|
Costomediastinal Recess
The costomediastinal recess is a potential space at the border of the mediastinal pleura and the costal pleura. It assists lung expansion during deep inspiration, although its role is not as significant as the costodiaphragmatic recess, which has a greater volume. The lung expands into the costomediastinal recess even during shallow inspiration. The costomediastinal recess is most obvious in the cardiac notch of the left lung. See also * Costodiaphragmatic recess (Costophrenic angle) * Cardiophrenic angle * Mediastinum The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the eso ... External links * - "Pleural Cavities and Lungs: The Costomediastinal Recess" * - "X-ray, chest, posteroanterior view" Diagram at port.ac.uk Pleura {{respiratory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorax
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the body, each in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. The chest may be affected by many diseases, of which the most common symptom is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thṓrax'' " breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via . Humans Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spine, and shoulder girdle. Contents The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleuræ
The pleural cavity, or pleural space (or sometimes intrapleural space), is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication between the membranes, and also to create a pressure gradient. The serous membrane that covers the surface of the lung is the visceral pleura and is separated from the outer membrane, the parietal pleura, by just the film of pleural fluid in the pleural cavity. The visceral pleura follows the fissures of the lung and the root of the lung structures. The parietal pleura is attached to the mediastinum, the upper surface of the diaphragm, and to the inside of the ribcage. Structure In humans, the left and right lungs are completely separated by the mediastinum, and there is no communication between their pleural cavities. Therefore, in cases of a unilateral pneumothorax, the contralateral lung will remain functioning normally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
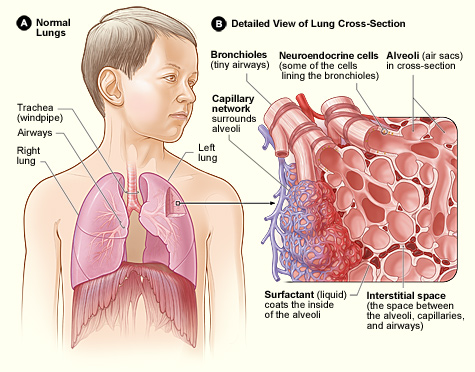
Lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a right lung and a left lung. They are situated within the thoracic cavity of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential Space
In anatomy, a potential space is a space between two adjacent structures that are normally pressed together (directly apposed). Many anatomic spaces are potential spaces, which means that they are potential rather than realized (with their realization being dynamic according to physiologic or pathophysiologic events). In other words, they are like an empty plastic bag that has not been opened (two walls collapsed against each other; no interior volume until opened) or a balloon that has not been inflated. The pleural space, between the visceral and parietal pleura of the lung, is a potential space. Though it only contains a small amount of fluid normally, it can sometimes accumulate fluid or air that widens the space. The pericardial space is another potential space that may fill with fluid (effusion) in certain disease states (e.g. pericarditis; a large pericardial effusion may result in cardiac tamponade). Examples * Costodiaphragmatic recess * Pericardial cavity *Epidural sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinal Pleura
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the mediastinum, the inside surfaces of the surrounding chest walls and the diaphragm. Although wrapped onto itself resulting in an apparent double layer, each lung is surrounded by a single, continuous pleural membrane. The portion of the pleura that covers the surface of each lung is often called the visceral pleura. This can lead to some confusion, as the lung is not the only visceral organ covered by the pleura. The pleura typically dips between the lobes of the lung as ''fissures'', and is formed by the invagination of lung buds into each thoracic sac during embryonic development. The portion of the pleura seen as the outer layer covers the chest wall, the diaphragm and the mediastinum and is often also misleadingly called the parietal pleu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costodiaphragmatic Recess
The costodiaphragmatic recess, also called the costophrenic recess or phrenicocostal sinus, costodiaphragmatic-recess Retrieved May 2011 Imaging In anatomy, the costophrenic angles are the places where the diaphragm (''-phrenic'') meets the ribs (''costo-''). Each costophrenic angle can normally be seen as on chest x-ray as a sharply-pointed, downward indentation (dark) between each hemi-diaphragm (white) and the adjacent chest wall (white). A small portion of each lung normally reaches into the costophrenic angle. The normal angle usually measures thirty degrees. Pleural effusion With pleural effusion, fluid often builds up in the costophrenic angle (due to gravity). This can push the lung upwards, resulting in "blunting" of the costophrenic angle. The posterior angle is the deepest. Obtuse angulation is sign of disease. Chest x-ray is the first test done to confirm an excess of pleural fluid. The lateral upright chest x-ray should be examined when a pleural effusion is su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes Animal communication#Auditory, vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costodiaphragmatic Recess
The costodiaphragmatic recess, also called the costophrenic recess or phrenicocostal sinus, costodiaphragmatic-recess Retrieved May 2011 Imaging In anatomy, the costophrenic angles are the places where the diaphragm (''-phrenic'') meets the ribs (''costo-''). Each costophrenic angle can normally be seen as on chest x-ray as a sharply-pointed, downward indentation (dark) between each hemi-diaphragm (white) and the adjacent chest wall (white). A small portion of each lung normally reaches into the costophrenic angle. The normal angle usually measures thirty degrees. Pleural effusion With pleural effusion, fluid often builds up in the costophrenic angle (due to gravity). This can push the lung upwards, resulting in "blunting" of the costophrenic angle. The posterior angle is the deepest. Obtuse angulation is sign of disease. Chest x-ray is the first test done to confirm an excess of pleural fluid. The lateral upright chest x-ray should be examined when a pleural effusion is su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiophrenic Angle
The cardiophrenic angle is the angle between the heart and the diaphragm, as seen on imaging (most commonly X-ray). There are two cardiophrenic angles, however the one on the right is obscured by the cardiohepatic angle (the angle between the heart and liver). See also * Costodiaphragmatic recess The costodiaphragmatic recess, also called the costophrenic recess or phrenicocostal sinus, costodiaphragmatic-recess Retrieved May 2011 Imaging In anatomy, the costophrenic angles are the places where the diaphragm (''-phrenic'') meets the rib ... ( Costophrenic angle) * Costomediastinal recess References Cardiac anatomy {{cardiovascular-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the vagus nerve, vagus, phrenic nerve, phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pulmonary pleurae, pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the Spine (anatomy), spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |