|
Commemorative Coins Of Switzerland
The coins of the Swiss franc are the official coins used in Switzerland and Liechtenstein. The name of the subunit is in French and internationally, in German, in Italian, and in Romansh. There are coins in denominations of 5 centimes, 10 centimes, 20 centimes, franc (50 centimes), 1 franc, 2 francs, and 5 francs. All coins have the legend of either or , the Latin name of the Swiss Confederation, along with the year number. The 5, 10, and 20 centimes coins show a head of Liberty in profile, designed by Karl Schwenzer (1879). The , 1, and 2 francs coins show a standing figure of the national personification ''Helvetia'', designed by Albert Walch (1860). The 5 francs coin on the obverse shows a portrait of an "alpine herdsman" (), designed by Paul Burkhard (1922), and on the reverse the federal coat of arms; [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHF Coins
CHF may refer to: Organizations * Chemical Heritage Foundation, former name of the Science History Institute, an institution that preserves and promotes understanding of the history of science * Chi Heng Foundation, a Hong Kong–based non-governmental organisation dedicated to addressing children impacted by AIDS * Chicago Humanities Festival, a foundation which organizes an annual series of lectures, concerts, and films * Children's Health Fund, a non-profit organization that provides health care to children and families * Children's Hunger Fund, a Christian non-profit organization that empowers local churches to meet the needs of impoverished community members * Commando Helicopter Force, a unit of the Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm * CHF International, former name of Global Communities, an international development and humanitarian aid organization * Community Health Fund, a Healthcare in Tanzania#Community Health Fund (CHF) and Tiba Kwa Kadi (TIKA), Tanzanian health insurance scheme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franc
The franc is any of various units of currency. One franc is typically divided into 100 centimes. The name is said to derive from the Latin inscription ''francorum rex'' (King of the Franks) used on early French coins and until the 18th century, or from the French ''franc'', meaning "frank" (and "free" in certain contexts, such as ''coup franc'', "free kick"). The countries that use francs today include Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and most of Francophone Africa. The Swiss franc is a major world currency today due to the prominence of Swiss financial institutions. Before the introduction of the euro in 1999, francs were also used in France, Belgium and Luxembourg, while Andorra and Monaco accepted the French franc as legal tender ( Monégasque franc). The franc was also used in French colonies including Algeria and Cambodia. The franc is sometimes Italianised or Hispanicised as the ''franco'', for instance in Luccan franco. Origins The franc was originally a French gold coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billon (alloy)
Billon () is an alloy of a precious metal (most commonly silver, but also gold) with a majority base metal content (such as copper). It is used chiefly for making coins, medals, and token coins. The word comes from the French , which means 'log'. History The use of billon coins dates from ancient Greece and continued through the Middle Ages. During the sixth and fifth centuries BC, some cities on Lesbos used coins made of 60% copper and 40% silver. In both ancient times and the Middle Ages, leaner mixtures were adopted, with less than 2% silver content. Billon coins are perhaps best known from the Roman Empire, where progressive debasements of the Roman ''denarius'' and the Roman provincial '' tetradrachm'' in the third century AD led to declining silver and increasing bronze Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10cts1879
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss National Bank
The Swiss National Bank (SNB; ; ; ; ) is the central bank of Switzerland, responsible for the nation's monetary policy and the sole issuer of Swiss franc banknotes. The primary goal of its mandate is to ensure price stability, while taking economic developments into consideration. The SNB is an ''Aktiengesellschaft'' under special regulations and has two head offices, one in Bern and the other in Zürich. History The bank formed as a result of the need for a reduction in the number of commercial banks issuing banknotes, which numbered 53 sometime after 1826. In the 1874 revision of the Federal Constitution it was given the task to oversee laws concerning the issuing of banknotes. In 1891, the Federal Constitution was revised again to entrust the Confederation with sole rights to issue banknotes. 1905 foundation The Swiss National Bank was founded under the law of 6 October 1905 ('the National Bank Act'), which entered into force on 16 January 1906. Business was started on 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banknotes Of The Swiss Franc
Banknotes of the Swiss franc are issued by the Swiss National Bank in denominations of 10, 20, 50, 100, 200 and 1,000 Swiss francs. Between 2016 and 2019, the eighth series, while remaining valid, was being replaced by the ninth series. All banknotes starting from the sixth series are exchangeable; banknotes from the fifth series ceased to be valid and were fully demonetised on 1 May 2000. History The first banknotes in Switzerland were issued in 1825 by the ''Caisse de dépôt'' of the city of Bern. During the 19th century the Cantons of Switzerland, cantons (states) of Switzerland had the right to print their own notes. Following the law of 8 March 1881 the Swiss National Bank had the exclusive right to issue banknotes in Switzerland. Its first notes were issued in 1907. Since then, nine series of Swiss franc notes have been printed, six of which have been completely released for use by the general public, and a new series started being released in 2016. Switzerland is unusu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swissmint
Swissmint is the official mint of the Swiss Confederation. Located in the Swiss capital city Bern, it is responsible for manufacturing Swiss franc coins, both of the currency and bullion variety. Apart from making coins for the government, Swissmint also manufactures medals and commemorative coins for private customers. Status Swissmint is an agency of the Swiss federal government. It is part of the Federal Finance Administration, which in turn belongs to the Federal Department of Finance. Since 1998, the Official Mint of the Confederation operates as an independent business unit under the name ''Swissmint''. As of 2005, Swissmint has 21 employees. Building The mint's building is a heritage site of national significance. It was built in 1903–06 based on designs by Theodor Gohl to replace an older building at the ''Gerberngraben''. The sober, industrial-style yellow brick building is fronted by a Neo-Renaissance façade in marble and sandstone. Notes and references See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a Physical unit, unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth of a kilogram. Originally defined in 1795 as "the absolute Mass versus weight, weight of a volume of pure water equal to Cube (algebra), the cube of the hundredth part of a metre [1 Cubic centimetre, cm3], and at Melting point of water, the temperature of Melting point, melting ice", the defining temperature (0 °C) was later changed to the temperature of maximum density of water (approximately 4 °C). Subsequent redefinitions agree with this original definition to within 30 Parts-per notation, parts per million (0.003%), with the maximum density of water remaining very close to 1 g/cm3, as shown by modern measurements. By the late 19th century, there was an effort to make the Base unit (measurement), base unit the kilogram and the gram a derived unit. In 1960, the new International System of Units defined a '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franc Germinal
The franc (; , ; sign: F or Fr), also commonly distinguished as the (FF), was a currency of France. Between 1360 and 1641, it was the name of coins worth 1 livre tournois and it remained in common parlance as a term for this amount of money. It was reintroduced (in decimal form) in 1795. After two centuries of inflation, it was redenominated in 1960, with each (NF) being worth 100 old francs. The NF designation was continued for a few years before the currency returned to being simply the franc. Many French residents, though, continued to quote prices of especially expensive items in terms of the old franc (equivalent to the new centime), up to and even after the introduction of the euro (for coins and banknotes) in 2002. The French franc was a commonly held international reserve currency of reference in the 19th and 20th centuries. Between 1998 and 2002, the conversion of francs to euros was carried out at a rate of 6.55957 francs to 1 euro. History The French Franc tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland As A Federal State
The rise of Switzerland as a federal state began on 12 September 1848, with the creation of a federal constitution in response to a 27-day civil war, the ''Sonderbundskrieg''. The constitution, which was heavily influenced by the United States Constitution and the ideas of the French Revolution, was modified several times during the following decades and wholly replaced in 1999. The 1848 constitution represented the first time, other than when the short-lived Helvetic Republic had been imposed, that the Swiss had a central government instead of being simply a collection of autonomous cantons bound by treaties. Sonderbund War In 1847, the period of Swiss history known as Restoration ended with a war between the conservative Roman Catholic and the liberal Protestant cantons (the ''Sonderbundskrieg''). The conflict between the Catholic and Protestant cantons had existed since the Reformation; in the 19th century the Protestant population had a majority. The ''Sonderbund'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schweizer Franken 1850
Schweizer (German meaning 'Swiss') may refer to: People * Bernard Schweizer (born 1962), American professor of English * Brandun Schweizer, American politician * David Schweizer (director) (1949 or 1950–2024), American theatre director * Eduard Schweizer (1913–2006), Swiss New Testament scholar * Irène Schweizer (born 1941), Swiss Jazz pianist * J. Otto Schweizer (1863–1955) Swiss-American sculptor * Julián Schweizer (born 1998), Uruguayan surfer * Karissa Schweizer (born 1996), American long-distance runner * Kaspar Gottfried Schweizer (1816–1873), Swiss astronomer * Katja Schweizer (née Weisser) (born 1978), German curler and coach * Matthias Eduard Schweizer (1818–1860), chemist, inventor of the Schweizer's reagent * Peter Schweizer (born 1964), American author * Schweizer brothers (Paul, William, and Ernest), brothers and founders of Schweizer Aircraft Other uses * Schweizer (chicken) * Schweizer Aircraft, an American producer of sailplanes and helicopters, owne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
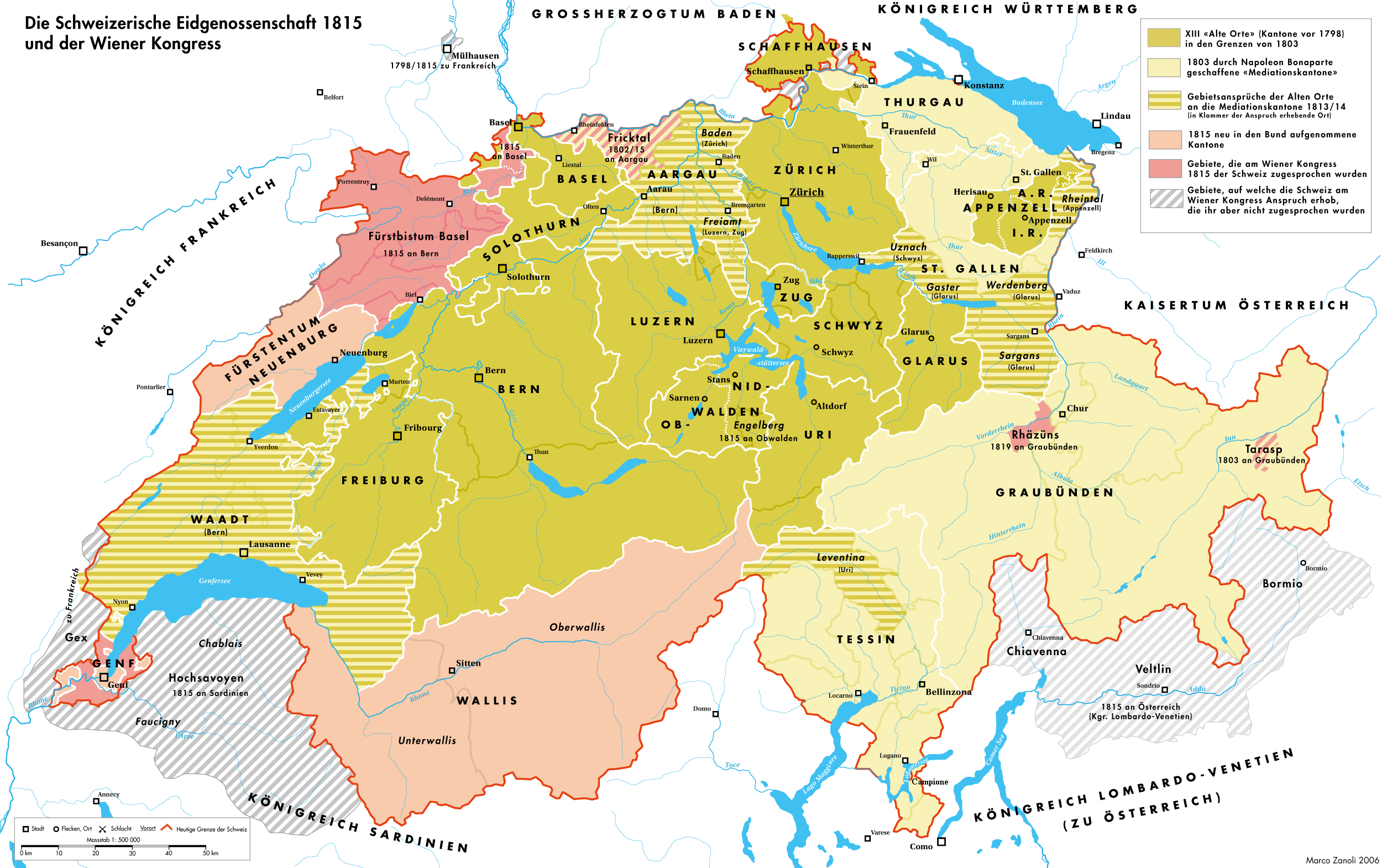
Restoration And Regeneration In Switzerland
The periods of Restoration and Regeneration in Swiss history lasted from 1814 to 1847. "Restoration" is the period of 1814 to 1830, the restoration of the ''Ancien Régime'' (federalism), reverting the changes imposed by Napoleon Bonaparte on the centralist Helvetic Republic from 1798 and the partial reversion to the old system with the Act of Mediation of 1803. "Regeneration" is the period of 1830 to 1848, when in the wake of the July Revolution the "restored" ''Ancien Régime'' was countered by the liberal movement. In the Protestant cantons, the rural population enforced liberal cantonal constitutions, partly in armed marches on the cities. This resulted in a conservative backlash in the Catholic cantons in the 1830s, raising the conflict to the point of civil war by 1847. Restoration When Napoleon's fall appeared imminent, the Act of Mediation was suspended in late December 1813, and lengthy discussions about future constitutions were initiated in all cantons of Switzer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |