|
Control Moment Gyroscope
A control moment gyroscope (CMG) is an attitude control device generally used in spacecraft attitude control systems. A CMG consists of a spinning rotor and one or more motorized gimbals that tilt the rotor’s angular momentum. As the rotor tilts, the changing angular momentum causes a gyroscopic torque that rotates the spacecraft. Comparison with Reaction Wheels CMGs and reaction wheels are two common types of spacecraft attitude control actuators and serve the same function, though they differ in mechanics and performance characteristics. The latter apply torque simply by changing rotor spin speed, but the former tilt the rotor's spin axis without necessarily changing its spin speed. CMGs are more mechanically complex than reaction wheels and typically more expensive, but are far more power efficient. For a few hundred watts and about 100 kg of mass, large CMGs have produced thousands of newton meters of torque. A reaction wheel of similar capability would require meg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spacecraft Attitude Control
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle or satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc. Controlling vehicle attitude requires actuators to apply the torques needed to orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, and algorithms to command the actuators based on the current attitude and specification of a desired attitude. Before and during attitude control can be performed, spacecraft attitude determination must be performed, which requires sensors for absolute or relative measurement. The broader integrated field that studies the combination of sensors, actuators and algorithms is called ''guidance, navigation and control'', which also involves non-attitude concepts, such as position determination and navigation. Motivation A spacecraft's attitude must typically be stabilized and controlled for a variety of reasons. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructed from a repurposed Saturn V third stage (the S-IVB), and took the place of the stage during launch. Operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation and hundreds of experiments. Skylab's orbit eventually decayed and it disintegrated in the atmosphere on July 11, 1979, scattering debris across the Indian Ocean and Western Australia. Overview Skylab was the only space station operated exclusively by the United States. A permanent station was planned starting in 1988, but its funding was canceled and U.S. participation shifted to the International Space Station in 1993. Skylab had a mass of with a Apollo command and service module (CSM) attached and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Solar Pressure
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun ** Solar eclipse, an eclipse of a sun in which it is obstructed by the moon ** Solar System, the planetary system made up by the Sun and the objects orbiting it * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from '' Mesmer'', 2017 * "Solar", a song by Sault from ''Air'', 2022 * ”Solar”, a song by Stam1na from '' Taival'', 2018 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atmospheric Drag
In fluid dynamics, drag, sometimes referred to as fluid resistance, is a force acting opposite to the direction of motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers, two solid surfaces, or between a fluid and a solid surface. Drag forces tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path. Unlike other resistive forces, drag force depends on velocity. Drag force is proportional to the relative velocity for low-speed flow and is proportional to the velocity squared for high-speed flow. This distinction between low and high-speed flow is measured by the Reynolds number. Drag is instantaneously related to vorticity dynamics through the Josephson-Anderson relation. Examples Examples of drag include: * Net aerodynamic or hydrodynamic force: Drag acting opposite to the direction of movement of a solid object such as cars, aircraft, and boat hulls. * Viscous drag of fluid in a pipe: Drag force on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gravity Gradient
Gravity gradiometry is the study of variations ( ''anomalies'') in the Earth's gravity field via measurements of the spatial gradient of gravitational acceleration. The gravity gradient tensor is a 3x3 tensor; it is given in coordinates by the Jacobian matrix of the acceleration vector (g= _x g_y g_zT), totaling 9 scalar quantities: : G=\nabla g = \begin \partial/\partial & \partial/\partial & \partial/\partial\\ \partial/\partial & \partial/\partial & \partial/\partial\\ \partial/\partial & \partial/\partial & \partial/\partial \end It has dimension of square reciprocal time, in units of s−2 (or mm−1s−2). Gravity gradiometry is used by oil and mineral prospectors to measure the density of the subsurface, effectively by measuring the rate of change of gravitational acceleration due to underlying rock properties. From this information it is possible to build a picture of subsurface anomalies which can then be used to more accurately target oil, gas and mineral deposits. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ISS Gyroscope
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). As the largest space station ever constructed, it primarily serves as a platform for conducting scientific experiments in microgravity and studying the space environment. The station is divided into two main sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), developed by Roscosmos, and the US Orbital Segment (USOS), built by NASA, ESA, JAXA, and CSA. A striking feature of the ISS is the Integrated Truss Structure, which connect the station’s vast system of solar panels and Spacecraft thermal control, radiators to its pressurized modules. These modules support diverse functions, including scientific research, crew habitation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
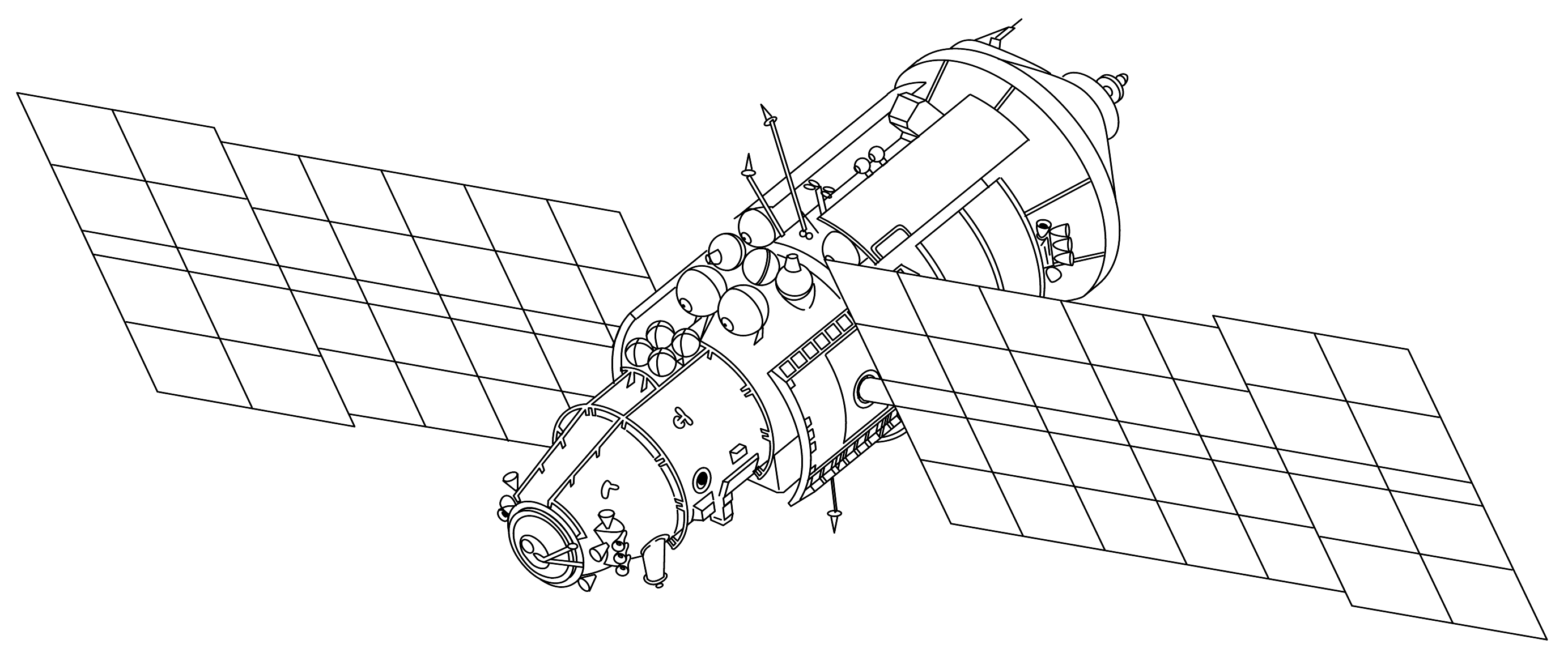
Kristall
The Kristall () (77KST, TsM-T, 11F77T) module was the fourth module and the third major addition to ''Mir''. As with previous modules, its configuration was based on the 77K (TKS) module, and was originally named "Kvant 3". It was launched on May 31, 1990 on Proton-K. It docked to Mir autonomously on June 10, 1990. Description Kristall had several materials processing furnaces. They were called Krater 5, Optizon 1, Zona 2, and Zona 3. It also had a biotechnology experiment called the Aniur electrophoresis unit. These experiments were capable of generating 100 kg of raw materials for use on Earth. Located in the docking node was the Priroda 5 camera which was used for Earth resources experiments. Kristall also had several astronomy and astrophysics experiments which were designed to augment experiments that were already located in Kvant-1. Kristall's solar panels were also different from others on Mir. They were designed to be "collapsible" which means that they could be de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Energia (corporation)
S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation "Energia" () is a Russian manufacturer of spacecraft and space station components. Its name is derived from the Russian word for energy and is also named for Sergei Korolev, Sergei Pavlovich Korolev, the first chief of its design bureau and the driving force behind early Soviet accomplishments in space exploration. Overview Energia is the largest company of the Russian space industry and one of its key players. It is responsible for all operations involving human spaceflight and is the lead developer of the Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz and Progress (spacecraft), Progress spacecraft, and the lead developer of the Russian end of the International Space Station (ISS). In the mid-2000s, the company employed 22,000–30,000 people. The enterprise has been awarded 4 Order of Lenin, Orders of Lenin, Order of the October Revolution and Russian Federation President's Message of Thanks. In addition, 14 cosmonauts employed by the company have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kvant-2
Kvant-2 (; English: Quantum-II/2) (77KSD, TsM-D, 11F77D) was the third module and second major addition to the Mir space station. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir. It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket. It docked to Mir on December 6. Its control system was designed by the NPO "Electropribor" (Kharkiv, Ukraine). Description Kvant-2 was the first Mir module based on the TKS spacecraft (77k module). Kvant-2 was divided into three compartments. They were the EVA airlock, the instrument/cargo compartment, and the instrument/experiment compartment. The instrument/cargo compartment could be sealed off and act as an extension or a back-up to the airlock. Before Kvant-2 docked to the station, EVAs had to be carried by depressurizing the docking node on the Core Module. Kvant-2 also carried the Soviet version of the Manned Maneuvering Unit for the Orlan space suit. It delivered the Salyut 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kvant-1
Kvant-1 (; English: Quantum-I/1) (37KE) was the first module to be attached in 1987 to the Mir Core Module, which formed the core of the Soviet space station ''Mir''. It remained attached to ''Mir'' until the entire space station was deorbited in 2001. The Kvant-1 module contained scientific instruments for astrophysical observations and materials science experiments. It was used to conduct research into the physics of active galaxies, quasars and neutron stars and it was uniquely positioned for studies of the Supernova SN 1987A. Furthermore, it supported biotechnology experiments in anti-viral preparations and fractions. Some additions to Kvant-1 during its lifetime were solar arrays and the ''Sofora'' and ''Rapana'' girders. The Kvant-1 module was based on the TKS spacecraft and was the first, experimental version of a planned series of '37K' type modules. The 37K modules featured a jettisonable TKS-E type propulsion module, also called the Functional Service Module (FSM). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Salyut 6
Salyut 6 () was a Soviet orbital space station, the eighth station of the Salyut programme, and alternatively known DOS-5 as it was the fifth of the Durable Orbital Station series of civilian space stations. It was launched on 29 September 1977 by a Proton rocket. Salyut 6 was the first space station to receive large numbers of crewed and uncrewed spacecraft for human habitation, crew transfer, international participation and resupply, establishing precedents for station life and operations which were enhanced on Mir and the International Space Station. Salyut 6 was the first "second generation" space station, representing a major breakthrough in capabilities and operational success. In addition to a new propulsion system and its primary scientific instrument—the BST-1M multispectral telescope—the station had two docking ports, allowing two craft to visit simultaneously. This feature made it possible for humans to remain aboard for several months. Six long-term residen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |