|
Complete Dentures
A complete denture (also known as a full denture, false teeth or plate) is a removable appliance used when all teeth within a jaw have been lost and need to be prosthetically replaced. In contrast to a partial denture, a complete denture is constructed when there are no more teeth left in an arch; hence, it is an exclusively tissue-supported prosthesis. A complete denture can be opposed by natural dentition, a partial or complete denture, fixed appliances or, sometimes, soft tissues. Epidemiology and causes of tooth loss There has been a decline in both the prevalence and incidence of tooth loss within the last decades; people retain their natural dentition for longer. Nonetheless there is still a great demand for complete dentures as more than 10% of adults aged 50–64 are completely edentulous, with age, smoking status and socioeconomic status being significant risk factors. Tooth loss can occur due to many reasons, such as: * Dental caries * Periodontal disease * Trauma * Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentures
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable ( removable partial denture or complete denture). However, there are many denture designs, some of which rely on bonding or clasping onto teeth or dental implants ( fixed prosthodontics). There are two main categories of dentures, the distinction being whether they fit onto the mandibular arch or on the maxillary arch. Medical uses Dentures can help people via: * Mastication: chewing ability is improved by the replacement of edentulous (lacking teeth) areas with denture teeth. * Aesthetics: the presence of teeth gives a natural appearance to the face, and wearing a denture to replace missing teeth provides support for the lips and cheeks and corrects the collapsed appearance that results from the loss of teeth. * Pronunciation: replacing missing teeth, especially the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endodontics
Endodontics () is the Specialty (dentistry), dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp. Overview Endodontics encompasses the study (practice) of the basic and clinical sciences of normal dental pulp, the etiology, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases and injuries of the dental pulp along with associated wikt:periradicular, periradicular conditions. In clinical terms, endodontics involves either preserving part, or all of the dental pulp in health, or removing all of the pulp in irreversible disease. This includes teeth with irreversibly inflamed and infected pulpal tissue. Not only does endodontics involve treatment when a dental pulp is present, but also includes preserving teeth which have failed to respond to non-surgical endodontic treatment, or for teeth that have developed new lesions, e.g., when root canal re-treatment is required, or periradicular surgery. Endodontic treatment is one of the most common procedures. If the den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endodontic Therapy
Root canal treatment (also known as endodontic therapy, endodontic treatment, or root canal therapy) is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth that is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of the decontaminated tooth from future microbial invasion. It is generally done when the cavity is too big for a normal filling. Root canals, and their associated pulp chamber, are the physical hollows within a tooth that are naturally inhabited by nerve tissue, blood vessels and other cellular entities. Endodontic therapy involves the removal of these structures, disinfection and the subsequent shaping, cleaning, and decontamination of the hollows with small files and irrigating solutions, and the obturation (filling) of the decontaminated canals. Filling of the cleaned and decontaminated canals is done with an inert filling such as gutta-percha and typically a zinc oxide eugenol-based cement. Epoxy resin is employed to bind gutta-percha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown (tooth)
In dentistry, the crown is the visible part of the tooth above the gingival margin and is an essential component of dental anatomy. Covered by Tooth enamel, enamel, the crown plays a crucial role in cutting, tearing, and grinding food. Its shape and structure vary depending on the type and function of the tooth (incisors, Canine tooth, canines, premolars, or Molar (tooth), molars), and differ between Deciduous teeth, primary dentition and Permanent teeth, permanent dentition. The crown also contributes to facial aesthetics, speech, and oral health. Anatomical crown vs clinical crown The anatomical crown refers to the portion of the tooth covered by enamel, regardless of whether it is visible. The clinical crown is the part of the tooth that is visible in the mouth. In a healthy young adult, the gums typically follow the contour where enamel meets the root, so the clinical and anatomical crowns are similar in size. However, with age or periodontal disease, this may change. Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
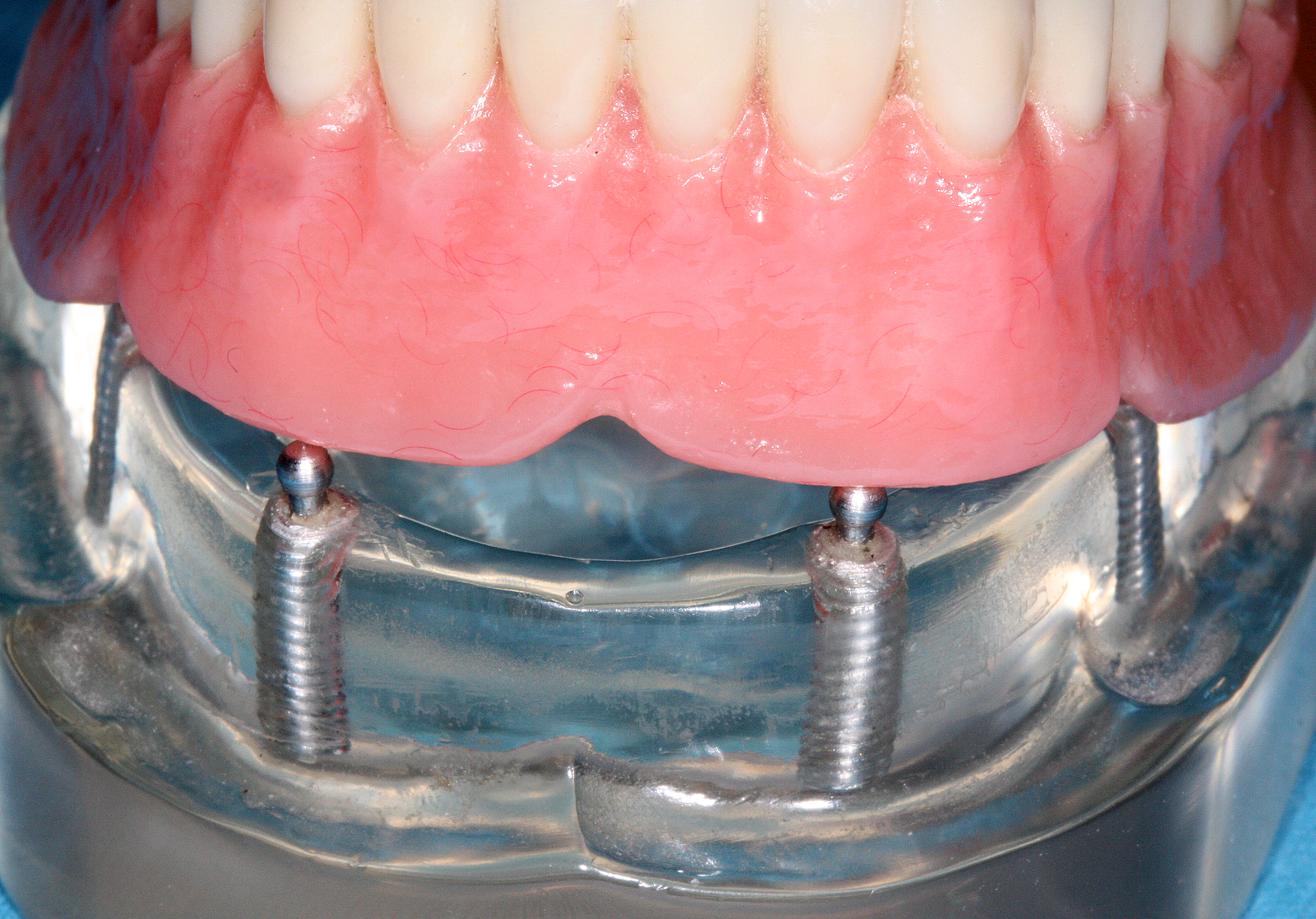
Dental Implant
A dental implant (also known as an endosseous implant or fixture) is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown (dentistry), crown, bridge (dentistry), bridge, dentures, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an Dental braces, orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biological process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or Zirconium dioxide, zirconia form an intimate bond to the bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic (a tooth, bridge, or denture) is attached to the implant or an abutment (dentistry), abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic or crown. Success or failure of implants depends primarily on the thickness and health of the bone and gingival tissues that surround ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overdenture
Overdenture is any removable dental prosthesis that covers and rests on one or more remaining natural teeth, the roots of natural teeth, and/or dental implants. It is one of the most practical measures used in preventive dentistry. Overdentures can be either tooth supported (conventional / immediate) or implant supported. It is found to help in the preservation of alveolar bone and delay the process of complete edentulism. An overdenture is a denture, the base of which covers one or more teeth, prepared roots or implants. An overdenture is usually used for elderly patients that have lost some teeth but not all, rendering them suitable for a set of full dentures. The overdenture is not rigid in the mouth; it is removable. An advantage of overdentures compared to full dentures is that the roots left in the maxilla (upper jaw) help preserve bone of the upper jaw, preventing bone resorption. Another advantage is that the sensory aspect is improved. The nerves in the roots are still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cause of tooth loss for adults worldwide. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Halitosis (bad breath) may also occur. Periodontal disease typically arises from the development of plaque biofilm, which harbors harmful bacteria such as ''Porphyromonas gingivalis'' and ''Treponema denticola''. These bacteria infect the gum tissue surrounding the teeth, leading to inflammation and, if left untreated, progressive damage to the teeth and gum tissue. Recent meta-analysis have shown that the composition of the oral microbiota and its response to periodontal disease differ between men and women. These differences are particularly notable in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Plaque
Dental plaque is a biofilm of microorganisms (mostly bacteria, but also fungi) that grows on surfaces within the mouth. It is a sticky colorless deposit at first, but when it forms Calculus (dental), tartar, it is often brown or pale yellow. It is commonly found between the teeth, on the front of teeth, behind teeth, on chewing surfaces, along the gums, gumline (supragingival), or below the gumline cervical margins (subgingival). Dental plaque is also known as microbial plaque, oral biofilm, dental biofilm, dental plaque biofilm or bacterial plaque biofilm. Bacterial plaque is one of the major causes for dental decay and gum disease. It has been observed that differences in the composition of dental plaque microbiota exist between men and women, particularly in the presence of periodontal disease, periodontitis. Progression and build-up of dental plaque can give rise to tooth decay – the localised destruction of the tissues of the tooth by acid produced from the bacterial degrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthodontics
Prosthodontics, also known as dental prosthetics or prosthetic dentistry, is the area of dentistry that focuses on dental prostheses. It is one of 12 dental specialties recognized by the American Dental Association (ADA), Royal College of Surgeons of England, Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh, Royal College of Surgeons of Ireland, Royal College of Surgeons of Glasgow, Royal College of Dentists of Canada, and Royal Australasian College of Dental Surgeons. The ADA defines it as "the dental specialty pertaining to the diagnosis, treatment planning, rehabilitation and maintenance of the oral function, comfort, appearance and health of patients with clinical conditions associated with missing or deficient teeth or oral and maxillofacial tissues using biocompatible substitutes." History Pierre Fauchard (died 1761) discovered many methods to replace lost teeth using substitutes made from carved blocks of ivory or bone. He also introduced dental braces to correct the pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masticatory Force
Masticatory force or force of mastication is the force created by the dynamic action of the masticatory muscles during the act of chewing. Masticatory muscles The muscles that power the jaw movements during chewing are known as the muscles of mastication or masticatory muscles, and are functionally classified as: * Jaw elevators: the masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid and superior belly of the lateral pterygoid * Jaw depressors; the anterior digastrics, geniohyoid, mylohyoid and inferior belly of the lateral pterygoid Measuring masticatory force The first device for measuring masticatory force ( gnathodynamometer) was created by Black in 1893. He determined that periodontal tissue is an important issue, which impacts the amount of force. Morill found out that masticatory muscles stop their contraction differently upon the appearance of pain signals from the periodontal tissue. Shreder used local anaesthesia to ignore the periodontal response to measure the maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal System
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal frame to which the organs and soft tissues attach; and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal structure supported by the hydrostatic pressure of body fluids. Vertebrates are animals with an endoskeleton centered around an axial vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bones and cartilages. Invertebrates are other animals that lack a vertebral column, and their skeletons vary, including hard-shelled exoskeleton (arthropods and most molluscs), plated internal shells (e.g. cuttlebones in some cephalopods) or rods (e.g. ossicles in echinoderms), hydrostatically supported body cavities (most), and spicules (sponges). Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |