|
Communes In Switzerland
Municipalities (, ' or '; ; ; ) are the lowest level of administrative division in Switzerland. Each municipality is part of one of the Swiss cantons, which form the Swiss Confederation. In most cantons, municipalities are also part of districts or other sub-cantonal administrative divisions. There are 2,121 municipalities . Their populations range between several hundred thousand (Zürich), and a few dozen people ( Kammersrohr, Bister), and their territory between 0.32 km² ( Rivaz) and 439 km² (Scuol). History The beginnings of the modern municipality system date back to the Helvetic Republic. Under the Old Swiss Confederacy, citizenship was granted by each town and village to only residents. These citizens enjoyed access to community property and in some cases additional protection under the law. Additionally, the urban towns and the rural villages had differing rights and laws. The creation of a uniform Swiss citizenship, which applied equally for citizens of the old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 E8 M² ...
This page is a progressive and labelled list of the SI area orders of magnitude, with certain examples appended to some list objects. to square metres 10−8 to 10−1 square metres 100 to 107 square metres 108 to 1014 square metres 1015 to 1026 square metres 1027 square metres and larger See also * Orders of magnitude * Lists of political and geographic subdivisions by total area References {{DEFAULTSORT:Orders Of Magnitude (Area) Area Area is the measure of a region's size on a surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while '' surface area'' refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a Municipal corporation, municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well as the means by which a mayor is elected or otherwise mandated. Depending on the system chosen, a mayor may be the chief executive officer of the municipal government, may simply chair a multi-member governing body with little or no independent power, or may play a solely ceremonial role. A mayor's duties and responsibilities may be to appoint and oversee municipal managers and employees, provide basic governmental services to constituents, and execute the laws and ordinances passed by a municipal governing body (or mandated by a state, territorial or national governing body). Options for selection of a mayor include direct election by the public, or selection by an elected governing council or board. The term ''mayor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive (government)
The executive branch is the part of government which executes or enforces the law. Function The scope of executive power varies greatly depending on the political context in which it emerges, and it can change over time in a given country. In democratic countries, the executive often exercises broad influence over national politics, though limitations are often applied to the executive. In political systems based on the separation of powers, government authority is distributed between several branches to prevent power from being concentrated in the hands of a single person or group. To achieve this, each branch is subject to checks by the other two; in general, the role of the legislature is to pass laws, which are then enforced by the executive, and interpreted by the judiciary. The executive can also be the source of certain types of law or law-derived rules, such as a decree or executive order. In those that use fusion of powers, typically parliamentary systems, such as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state. Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of a higher-level political or administrative unit, such as a nation or state. Local governments generally act within the powers and functions assigned to them by law or directives of a higher level of government. In Federation, federal states, local government generally comprises a third or fourth level of government, whereas in unitary states, local government usually occupies the second or third level of government. The institutions of local government vary greatly between countries, and even where similar arrangements exist, country-specific terminology often varies. Common designated names for different types of local government entities include county, counties, districts, city, cities, townships, towns, boroughs, Parish (administrative division), parishes, municipality, municipalities, mun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Commons
The commons is the cultural and natural resources accessible to all members of a society, including natural materials such as air, water, and a habitable Earth. These resources are held in common even when owned privately or publicly. Commons can also be understood as natural resources that groups of people (communities, user groups) manage for individual and collective benefit. Characteristically, this involves a variety of informal norms and values (social practice) employed for a governance mechanism. Commons can also be defined as a social practice of governing a resource not by state or market but by a community of users that self-governs the resource through institutions that it creates. Definition and modern use The Digital Library of the Commons defines "commons" as "a general term for shared resources in which each stakeholder has an equal interest". The term "commons" derives from the traditional English legal term for common land, which are also known as "commons", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Of Origin
In Switzerland, the place of origin (, literally "home place" or "citizen place"; ; , literally "place of relevance") denotes where a Swiss citizen has their municipal citizenship, usually inherited from previous generations. It is not to be confused with the place of birth or place of residence, although two or all three of these locations may be identical depending on the person's circumstances. Citizens of Liechtenstein also have a Place of origin (Heimatort). Acquisition of municipal citizenship Swiss citizenship has three tiers. For a person applying to naturalise as a Swiss citizen, these tiers are as follows: *Municipal citizenship, granted by the place of residence after fulfilling several preconditions, such as sufficient knowledge of the local language, integration into local society, and a minimum number of years lived in said municipality. *Cantonal (state) citizenship, for which a Swiss municipal citizenship is required. This requires a certain number of years l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Of Birth
The place of birth (POB) or birthplace is the place where a person was born. This place is often used in legal documents, together with name and date of birth, to uniquely identify a person. Practice regarding whether this place should be a country, a territory or a city/town/locality differs in different countries, but often city or territory is used for native-born citizen passports and countries for foreign-born ones. As a general rule with respect to passports, if the place of birth is to be a country, it's determined to be the country that currently has ''sovereignty'' over the actual place of birth, regardless of when the birth actually occurred. The place of birth is not necessarily the place where the parents of the new baby live. If the baby is born in a hospital in another place, that place is the place of birth. In many countries, this also means that the government requires that the birth of the new baby is registered in the place of birth. Some countries place less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Federal Constitution
The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation (SR 10; (BV); (Cst.); (Cost.); ) of 18 April 1999 (SR 101) is the third and current federal constitution of Switzerland. It establishes the Swiss Confederation as a federal republic of 26 cantons (states). The document contains a catalogue of individual and popular rights (including the right to call for popular referendums on federal laws and constitutional amendments), delineates the responsibilities of the cantons and the Confederation and establishes the federal authorities of government. The Constitution was adopted by a referendum on 18 April 1999, in which a majority of the people and the cantons voted in favour. It replaced the prior federal constitution of 1874, which it was intended to bring up to date without changing its substance. History Prior to 1798, the Swiss Confederacy was a confederation of independent states, not a federal state; as such it was based on treaties rather than a constitution. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
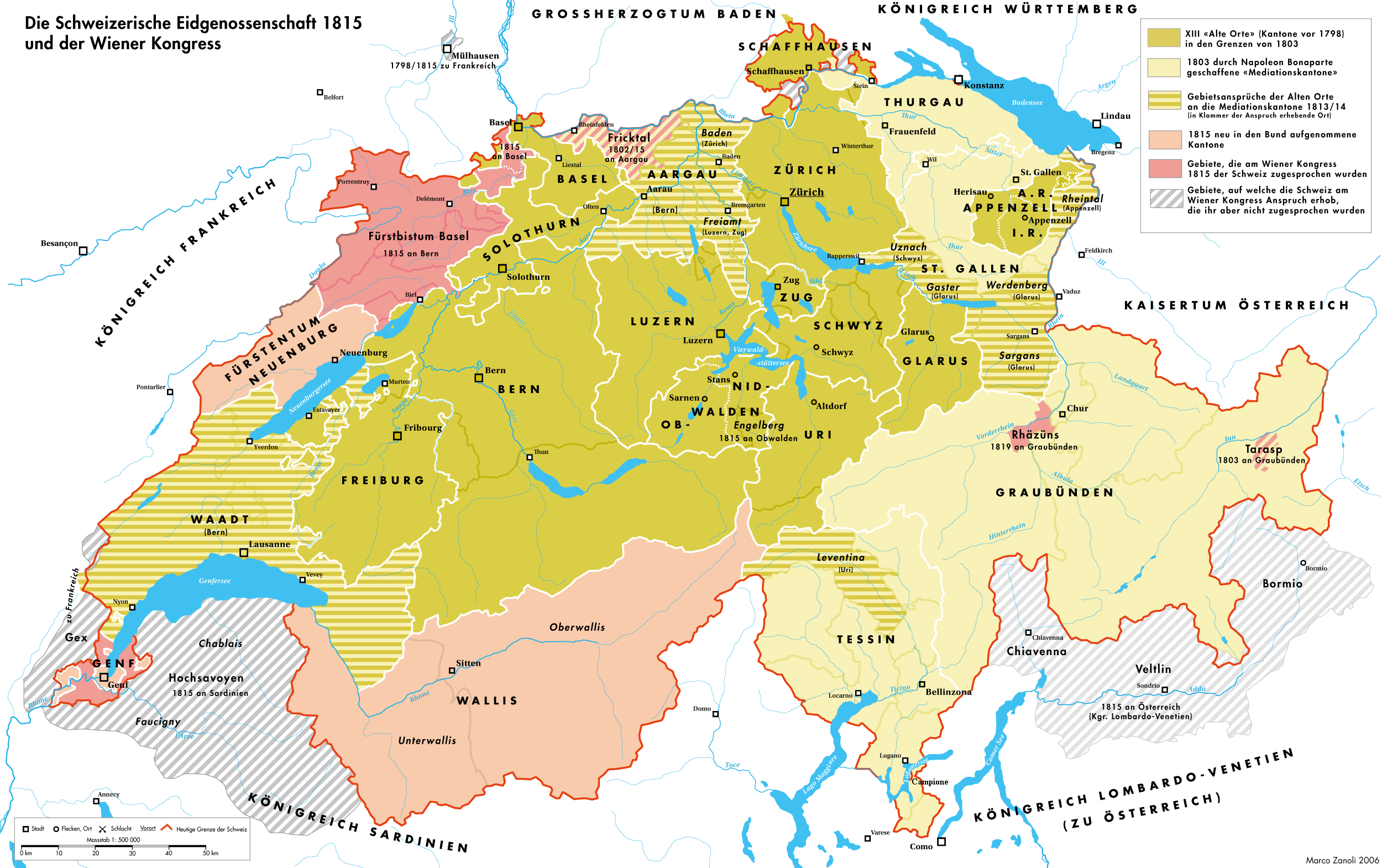
Restoration (Switzerland)
The periods of Restoration and Regeneration in Swiss history lasted from 1814 to 1847. "Restoration" is the period of 1814 to 1830, the restoration of the ''Ancien Régime'' (federalism), reverting the changes imposed by Napoleon Bonaparte on the centralist Helvetic Republic from 1798 and the partial reversion to the old system with the Act of Mediation of 1803. "Regeneration" is the period of 1830 to 1848, when in the wake of the July Revolution the "restored" ''Ancien Régime'' was countered by the liberal movement. In the Protestant cantons, the rural population enforced liberal cantonal constitutions, partly in armed marches on the cities. This resulted in a conservative backlash in the Catholic cantons in the 1830s, raising the conflict to the point of civil war by 1847. Restoration When Napoleon's fall appeared imminent, the Act of Mediation was suspended in late December 1813, and lengthy discussions about future constitutions were initiated in all cantons of Switz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, French Consulate, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 to abolish the Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasion of Old Swiss Confederacy, Switzerland by French troops in 1798, and replace it with the Swiss Confederation (Napoleonic), Swiss Confederation. After the withdrawal of French troops in July 1802, the Republic collapsed (in the ''Stecklikrieg'' civil war). The Act of Mediation was Napoleon's attempt at a compromise between the ''Early Modern Switzerland, Ancien Régime'' and a republic. This intermediary stage of Swiss history lasted until the Restauration (Switzerland), Restoration of 1815. The Act also destroyed the statehood of Tarasp and gave it to Graubunden. End of the Helvetic Republic Following the French Revolutionary Wars: Campaigns of 1798, French invasion of 1798, the decentralized and Aristocracy (government), aristocratic Old Swiss Confederation was replaced with the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bürgergemeinde
The Bürgergemeinde (also Burgergemeinde, Ortsgemeinde, Ortsbürgergemeinde, Tagwen, commune bourgeoise, vischnanca burgaisa; ) is a statutory corporation in public law in Switzerland. It includes all individuals who are citizens of the Bürgergemeinde, usually by having inherited the ''Bourgeoisie'' (citizenship), regardless of where they were born or where they may currently live. Membership of the Bürgergemeinde of a municipality is not to be confused with holding the municipality's citizenship, which, in certain cantons such as Valais, are two distinct legal concepts. Instead of the place of birth, Swiss legal documents, e.g. passports, contain the ''Heimatort'' (place of origin). It is, however, possible for a person to not possess bourgeoisie of the municipality from which they originate; laws relating to these matters vary depending on the canton in which the Bürgergemeinde is located. The ''Bürgergemeinde'' also often holds and administers the common property which had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |