|
Cost
Cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost. In this case, money is the input that is gone in order to acquire the thing. This acquisition cost may be the sum of the cost of production as incurred by the original producer, and further costs of transaction as incurred by the acquirer over and above the price paid to the producer. Usually, the price also includes a mark-up for profit over the cost of production. More generalized in the field of economics Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ..., cost is a metric that is totaling up as a result of a process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opportunity Cost
In microeconomic theory, the opportunity cost of a choice is the value of the best alternative forgone where, given limited resources, a choice needs to be made between several mutually exclusive alternatives. Assuming the best choice is made, it is the "cost" incurred by not enjoying the ''benefit'' that would have been had if the second best available choice had been taken instead. The '' New Oxford American Dictionary'' defines it as "the loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen". As a representation of the relationship between scarcity and choice, the objective of opportunity cost is to ensure efficient use of scarce resources. It incorporates all associated costs of a decision, both explicit and implicit. Thus, opportunity costs are not restricted to monetary or financial costs: the real cost of output forgone, lost time, pleasure, or any other benefit that provides utility should also be considered an opportunity cost. Types Expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
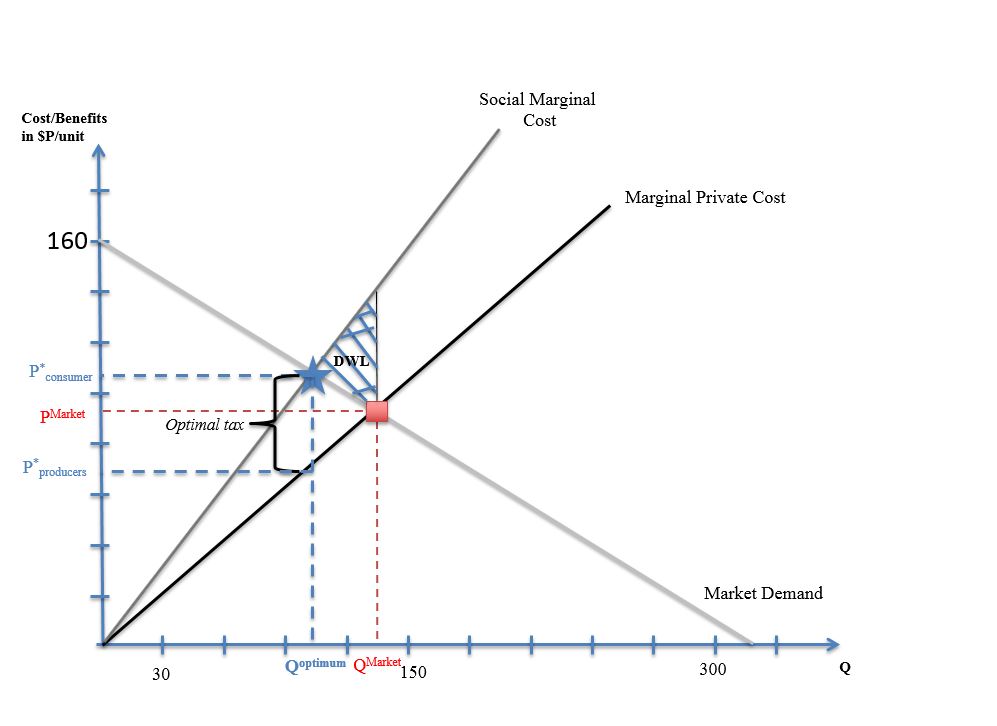
Externality
In economics, an externality is an Indirect costs, indirect cost (external cost) or indirect benefit (external benefit) to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced components that are involved in either consumer or producer consumption. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. The Air pollution#Health effects, cost of air pollution to society is not paid by either the producers or users of motorized transport. Water pollution from mills and factories are another example. All (water) consumers are made worse off by pollution but are not compensated by the market for this damage. The concept of externality was first developed by Alfred Marshall in the 1890s and achieved broader attention in the works of economist Arthur Cecil Pigou, Arthur Pigou in the 1920s. The prototypical example of a negative externality is environmental pollution. Pigou argued that a tax, equal to the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Of Goods Sold
Cost of goods sold (COGS) (also cost of products sold (COPS), or cost of sales) is the carrying value of goods sold during a particular period. Costs are associated with particular goods using one of the several formulas, including specific identification, first-in first-out (FIFO), or average cost. Costs include all costs of purchase, costs of conversion and other costs that are incurred in bringing the inventories to their present location and condition. Costs of goods made by the businesses include material, labor, and allocated overhead. The costs of those goods which are not yet sold are deferred as costs of inventory until the inventory is sold or written down in value. Overview Many businesses sell goods that they have bought or produced. When the goods are bought or produced, the costs associated with such goods are capitalized as part of inventory (or stock) of goods. These costs are treated as an expense in the period the business recognizes income from sale of the good ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Cost
Social cost in neoclassical economics is the sum of the private costs resulting from a transaction and the costs imposed on the consumers as a consequence of being exposed to the transaction for which they are not compensated or charged. In other words, it is the sum of private and external costs. This might be applied to any number of economic problems: for example, social cost of carbon has been explored to better understand the costs of carbon emissions for proposed economic solutions such as a carbon tax. Private costs refer to direct costs to the producer for producing the good or service. Social cost includes these private costs and the additional costs (or external costs) associated with the production of the good which are not accounted for by the free market. In short, when the consequences of an action cannot be taken by the initiator, we will have external costs in the society. We will have private costs when initiator can take responsibility for agent's action.de V. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost–benefit Analysis
Cost–benefit analysis (CBA), sometimes also called benefit–cost analysis, is a systematic approach to estimating the strengths and weaknesses of alternatives. It is used to determine options which provide the best approach to achieving benefits while preserving savings in, for example, transactions, activities, and functional business requirements. A CBA may be used to compare completed or potential courses of action, and to estimate or evaluate the value against the cost of a decision, project, or policy. It is commonly used to evaluate business or policy decisions (particularly public policy), commercial transactions, and project investments. For example, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission must conduct cost–benefit analyses before instituting regulations or deregulations. CBA has two main applications: # To determine if an investment (or decision) is sound, ascertaining if – and by how much – its benefits outweigh its costs. # To provide a basis for comparing in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Overrun
A cost overrun, also known as a cost increase or budget overrun, involves unexpected incurred costs. When these costs are in excess of budgeted amounts due to a value engineering underestimation of the actual cost during budgeting, they are known by these terms. Cost overruns are common in infrastructure, building, and technology projects. For IT projects, a 2004 industry study by the Standish Group found an average cost overrun of 43 percent; 71 percent of projects came in over budget, exceeded time estimates, and had estimated too narrow a scope; and total waste was estimated at $55 billion per year in the US alone. Many major construction projects have incurred cost overruns; cost estimates used to decide whether important transportation infrastructure should be built can mislead grossly and systematically. Cost overrun is distinguished from cost escalation, which is an ''anticipated'' growth in a budgeted cost due to factors such as inflation. Causes Recent works by Ahi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Cost
Economic cost is the combination of losses of any goods that have a value attached to them by any one individual. Economic cost is used mainly by economists as means to compare the prudence of one course of action with that of another. The comparison includes the gains and losses precluded by taking a course of action as well as those of the course taken itself. Economic cost differs from accounting cost because it includes opportunity cost. (Some sources refer to accounting cost as ''explicit cost'' and opportunity cost as ''implicit cost''.) Aspects of economic costs *Variable cost: Variable costs are the costs paid to the variable input. Inputs include labor, capital, materials, power and land and buildings. Variable inputs are inputs whose use vary with output. Conventionally the variable input is assumed to be labor. ** Total variable cost (TVC) is the same as variable costs. * Fixed cost (TFC) are the costs of the fixed assets those that do not vary with production. **Tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead (business)
In business, an overhead or overhead expense is an ongoing expense of operating a business. Overheads are the expenditure which cannot be conveniently traced to or identified with any particular revenue unit, unlike operating expenses such as raw material and labor. Overheads cannot be immediately associated with the products or services being offered, and so do not directly generate profits. However, they are still vital to business operations as they provide critical support for the business to carry out profit making activities. One example would be the rent for a factory, which allows workers to manufacture products which can then be sold for a profit. Such expenses are incurred for output generally and not for particular work order; e.g., wages paid to watch and ward staff, heating and lighting expenses of factory, etc. Overheads are an important cost element, alongside direct materials and direct labor. Overheads are often related to accounting concepts such as fixed costs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Basis
Basis (or cost basis), as used in United States tax law, is the original cost of property, adjusted for factors such as depreciation. When a property is sold, the taxpayer pays/(saves) taxes on a capital gain/(loss) that equals the amount realized on the sale minus the sold property's basis. Cost basis is needed because tax is due based on the gain in value of an asset. For example, if a person buys a rock for $20, and sells the same rock for $20, there is no tax, since there is no profit. If, however, that person buys a rock for $20 and then sells the same rock for $25, then there is a capital gain on the rock of $5, which is thus taxable. The purchase price of $20 is analogous to cost of sales. Typically, capital gains tax is due only when an asset is sold. However, the rules for this are very complicated. If tax is paid because the value has increased, the new value will be the cost basis for any future tax. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Publication 551 contains the IRS's d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing Cost
Manufacturing cost is the sum of costs of all resources consumed in the process of making a product. The manufacturing cost is classified into three categories: direct materials cost, direct labor cost and manufacturing overhead. It is a factor in total delivery cost. Direct materials cost Direct materials are the raw materials that become a part of the finished product. Manufacturing adds value to raw materials by applying a chain of operations to maintain a deliverable product. There are many operations that can be applied to raw materials such as welding, cutting and painting. It is important to differentiate between direct materials and indirect materials. Direct labour cost The direct labour cost is the cost of workers who can be easily identified with the unit of production. Types of labour who are considered to be part of the direct labour cost are the assembly workers on an assembly line. Manufacturing overhead Manufacturing overhead is any manufacturing cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation expected, required, or given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, especially when the product is a service rather than a physical good, the price for the service may be called something else such as "rent" or "tuition". Prices are influenced by production costs, supply of the desired product, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions. Price can be quoted in currency, quantities of goods or vouchers. * In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (More specifically, for raw materials they are expressed as currency per unit weight, e.g. euros per kilogram or Rands per KG.) * Although prices could be quoted as quantities of other goods or services, this sort of barter exchange is rarely seen. Prices are sometimes quoted in terms of vouc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |