * Francesco Berni (1497–1536), Italian writer * Francesco Canova da Milano (1497–1543), Italian lutenist and composer * Francesco Primaticcio (1504–1570), Italian painter, architect, and sculptor * Francesco Albani (1578–1660), Italian painter * Francesco Borromini (1599–1667), Swiss sculptor and architect * Francesco Cavalli (1602–1676), Italian comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Bussone Da Carmagnola
Francesco Bussone, often called Count of Carmagnola (5 May 1432), was an Italian condottiero. Life Bussone was born at Carmagnola, near Turin, in a humble peasant family. He began his military career when twelve years old under Facino Cane, a condottiero then in the service of the Marquess of Montferrat and later Gian Galeazzo Visconti, duke of Milan. On the death of Cane, the duchy was divided among his captains; but Gian Galeazzo's son and heir, Filippo Maria, determined to reconquer it by force of arms. Facino Cane being dead, Visconti applied to Carmagnola, then in his thirtieth year, and gave him command of the army. Carmagnola's success was astonishingly rapid: he subdued Bergamo, Brescia, Parma, Genoa, and other cities. Soon the whole duchy was brought once more under Visconti's sway. But Filippo Maria, although he rewarded Carmagnola generously, feared that he might become a danger to himself, and instead of giving him further military commands made him governor of Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Of Proof
In a legal dispute, one party has the burden of proof to show that they are correct, while the other party has no such burden and is presumed to be correct. The burden of proof requires a party to produce evidence to establish the truth of facts needed to satisfy all the required legal elements of the dispute. It is also known as the onus of proof. The burden of proof is usually on the person who brings a claim in a dispute. It is often associated with the Latin maxim ''semper necessitas probandi incumbit ei qui agit'', a translation of which is: "the necessity of proof always lies with the person who lays charges." In civil suits, for example, the plaintiff bears the burden of proof that the defendant's action or inaction caused injury to the plaintiff, and the defendant bears the burden of proving an affirmative defense. The burden of proof is on the prosecutor for criminal cases, and the defendant is presumed innocent. If the claimant fails to discharge the burden of proof t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secret Trial
A secret trial is a trial that is not open to the public or generally reported in the news, especially any in-trial proceedings. Generally, no official record of the case or the judge's verdict is made available. Often there is no indictment. Secret trials have been characteristic of many dictatorships in the modern era, but are also used in many democratic nations, with the explanation of being necessary for national security. They are a hotly debated topic in many circles, but are generally accepted in the western world as they are seen as protecting the " greater good". Australia It is possible that some wholly-secret trials occurred in Australia during World War I or World War II. In the 21st century, several secret trials have occurred or are set to occur in Australia: * In 2018, " Witness J" was tried and imprisoned by the Australian government in near-total secrecy. The existence of Witness J was discovered only by chance by a judge, and the scant details were reported t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering, as a subfield of the intelligence field, is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence). A person who commits espionage on a mission-specific contract is called an ''espionage agent'' or ''spy''. A person who commits espionage as a fully employed officer of a government is called an intelligence officer. Any individual or spy ring (a cooperating group of spies), in the service of a government, company, criminal organization, or independent operation, can commit espionage. The practice is clandestine, as it is by definition unwelcome. In some circumstances, it may be a legal tool of law enforcement and in others, it may be illegal and punishable by law. Espionage is often part of an institutional effort by a government or commercial concern. However, the term tends to be associated with state spying on potential or actual enemies for military purposes. Spying involving corporations is known as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state (polity), state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to Coup d'état, overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplomats, its officials, or its secret services for a hostile foreign power, or Regicide, attempting to kill its head of state. A person who commits treason is known in law as a traitor. Historically, in common law countries, treason also covered the murder of specific social superiors, such as the murder of a husband by his wife or that of a master by his servant. Treason (i.e., disloyalty) against one's monarch was known as ''high treason'' and treason against a lesser superior was ''petty treason''. As jurisdictions around the world abolished petty treason, "treason" came to refer to what was historically known as high treason. At times, the term ''traitor'' has been used as a political epithet, regardless of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by the pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, and essayist. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has produced," with William Faulkner calling him "the father of American literature." Twain's novels include ''The Adventures of Tom Sawyer'' (1876) and its sequel, ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn'' (1884), with the latter often called the "Great American Novel." He also wrote ''A Connecticut Yankee in King Arthur's Court'' (1889) and ''Pudd'nhead Wilson'' (1894) and cowrote ''The Gilded Age: A Tale of Today'' (1873) with Charles Dudley Warner. The novelist Ernest Hemingway claimed that "All modern American literature comes from one book by Mark Twain called ''Huckleberry Finn''." Twain was raised in Hannibal, Missouri, which later provided the setting for both ''Tom Sawyer'' and ''Huckleberry Finn''. He served an apprenticeship with a printer early in his career, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vote Buying
Vote buying (also referred to as electoral clientelism and patronage politics) occurs when a political party or candidate distributes money or resources to a voter in an upcoming election with the expectation that the voter votes for the actor handing out monetary rewards. Vote buying can take various forms such as a monetary exchange, as well as an exchange for necessary goods or services. This practice is often used to incentivise or persuade voters to turn out to elections and vote in a particular way. Although this practice is illegal in many countries such as the United States, Argentina, Mexico, Kenya, Brazil and Nigeria, its prevalence remains worldwide. In some parts of the United States in the mid- and late 19th century, members of competing parties would vie, sometimes openly and other times with much greater secrecy, to buy and sell votes. Voters would be compensated with cash or the covering of one's house/tax payment. To keep the practice of vote buying secret, parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banqueting
A banquet (; ) is a formal large meal where a number of people consume food together. Banquets are traditionally held to enhance the prestige of a host, or reinforce social bonds among joint contributors. Modern examples of these purposes include a charitable gathering, a ceremony, or a celebration. They often involve speeches in honor of the topic or guest of honour. The older English term for a lavish meal was feast, and "banquet" originally meant a specific and different kind of meal, often following a feast, but in a different room or even building, which concentrated on sweet foods of various kinds. These became highly fashionable as sugar became much more common in Europe at the start of the 16th century. It was a grand form of the dessert course, and special banqueting houses, often on the roof or in the grounds of large houses, were built for them. Such meals are also called a "sugar collation". Social meanings Banquets feature luxury foods, often including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumptuary Laws
Sumptuary laws (from Latin ) are laws that regulate consumption. '' Black's Law Dictionary'' defines them as "Laws made for the purpose of restraining luxury or extravagance, particularly against inordinate expenditures for apparel, food, furniture, or shoes, etc." Historically, they were intended to regulate and reinforce social hierarchies and morals through restrictions on clothing, food, and luxury expenditures, often depending on a person's social rank. Societies have used sumptuary laws for a variety of purposes. They were used to try to regulate the balance of trade by limiting the market for expensive imported goods. They made it easy to identify social rank and privilege, and as such could be used for social discrimination and to stabilize social hierarchies. They could also be used to prevent, or at least reduce opportunities for political bribery and corruption. The laws often prevented commoners from imitating the appearance of aristocrats, and could be used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
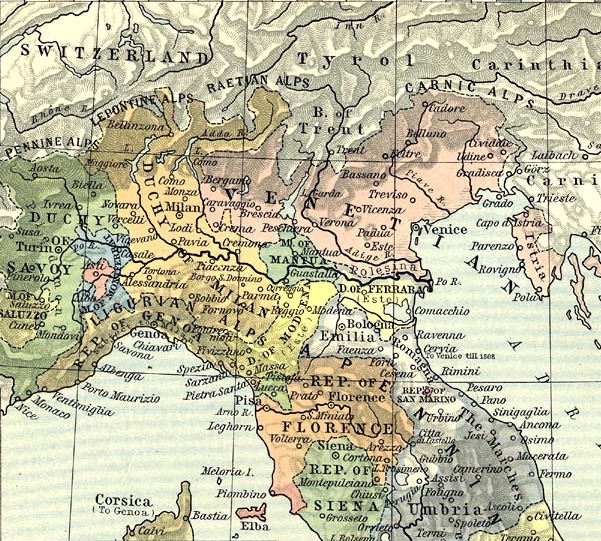
War Of The League Of Cambrai
The War of the League of Cambrai, sometimes known as the War of the Holy League and several other names, was fought from February 1508 to December 1516 as part of the Italian Wars of 1494–1559. The main participants of the war, who fought for its entire duration, were Early modern France, France, the Papal States, and the Republic of Venice; they were joined at various times by nearly every significant power in Western Europe, including Spain, the Holy Roman Empire, Kingdom of England, England, the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, the Duchy of Ferrara, and the Swiss mercenaries, Swiss. The war started with the ''Italienzug'' of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian I, King of the Romans, crossing into Venetian territory in February 1508 with his army on the way to be Coronation of the Holy Roman Emperor, crowned Holy Roman emperor by the pope in Rome. Meanwhile, Pope Julius II, intending to curb Venetian influence in northern History of Italy during foreig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |