|
Correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are '' linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. However, in g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pearson Product-moment Correlation Coefficient
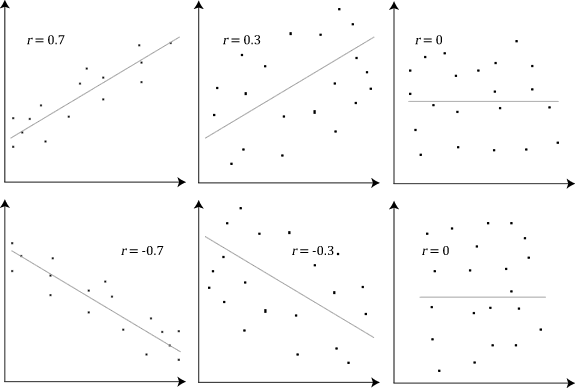
In statistics, the Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) is a correlation coefficient that measures linear correlation between two sets of data. It is the ratio between the covariance of two variables and the product of their standard deviations; thus, it is essentially a normalized measurement of the covariance, such that the result always has a value between −1 and 1. As with covariance itself, the measure can only reflect a linear correlation of variables, and ignores many other types of relationships or correlations. As a simple example, one would expect the age and height of a sample of children from a school to have a Pearson correlation coefficient significantly greater than 0, but less than 1 (as 1 would represent an unrealistically perfect correlation). Naming and history It was developed by Karl Pearson from a related idea introduced by Francis Galton in the 1880s, and for which the mathematical formula was derived and published by Auguste Bravais in 1844. The naming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Correlation Examples2
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causality, causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are ''line (geometry), linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the human height, height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causality, causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Correlation Coefficient
A correlation coefficient is a numerical measure of some type of linear correlation, meaning a statistical relationship between two variables. The variables may be two columns of a given data set of observations, often called a sample, or two components of a multivariate random variable with a known distribution. Several types of correlation coefficient exist, each with their own definition and own range of usability and characteristics. They all assume values in the range from −1 to +1, where ±1 indicates the strongest possible correlation and 0 indicates no correlation. As tools of analysis, correlation coefficients present certain problems, including the propensity of some types to be distorted by outliers and the possibility of incorrectly being used to infer a causal relationship between the variables (for more, see Correlation does not imply causation). Types There are several different measures for the degree of correlation in data, depending on the kind of data: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Karl Pearson
Karl Pearson (; born Carl Pearson; 27 March 1857 – 27 April 1936) was an English biostatistician and mathematician. He has been credited with establishing the discipline of mathematical statistics. He founded the world's first university statistics department at University College London in 1911, and contributed significantly to the field of biometrics and meteorology. Pearson was also a proponent of Social Darwinism and eugenics, and his thought is an example of what is today described as scientific racism. Pearson was a protégé and biographer of Sir Francis Galton. He edited and completed both William Kingdon Clifford's ''Common Sense of the Exact Sciences'' (1885) and Isaac Todhunter's ''History of the Theory of Elasticity'', Vol. 1 (1886–1893) and Vol. 2 (1893), following their deaths. Early life and education Pearson was born in Islington, London, into a Quaker family. His father was William Pearson QC of the Inner Temple, and his mother Fanny (née Smit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Correlation Does Not Imply Causation
The phrase "correlation does not imply causation" refers to the inability to legitimately deduce a cause-and-effect relationship between two events or variables solely on the basis of an observed association or correlation between them. The idea that "correlation implies causation" is an example of a questionable-cause logical fallacy, in which two events occurring together are taken to have established a cause-and-effect relationship. This fallacy is also known by the Latin phrase ''cum hoc ergo propter hoc'' ('with this, therefore because of this'). This differs from the fallacy known as '' post hoc ergo propter hoc'' ("after this, therefore because of this"), in which an event following another is seen as a necessary consequence of the former event, and from conflation, the errant merging of two events, ideas, databases, etc., into one. As with any logical fallacy, identifying that the reasoning behind an argument is flawed does not necessarily imply that the resulting c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient
In statistics, Spearman's rank correlation coefficient or Spearman's ''ρ'' is a number ranging from -1 to 1 that indicates how strongly two sets of ranks are correlated. It could be used in a situation where one only has ranked data, such as a tally of gold, silver, and bronze medals. If a statistician wanted to know whether people who are high ranking in sprinting are also high ranking in long-distance running, they would use a Spearman rank correlation coefficient. The coefficient is named after Charles Spearman and often denoted by the Greek letter \rho (rho) or as r_s. It is a nonparametric measure of rank correlation ( statistical dependence between the rankings of two variables). It assesses how well the relationship between two variables can be described using a monotonic function. The Spearman correlation between two variables is equal to the Pearson correlation between the rank values of those two variables; while Pearson's correlation assesses linear relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Uncorrelated
In probability theory and statistics, two real-valued random variables, X, Y, are said to be uncorrelated if their covariance, \operatorname ,Y= \operatorname Y- \operatorname \operatorname /math>, is zero. If two variables are uncorrelated, there is no linear relationship between them. Uncorrelated random variables have a Pearson correlation coefficient, when it exists, of zero, except in the trivial case when either variable has zero variance (is a constant). In this case the correlation is undefined. In general, uncorrelatedness is not the same as orthogonality, except in the special case where at least one of the two random variables has an expected value of 0. In this case, the covariance is the expectation of the product, and X and Y are uncorrelated if and only if In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, "if and only if" (often shortened as "iff") is paraphrased by the biconditional, a logical connective between statements. The bicondit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Joint Normality
In probability theory and statistics, the multivariate normal distribution, multivariate Gaussian distribution, or joint normal distribution is a generalization of the one-dimensional ( univariate) normal distribution to higher dimensions. One definition is that a random vector is said to be ''k''-variate normally distributed if every linear combination of its ''k'' components has a univariate normal distribution. Its importance derives mainly from the multivariate central limit theorem. The multivariate normal distribution is often used to describe, at least approximately, any set of (possibly) correlated real-valued random variables, each of which clusters around a mean value. Definitions Notation and parametrization The multivariate normal distribution of a ''k''-dimensional random vector \mathbf = (X_1,\ldots,X_k)^ can be written in the following notation: : \mathbf\ \sim\ \mathcal(\boldsymbol\mu,\, \boldsymbol\Sigma), or to make it explicitly known that \mathbf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Causality
Causality is an influence by which one Event (philosophy), event, process, state, or Object (philosophy), object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cause is at least partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is at least partly dependent on the cause. The cause of something may also be described as the reason for the event or process. In general, a process can have multiple causes,Compare: which are also said to be ''causal factors'' for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future. Some writers have held that causality is metaphysics , metaphysically prior to notions of time and space. Causality is an abstraction that indicates how the world progresses. As such it is a basic concept; it is more apt to be an explanation of other concepts of progression than something to be explained by other more fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bivariate Data
In statistics, bivariate data is data on each of two variables, where each value of one of the variables is paired with a value of the other variable. It is a specific but very common case of multivariate data. The association can be studied via a tabular or graphical display, or via sample statistics which might be used for inference. Typically it would be of interest to investigate the possible association between the two variables. The method used to investigate the association would depend on the level of measurement of the variable. This association that involves exactly two variables can be termed a bivariate correlation, or bivariate association. For two quantitative variables (interval or ratio in level of measurement), a scatterplot can be used and a correlation coefficient or regression model can be used to quantify the association. For two qualitative variables (nominal or ordinal in level of measurement), a contingency table can be used to view the data, and a meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
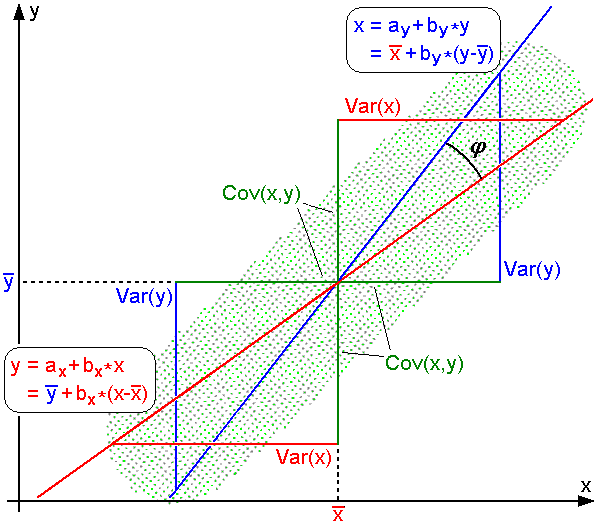
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of the joint variability of two random variables. The sign of the covariance, therefore, shows the tendency in the linear relationship between the variables. If greater values of one variable mainly correspond with greater values of the other variable, and the same holds for lesser values (that is, the variables tend to show similar behavior), the covariance is positive. In the opposite case, when greater values of one variable mainly correspond to lesser values of the other (that is, the variables tend to show opposite behavior), the covariance is negative. The magnitude of the covariance is the geometric mean of the variances that are in common for the two random variables. The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, correlation coefficient normalizes the covariance by dividing by the geometric mean of the total variances for the two random variables. A distinction must be made between (1) the covariance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |