|
Comparison Of Window Managers
This article compares variety of different X window managers. For an introduction to the topic, see X Window System. General information Features See also * Comparison of X Window System desktop environments * Window manager * List of Wayland compositors References External links Comparison of extensible window managerscompares window managers "extensible" by user scripts, like Sawfish, xmonad, etc. ''The Comprehensive List of Window Managers for Unix'' {{X desktop environments and window managers Window managers A window manager is system software that controls the placement and appearance of windows within a windowing system in a graphical user interface. Most window managers are designed to help provide a desktop environment. They work in conjunction ... X window managers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Window Manager
An X window manager is a window manager that runs on top of the X Window System, a windowing system mainly used on Unix-like systems. Unlike MacOS Classic, macOS, and Microsoft Windows platforms (excepting Microsoft Windows explorer.exe shell replacements), which have historically provided a vendor-controlled, fixed set of ways to control how windows and panes display on a screen, and how the user may interact with them, window management for the X Window System was deliberately kept separate from the software providing the graphical display. The user can choose between various third-party window managers, which differ from one another in several ways, including: * customizability of appearance and functionality: ** textual menus used to start programs and/or change options ** docks and other graphical ways to start programs ** multiple desktops and virtual desktops (desktops larger than the physical monitor size), and pagers to switch between them * consumption of me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compositing Window Manager
A compositing window manager, or compositor, is a window manager that provides applications with an off-screen buffer for each window. The window manager composites the window buffers into an image representing the screen and writes the result into the display memory. Compositing window managers may perform additional processing on buffered windows, applying 2D and 3D animated effects such as blending, fading, scaling, rotation, duplication, bending and contortion, shuffling, blurring, redirecting applications, and translating windows into one of a number of displays and virtual desktops. Computer graphics technology allows for visual effects to be rendered in real time such as drop shadows, live previews, and complex animation. Since the screen is double buffered, it does not flicker during updates. The most commonly used compositing window managers include: * for Linux, BSD, Hurd and OpenSolaris: Compiz, KWin, Xfwm, Enlightenment, Mutter, xcompmgr and picom; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I3 (window Manager)
i3 is a tiling window manager designed for X11, inspired by wmii and written in C. It supports tiling, stacking, and tabbing layouts, which it handles dynamically. Its configuration is achieved via a plain text file and extending i3 is possible using its Unix domain socket and JSON based IPC interface from many programming languages. Like wmii, i3 uses a control system very similar to that of vi and Vim. By default, window focus is controlled by what the documentation refers to as the 'Mod1' key (Alt key/Windows key) plus the right-hand home row keys (Mod1+J,K,L,Semicolon), while window movement is controlled by the addition of the Shift key (Mod1+Shift+J,K,L,Semicolon). Design goals i3's primary design goals are to possess well-written, documented code that encourages user contribution; to use XCB instead of Xlib; to implement multi-monitor features correctly, so that each workspace is assigned to a virtual screen, and monitor additions and removals are non-destructiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C++ (programming Language)
C++ (pronounced "C plus plus") is a high-level general-purpose programming language created by Danish computer scientist Bjarne Stroustrup as an extension of the C programming language, or "C with Classes". The language has expanded significantly over time, and modern C++ now has object-oriented, generic, and functional features in addition to facilities for low-level memory manipulation. It is almost always implemented as a compiled language, and many vendors provide C++ compilers, including the Free Software Foundation, LLVM, Microsoft, Intel, Embarcadero, Oracle, and IBM, so it is available on many platforms. C++ was designed with systems programming and embedded, resource-constrained software and large systems in mind, with performance, efficiency, and flexibility of use as its design highlights. C++ has also been found useful in many other contexts, with key strengths being software infrastructure and resource-constrained applications, including desktop app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FVWM
The F Virtual Window Manager is a virtual window manager for the X Window System. Originally a twm derivative, FVWM has evolved into a powerful and highly configurable environment for Unix-like systems. History In 1993, during his work analyzing acoustic signatures for the United States Department of Defense, Robert Nation began hacking twm with the intent of simultaneously reducing memory usage and adding support for virtual desktops. Already known for his rxvt terminal emulator, Nation worked on reducing the memory consumption of his new window manager. Deciding to test FVWM's reception, on June 1, 1993, he bundled it with a rxvt release. In 1994 Rob Nation stopped developing FVWM and made Charles Hines the maintainer. Rob Nation's last release of FVWM was fvwm-1.24r. The post-Rob Nation version of FVWM uses a different configuration file format and has a significantly different architecture. Many Linux distributions, as a result, distributed both fvwm-1.24r and later re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLWM
The Fast Light Window Manager is a stacking window manager written in C++ and available for redistribution under the terms of the GNU General Public Licence. FLWM is the default window manager for Tiny Core Linux. Features Features of the FLWM window manager include: * Small (i386: 43.6 kB package, 156.0 kB installed, ia64: 58.1 kB package, 216.0 kB installed) * Stacking windows * Written in C++ * Freely redistributable under the terms of the GPL-2.0-or-later license * Based on the FLTK toolkit * Window decorations include borders and a vertical titlebar * sloppy focus with click to focus (no autoraise) * Multiple desktops * Desktop switching via menu or through keyboard navigation * No support for themes. Colors are customizable via command line arguments. See also * Comparison of X window managers This article compares variety of different X window managers. For an introduction to the topic, see X Window System. General information Features See al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluxbox
Fluxbox is a stacking window manager for the X Window System, which started as a fork of Blackbox 0.61.1 in 2001, with the same aim to be lightweight. Its user interface has only a taskbar, a pop-up menu accessible by right-clicking on the desktop, and minimal support for graphical icons. All basic configurations are controlled by text files, including the construction of menus and the mapping of key-bindings. Fluxbox has high compliance to the Extended Window Manager Hints specification. Fluxbox is basic in appearance, but it can show a few options for improved attractiveness: colors, gradients, borders, and several other basic appearance attributes can be specified. Recent versions support rounded corners and graphical elements. Effects managers such as xcompmgr, cairo-compmgr and transset-df (deprecated) can add true transparency to desktop elements and windows. Enhancements can also be provided by using iDesk or fbdesk, SpaceFM, PCMan File Manager or the ROX Desktop. Flux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emacs Lisp
Emacs Lisp is a dialect of the Lisp programming language used as a scripting language by Emacs (a text editor family most commonly associated with GNU Emacs and XEmacs). It is used for implementing most of the editing functionality built into Emacs, the remainder being written in C, as is the Lisp interpreter. Emacs Lisp is also termed Elisp, although there is also an older, unrelated Lisp dialect with that name. Users of Emacs commonly write Emacs Lisp code to customize and extend Emacs. Other options include the ''Customize'' feature that's been in GNU Emacs since version 20. Itself written in Emacs Lisp, Customize provides a set of preferences pages allowing the user to set options and preview their effect in the running Emacs session. When the user saves their changes, Customize simply writes the necessary Emacs Lisp code to the user's config file, which can be set to a special file that only Customize uses, to avoid the possibility of altering the user's own file. Ema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BSD License
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD license was used for its namesake, the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), a Unix-like operating system. The original version has since been revised, and its descendants are referred to as modified BSD licenses. BSD is both a license and a class of license (generally referred to as BSD-like). The modified BSD license (in wide use today) is very similar to the license originally used for the BSD version of Unix. The BSD license is a simple license that merely requires that all code retain the BSD license notice if redistributed in source code format, or reproduce the notice if redistributed in binary format. The BSD license (unlike some other licenses e.g. GPL) does not require that source code be distributed at all. Terms In additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
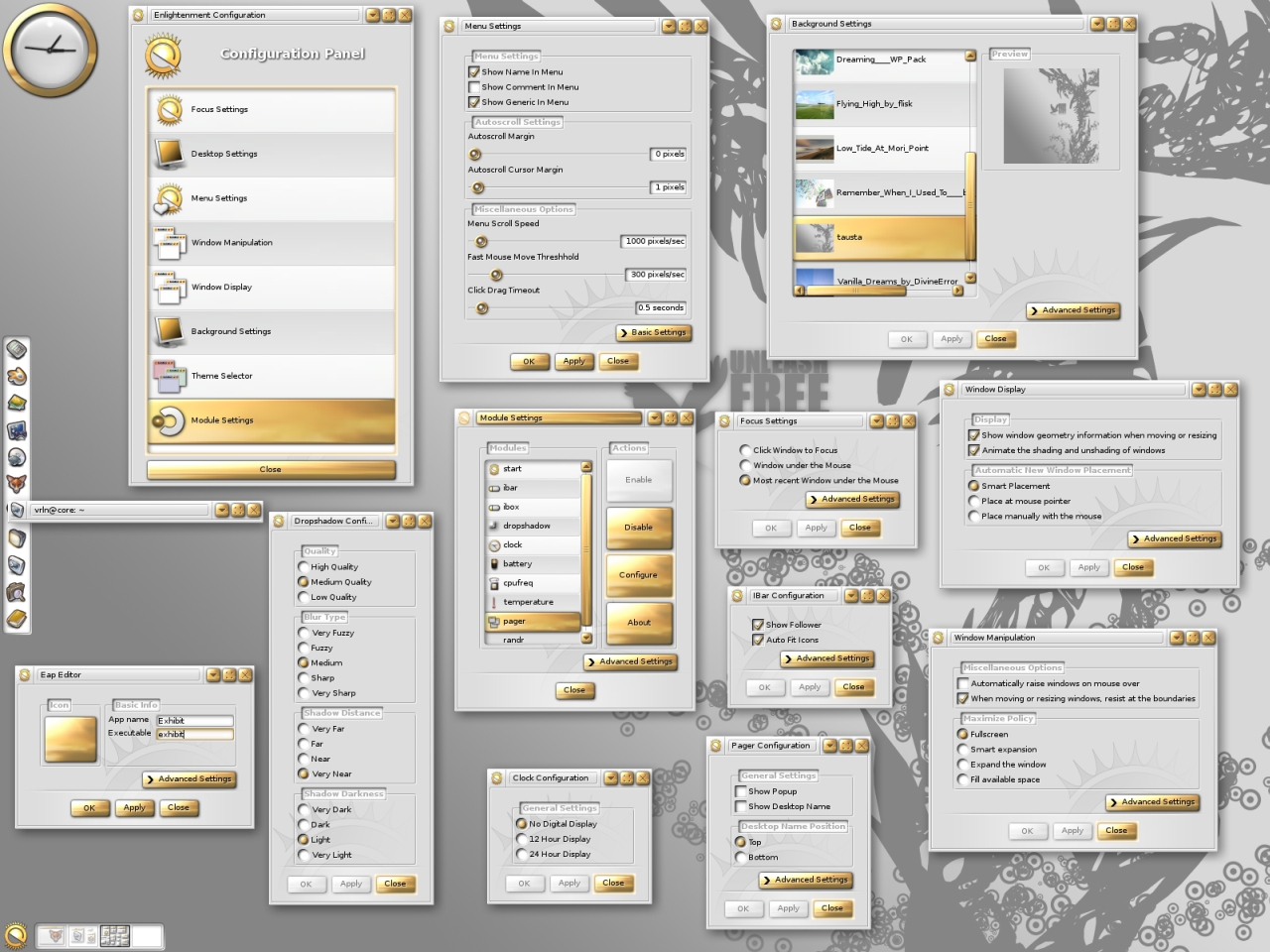
Enlightenment (window Manager)
Enlightenment, also known simply as E, is a compositing window manager for the X Window System. Since version 20, Enlightenment is also a Wayland compositor. Enlightenment developers have referred to it as "the original eye-candy window manager." Enlightenment includes functions to provide a graphical shell and can be used in conjunction with programs written for GNOME or KDE. When used together with the Enlightenment Foundation Libraries (EFL), Enlightenment can refer to an entire desktop environment. History The first version of Enlightenment was released by Rasterman ( Carsten Haitzler) in 1997. Version 0.17, also referred to as E17, was in development for 12 years starting in December 2000 until 21 December 2012 when it was officially released as stable. During the development period it was also referred to as DR17 (Development Release 17). It is a complete rewrite on DR16 and was designed to be a full-fledged desktop shell, based on the new Enlightenment Foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |