|
Control Theory (sociology)
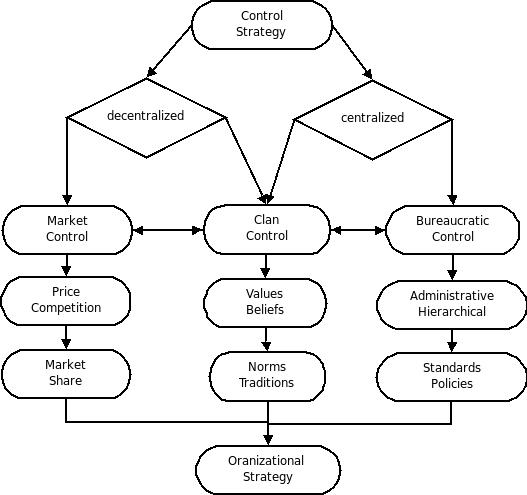
Control theory in sociology is the idea that two control systems—inner controls and outer controls—work against our tendencies to deviate. Control theory can either be classified as centralized or decentralized. Decentralized control is considered market control. Centralized control is considered bureaucratic control. Some types of control such as clan control are considered to be a mixture of both decentralized and centralized control. Decentralized control or market control is typically maintained through factors such as price, competition, or market share. Centralized control such as bureaucratic control is typically maintained through administrative or hierarchical techniques such as creating standards or policies. An example of mixed control is clan control which has characteristics of both centralized and decentralized control. Mixed control or clan control is typically maintained by keeping a set of values and beliefs or norms and traditions. Containment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Strategy
Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects which are also studied are controllability and observability. Control the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Reckless
Walter Cade Reckless (January 19, 1899 – September 20, 1988) was an American criminologist known for his containment theory (in social control theory), who was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and died in Dublin, Ohio. Biography Reckless earned his PhD in sociology (1925) from the University of Chicago. While at the Chicago school, he joined with sociologists Robert Park and Ernest Burgess in conducting observation studies of crime in Chicago, Illinois. This research led to his dissertation, ''The Natural History of Vice Areas in Chicago'' (1925), which was published as "Vice in Chicago" (1933), a landmark sociological study of fraud, prostitution, and organized crime in the city's "vice" districts. As a professor of sociology at Vanderbilt University (1925–1940), Reckless shifted his focus to the study of juvenile delinquency. In their 1932 book ''Juvenile Delinquency'', he and Mapheus Smith (professor at the University of Kansas) focused on juvenile offenders; the book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criminology
Criminology (from Latin , 'accusation', and Ancient Greek , ''-logia'', from λόγος ''logos'', 'word, reason') is the interdisciplinary study of crime and deviant behaviour. Criminology is a multidisciplinary field in both the behavioural and social sciences, which draws primarily upon the research of sociologists, political scientists, economists, legal sociologists, psychologists, philosophers, psychiatrists, social workers, biologists, social anthropologists, scholars of law and jurisprudence, as well as the processes that define administration of justice and the criminal justice system. The interests of criminologists include the study of the nature of crime and criminals, origins of criminal law, etiology of crime, social reaction to crime, and the functioning of law enforcement agencies and the penal institutions. It can be broadly said that criminology directs its inquiries along three lines: first, it investigates the nature of criminal law and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deborah Carr
Deborah Carr is an American sociologist, academic, and author. She is the Arts & Sciences Distinguished Professor of Sociology and the inaugural director of the Center of Innovation in Social Science at Boston University. In 2024, she was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.New Academy Members Elected in 2024 ''American Academy of Arts & Sciences''. Retrieved August 1, 2024.Carr and Schmidt elected to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences ''BU Arts & Sciences''. April 24, 2024. Retrieved August 1, 2024.Most, Doug. 2024. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard P
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", " Dick", " Dickon", " Dickie", " Rich", " Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English (the name was introduced into England by the Normans), German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Portuguese and Spanish "Ricardo" and the Italian "Riccardo" (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Anders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitchell Duneier
Mitchell Duneier is an American sociologist and ethnographer. He is currently Maurice P. During Professor and department chair of Sociology at Princeton University and has also served as a regular Visiting Distinguished Professor of Sociology at the Graduate Center, CUNY. Duneier earned his doctorate from the University of Chicago in 1992. His first book, ''Slim's Table: Race, Respectability, and Masculinity'', won the 1994 American Sociological Association's award for Distinguished Scholarly Publication. He is also the author of ''Sidewalk (1999)'', which won the Los Angeles Times Book Prize and the C. Wright Mills Award. In 2016, he published ''Ghetto: The Invention of a Place, the History of an Idea'' with Farrar, Straus and Giroux, which was one of the New York Times Book Review Notable Books of the Year and one of the Best Books of the Year by ''Publishers Weekly''. He was elected to membership in the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 2021. Duneier taught at the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Control Theory
In criminology, social control theory proposes that exploiting the process of socialization and social learning builds self-control and reduces the inclination to indulge in behavior recognized as antisocial. It derived from functionalist theories of crime and was developed by Ivan Nye (1958), who proposed that there were three types of control: * Direct: by which punishment is threatened or applied for wrongful behavior, and compliance is rewarded by parents, family, and authority figures. * Indirect: by identification with those who influence behavior, say because their delinquent act might cause pain and disappointment to parents and others with whom they have close relationships. * Internal: by which a youth refrains from delinquency through the conscience or superego. Definition Social control theory proposes that people's relationships, commitments, values, norms, and beliefs encourage them not to break the law. Thus, if moral codes are internalized and individuals are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employment
Employment is a relationship between two party (law), parties Regulation, regulating the provision of paid Labour (human activity), labour services. Usually based on a employment contract, contract, one party, the employer, which might be a corporation, a not-for-profit organization, a co-operative, or any other entity, pays the other, the employee, in return for carrying out assigned work. Employees work in return for wage, wages, which can be paid on the basis of an hourly rate, by piecework or an annual salary, depending on the type of work an employee does, the prevailing conditions of the sector and the bargaining power between the parties. Employees in some sectors may receive gratuity, gratuities, bonus payments or employee stock option, stock options. In some types of employment, employees may receive benefits in addition to payment. Benefits may include health insurance, housing, and disability insurance. Employment is typically governed by Labour law, employment laws, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travis Hirschi
Travis Warner Hirschi (April 15, 1935 – January 2, 2017) was an American sociologist and an emeritus professor of sociology at the University of Arizona. He helped to develop the modern version of the social control theory of crime and later the self-control theory of crime. Biography Hirschi was born in Rockville, Utah. He attended the University of Utah in the 1950s, where he obtained undergraduate and master's degrees. In 1955, Hirschi married Anna Yergensen. He spent two years as a U.S. Army data analyst. He received a Ph.D. in sociology from the University of California, Berkeley in 1968. In his 1969 work ''Causes of Delinquency'', Hirschi posited his version of social control theory. He wrote that social bonds encouraged conforming behavior and prevented most people from committing crimes. In 1977, he and Michael Hindelang published a study which showed that IQ and social class were equally predictive of crime; IQ had been previously discounted as a correlate of crimin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conform
Conformity or conformism is the act of matching attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors to group norms, politics or being like-minded. Norms are implicit, specific rules, guidance shared by a group of individuals, that guide their interactions with others. People often choose to conform to society rather than to pursue personal desires – because it is often easier to follow the path others have made already, rather than forging a new one. Thus, conformity is sometimes a product of group communication. This tendency to conform occurs in small groups and/or in society as a whole and may result from subtle unconscious influences (predisposed state of mind), or from direct and overt social pressure. Conformity can occur in the presence of others, or when an individual is alone. For example, people tend to follow social norms when eating or when watching television, even if alone. Solomon Asch, a social psychologist whose obedience research remains among the most influential in psycholog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crime
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a State (polity), state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definitions of", in Cane and Conoghan (editors), ''The New Oxford Companion to Law'', Oxford University Press, 2008 (), p. 263Google Books). though statutory definitions have been provided for certain purposes. The most popular view is that crime is a Category of being, category created by law; in other words, something is a crime if declared as such by the relevant and applicable law. One proposed definition is that a crime or offence (or criminal offence) is an act harmful not only to some individual but also to a community, society, or the state ("a public wrong"). Such acts are forbidden and punishable by law. The notion that acts such as murder, rape, and theft are to be prohibited exists worldwide. What precisely is a criminal offence is def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societies are characterized by patterns of relationships ( social relations) between individuals who share a distinctive culture and institutions; a given society may be described as the sum total of such relationships among its constituent members. Human social structures are complex and highly cooperative, featuring the specialization of labor via social roles. Societies construct roles and other patterns of behavior by deeming certain actions or concepts acceptable or unacceptable—these expectations around behavior within a given society are known as societal norms. So far as it is collaborative, a society can enable its members to benefit in ways that would otherwise be difficult on an individual basis. Societies vary based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |