|
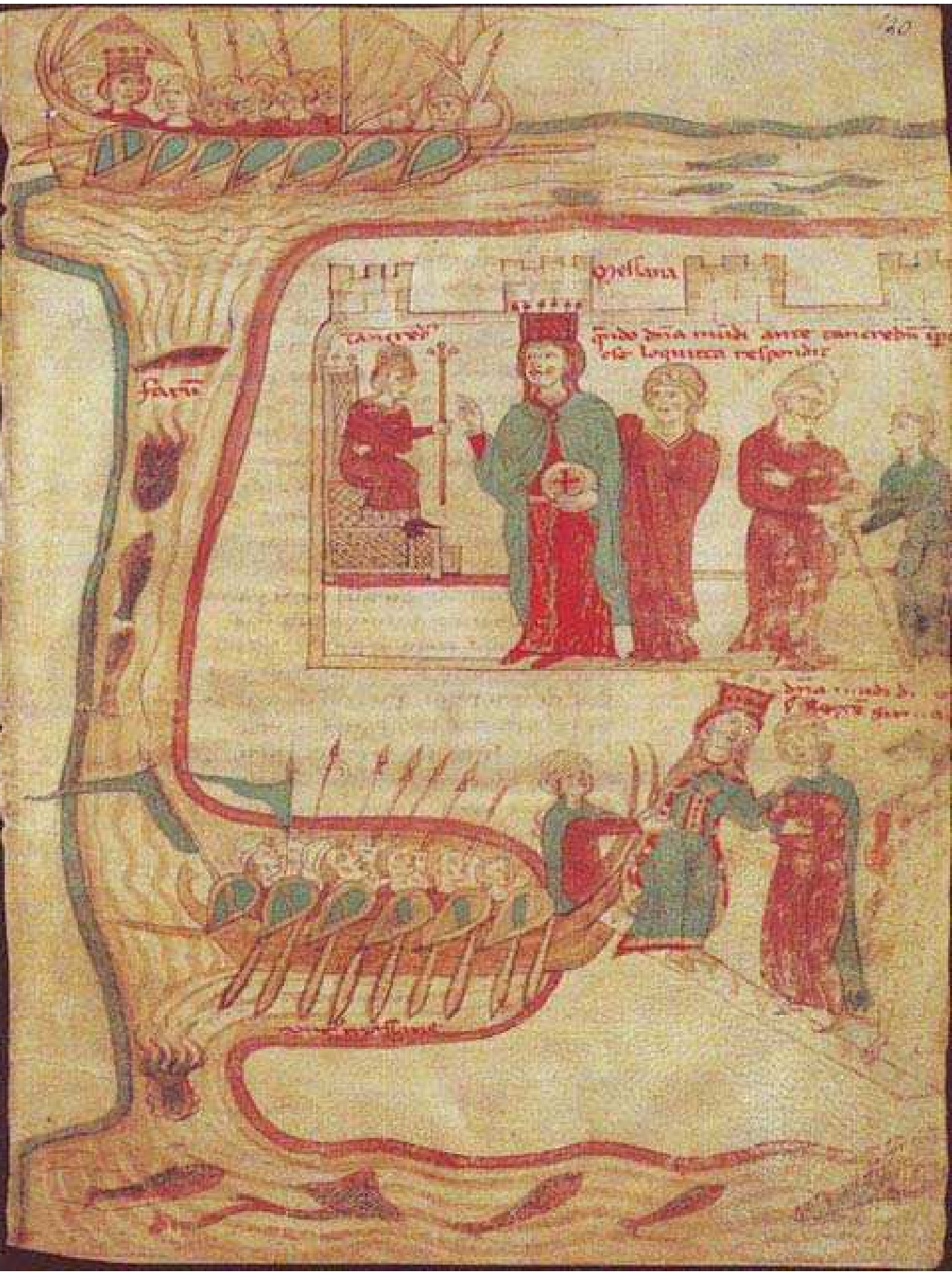
Constance I Of Sicily
Constance I (; 2 November 1154 – 27 November 1198) was the queen of Sicily from 1194 until her death and Holy Roman empress from 1191 to 1197 as the wife of Emperor Henry VI. As queen regnant of Sicily, she reigned jointly with her spouse and later with her infant son, the future Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II. She is particularly notable for her actions against her own family, the Norman kings of Sicily; she played an important role in the end of the Hauteville presence in Sicily. Despite being the sole heir to the throne of Sicily, she did not marry until she was 30 due to an ominous prophecy. Shortly after becoming empress, she was involved in the succession war against her illegitimate nephew King Tancred for the Sicilian throne, during which she was captured, though she was later released unharmed. In the history of Holy Roman Empire only two empresses were captured, with the other being her mother-in-law Empress Beatrice. Shortly before ascending the Sicilian thron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empress
The Holy Roman Empress or Empress of the Holy Roman Empire (''Kaiserin des Heiligen Römischen Reiches'') was the wife or widow of the Holy Roman Emperor. The elective dignity of Holy Roman emperor was restricted to males only, but some empresses, such as Theophanu and Maria Theresa, were '' de facto'' rulers of the Empire. Holy Roman Empresses Before 924, the title of emperor was not always associated with the German kingdom; rather, it was initially associated with the Carolingian dynasty, and then possessed by several other figures of the 9th and 10th centuries. Their wives were thus empresses, but not necessarily German queens. Carolingian Holy Roman Empresses/Queens of Germany With the elevation of Otto I of Germany in 962 to the Imperial title, the title of Roman King or Emperor became inalienably associated with the Kingdom of Germany - although a King of Germany might not bear the title of Emperor, it would be impossible to become a Holy Roman Emperor without being K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. For most of its history the Empire comprised the entirety of the modern countries of Germany, Czechia, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Slovenia, and Luxembourg, most of north-central Italy, and large parts of modern-day east France and west Poland. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne Roman emperor, reviving the title more than three centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The title lapsed in 924, but was revived in 962 when Otto I, OttoI was crowned emperor by Pope John XII, as Charlemagne's and the Carolingian Empire's successor. From 962 until the 12th century, the empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Of Capua
Henry (''Arricus'' or ''Arrico'') (1160–1172) was the youngest and second surviving son of William I of Sicily by Margaret of Navarre. By his father's will he succeeded to the title Prince of Capua, an appanage to the throne, while his brother William II succeeded to the throne. Henry's coronation as prince was postponed from the death of his father (1166). Henry was present with William at Taranto, where the young king awaited his Greek bride. They planned to return via Capua and there invest Henry with his principality, but not far off from the town, Henry came down with a high fever. He was hurried to Salerno and thence to Palermo, but died within the month. According to legend, he was betrothed to a daughter of Malcolm IV of Scotland on his deathbed, but this is false. Malcolm had no issue. He was originally buried in the chapel of Saint Mary Magdalene, but was moved by his brother to Monreale, the final resting place of most of his family. The death of Henry made his aunt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Du Perche
Stephen du Perche (1137 or 1138 – 1169) was the chancellor of the Kingdom of Sicily (1166–68) and Archbishop of Palermo (1167–68) during the early regency of his cousin, the queen dowager Margaret of Navarre (1166–71). Stephen is described by the contemporary chronicler Hugo Falcandus as "a son of the count of Perche", Rotrou III. He was a young man when he entered politics, born at the earliest in 1137 or 1138. He may have been named after King Stephen of England, at the time ruling the Duchy of Normandy. Arrival in Italy In 1166, Margaret appealed to her other cousin, Rotrou, Archbishop of Rouen, to send her a family member to aid and support her in government. Coincidentally, Stephen was at that moment preparing to go on crusade to the Holy Land and so decided to visit Palermo, the capital of Sicily, for a few months. There he ended up staying for two years. He was very young at the time, described as ''puer'' and ''adolescens'' by William of Tyre, and may have s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William II Of Sicily
William II (December 115311 November 1189), called the Good, was king of Sicily from 1166 to 1189. From surviving sources William's character is indistinct. Lacking in military enterprise, secluded and pleasure-loving, he seldom emerged from his palace life at Palermo. Yet his reign is marked by an ambitious foreign policy and a vigorous diplomacy. Champion of the papacy and in secret league with the Lombard cities, he was able to defy the common enemy, Frederick Barbarossa. In the ''Divine Comedy'', Dante places William II in Paradise. He is also referred to in Boccaccio's '' Decameron'' (tale IV.4, where he reportedly has two children, and tale V.7). William was nicknamed "the Good" only in the decades following his death. It is due less to his character than to the cessation of the internal troubles that plagued his father's reign and the wars that erupted under his successor. Under the Staufer dynasty his reign was characterised as a golden age of peace and justice. His nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Taylor Simeti
Mary Taylor Simeti is an American author specializing in Sicilian cuisine and its history. She is a former regular contributor to the ''New York Times'' and to the ''Financial Times''. Biography Mary Taylor Simeti was born in 1941 in New York City. She is the daughter of Francis Henry Taylor, then director of the Metropolitan Museum of Art. In 1962 she graduated from Radcliffe College with a major in history. She travelled to Sicily to work with social activist Danilo Dolci. In Sicily she met her future husband, Antonio Simeti, professor of agricultural economics at the University of Palermo. Together they restored the Simetis' farm near Alcamo Alcamo (; ) is the fourth-largest town and communes of Italy, commune of the Province of Trapani, Sicily, with a population of 44.925 inhabitants. It is on the borderline with the Metropolitan City of Palermo at a distance of about 50 kilometr ... where they produce organic olive oil and wine. Books * “On Persephone’s Island. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santissimo Salvatore, Palermo
The Church of Most Holy Saviour (Italian language, Italian: Chiesa del Santissimo Salvatore) is a Baroque architecture, Baroque-style, Roman Catholic church in Palermo, Italy. It is located at #396 of the ancient main street of Palermo, the Cassaro, Palermo, Cassaro, presently Via Vittorio Emanuele, in the ancient Albergaria (Palazzo Reale), Albergaria Quarter (urban subdivision), quarter. History The site of the present church was formerly the location of a Basilian monks, Basilian (Eastern Rite) monastery and church dedicated to the Saviour, founded in 1072 by the Norman Robert Guiscard. Royal patronage of the church and monastery continued under House of Hohenstaufen, Hohenstaufen rule. It was said that Constance I of Sicily, Constance, Queen of Sicily (1154-1198) was confined to the church as a nun from her childhood until the age of 30, due to the prediction that "her marriage would destroy Sicily". In 1501, the monastery was converted to the Latin Rite. In 1528, a new chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Mulieribus Claris
''De Mulieribus Claris'' or ''De Claris Mulieribus'' (Latin for "Concerning Famous Women") is a collection of biographies of historical and mythological women by the Florentine author Giovanni Boccaccio, composed in Latin prose in 1361–1362. It is the first collection devoted exclusively to biographies of women in post-ancient Western literature. At the same time as he was writing ''On Famous Women'', Boccaccio also compiled a collection of biographies of famous men,'' De Casibus Virorum Illustrium'' (''On the Fates of Famous Men''). The famous women *1. Eve, the first woman in the Bible *2. Semiramis, queen of the Assyrians *3. Opis, wife of Saturn *4. Juno, goddess of the Kingdoms *5. Ceres, goddess of the harvest and queen of Sicily *6. Minerva, Roman goddess of wisdom, justice, law, victory, and the sponsor of arts, trade, and strategy *7. Venus, queen of Cyprus *8. Isis, queen and goddess of Egypt *9. Europa, queen of Crete *10. Libya, queen of Libya *11 and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
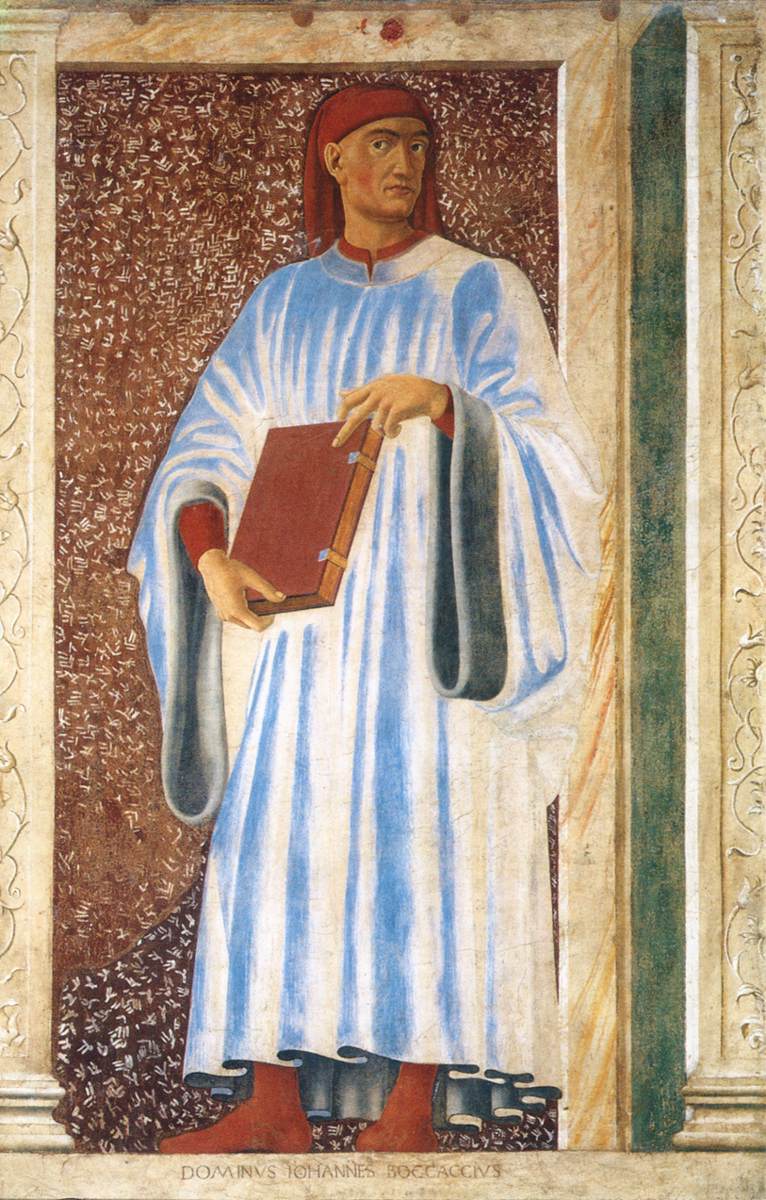
Giovanni Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio ( , ; ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian people, Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so well known as a writer that he was sometimes simply known as "the Certaldese" and one of the most important figures in the European literary panorama of the 14th century, fourteenth century. Some scholars (including Vittore Branca) define him as the greatest European prose writer of his time, a versatile writer who amalgamated different literary trends and genres, making them converge in original works, thanks to a creative activity exercised under the banner of experimentalism. His most notable works are ''The Decameron'', a collection of short stories, and ''De Mulieribus Claris, On Famous Women''. ''The Decameron'' became a determining element for the Italian literary tradition, especially after Pietro Bembo elevated the Boccaccian styl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marjorie Chibnall
Marjorie McCallum Chibnall (27 September 1915 – 23 June 2012) was an English historian, medievalist and Latin translator. She edited the ''Historia Ecclesiastica'' by Orderic Vitalis, with whom she shared the same birthplace of Atcham in Shropshire. Biography Born into a farming family at Atcham in Shropshire in 1915, Chibnall was educated at Shrewsbury Priory County Girls' School and Lady Margaret Hall, Oxford, where she was taught by Evelyn Jamison, V. H. Galbraith and F. M. Powicke. In 1947, she married the biochemist and amateur medieval historian Albert Chibnall, who died in 1988. They had a son and a daughter. She died in Sheffield on 23 June 2012, at the age of 96. Scholarly life Marjorie Chibnall took her BLitt at the University of Cambridge on the subject of ecclesiastical law, before moving on for her doctorate to a study of the relations between the mighty Bec Abbey in Normandy and its dependent English priories. She completed her doctorate in 1939 unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zachary Nugent Brooke
Zachary Nugent Brooke (1 December 1883 – 2 October 1946) was a British medieval historian. Life Born on 1 December 1883, Brooke was educated at Bradfield College in Berkshire and St John's College, Cambridge. In 1908, he was elected to a Drosier Fellowship at Gonville and Caius College, University of Cambridge. He was appointed as the second Professor of Medieval History at Cambridge in 1944. He was appointed as a Fellow of the British Academy in 1940. Retrieved 21 December 2019. Brooke is buried at the Parish of the Ascension Burial Ground, off Huntingdon Road, Cambridge, with his wife Rosa Grace B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles William Previté-Orton
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (James (wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/ǵerh₂-">ĝer-, where the ĝ is a palatal consonant, meaning "to rub; to be old; grain." An old man has been worn away and is now grey with age. In some Slavic languages, the name ''Drago (given name), Drago'' (and variants: ''Dragom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |