|
Color Blind Glasses
Color blind glasses or color correcting lenses are light filters, usually in the form of glasses or contact lenses, that attempt to alleviate color blindness, by bringing deficient color vision closer to normal color vision or to make certain Color blindness#Color tasks, color tasks easier to accomplish. Despite its Viral video, viral status, the academic literature is generally skeptical of the efficacy of color correcting lenses. Color blindness Color blindness (color vision deficiency) is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. It can impair daily Color blindness#Color tasks, color tasks such as selecting ripe fruit or choosing clothing, as well as safety-related tasks such as interpreting traffic lights. While the disability of color blindness is considered minor, the use of color in safety systems excludes the color blind from many occupations. Screening for color blindness in these occupations is accomplished with color vision tests, often the Ishihara t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses (American English), spectacles (Commonwealth English), or colloquially as specs, are vision eyewear with clear or tinted lenses mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically utilizing a bridge over the nose and hinged arms, known as temples or temple pieces, that rest over the ears for support. Glasses are typically used for vision correction, such as with reading glasses and glasses used for nearsightedness; however, without the specialized lenses, they are sometimes used for cosmetic purposes. Safety glasses are eye protection, a form of personal protective equipment ( PPE) that are worn by workers around their eyes for protection. Safety glasses act as a shield to protect the eyes from any type of foreign debris that may cause irritation or injury; these glasses may have protection on the sides of the eyes as well as in the lenses. Some types of safety glasses are used to protect against visible and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamerism (color)
In colorimetry, metamerism is a perceived matching of colors with different (nonmatching) spectral power distributions. Colors that match this way are called metamers. A spectral power distribution describes the proportion of total light given off (emitted, transmitted, or reflected) by a color sample at each visible wavelength; it defines the complete information about the light coming from the sample. However, the human eye contains only three color receptors (three types of cone cells), which means that all colors are reduced to three sensory quantities, called the tristimulus values. Metamerism occurs because each type of cone responds to the cumulative energy from a broad range of wavelengths, so that different combinations of light across all wavelengths can produce an equivalent receptor response and the same tristimulus values or color sensation. In color science, the set of sensory spectral sensitivity curves is numerically represented by color matching functions. Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmittance EnChroma
Electromagnetic radiation can be affected in several ways by the medium in which it propagates. It can be scattered, absorbed, and reflected and refracted at discontinuities in the medium. This page is an overview of the last 3. The transmittance of a material and any surfaces is its effectiveness in transmitting radiant energy; the fraction of the initial (incident) radiation which propagates to a location of interest (often an observation location). This may be described by the transmission coefficient. Surface Transmittance Hemispherical transmittance Hemispherical transmittance of a surface, denoted ''T'', is defined as :T = \frac, where *Φet is the radiant flux ''transmitted'' by that surface into the hemisphere on the opposite side from the incident radiation; *Φei is the radiant flux received by that surface. Hemispheric transmittance may be calculated as an integral over the directional transmittance described below. Spectral hemispherical transmittance Spect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FALANT
The Farnsworth Lantern Test, or FALANT, is a color vision test originally developed specifically to screen sailors for tasks requiring color vision, such as identifying signal lights at night. It screens for red-green deficiencies, but not the much rarer blue color deficiency. History The test was developed by Dr. Dean Farnsworth (Commander, United States Navy) while stationed at the Naval Submarine Research Laboratory in New London, Connecticut during World War II. After its adoption by the United States Navy in 1954 as the standard color vision test for sailors aboard ship, it has additionally been used to screen flying personnel. Test procedure The test consists of showing a pair of vertically oriented lights consisting of combinations of either red, green or yellow-white. The test subject is asked to identify the two colors (some of which are identical). Nine color pairs are administered during the test, beginning with a red/green combination, to allow the patient to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
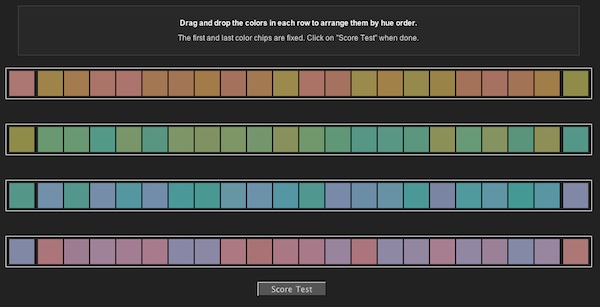
Farnsworth–Munsell 100 Hue Test
The Farnsworth–Munsell 100 Hue Color Vision test is a color vision test often used to test for color blindness. The system was developed by Dean Farnsworth in the 1940s and it tests the ability to isolate and arrange minute differences in various color targets with constant lightness, value and colorfulness, chroma that cover all the visual hues described by the Munsell color system. There are several variations of the test, one featuring 100 color hues and one featuring 15 color hues. Originally taken in an analog environment with physical hue tiles, the test is now taken from computer consoles. An accurate quantification of color vision accuracy is particularly important to designers, photographers and colorists, who all rely on accurate color vision to produce quality content. Vision tests 100 hue test The most common form of the Farnsworth–Munsell 100 Hue Color Vision Test contains four distinct rows of similar color hues, each containing 25 distinct variations of each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most prominently, they are found in photoreceptor cells of the retina. Five classical groups of opsins are involved in Visual perception, vision, mediating the conversion of a photon of light into an electrochemical signal, the first step in the Visual phototransduction, visual transduction cascade. Another opsin found in the mammalian retina, melanopsin, is involved in circadian rhythms and Pupillary light reflex, pupillary reflex but not in vision. Humans have in total nine opsins. Beside vision and light perception, opsins may also sense temperature, sound, or chemicals. Structure and function Animal opsins detect light and are the molecules that allow us to see. Opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which are chemoreceptors and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalous Trichromacy
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color perception. Color blindness is usually a sex-linked inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic condition called congenital red–green color blindness (including protan and deutan types), which affects ''up to'' 1 in 12 males (8%) and 1 in 200 females (0.5%). The condition is more prevalent in males, because the opsin genes responsible are located on the X chromosome. Rarer genetic conditions causing color blindness include congenital blue–yellow color blindness (tritan type), blue cone monochromacy, and achromatopsia. Color blindness can also result from physical or chemical damage to the eye, the optic nerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Sensitivity
Spectral sensitivity is the relative efficiency of detection, of light or other signal, as a function of the frequency or wavelength of the signal. In visual neuroscience, spectral sensitivity is used to describe the different characteristics of the photopigments in the rod cells and cone cells in the retina of the eye. It is known that the rod cells are more suited to scotopic vision and cone cells to photopic vision, and that they differ in their sensitivity to different wavelengths of light. It has been established that the maximum spectral sensitivity of the human eye under daylight conditions is at a wavelength of 555 nm, while at night the peak shifts to 507 nm. In photography, film and sensors are often described in terms of their spectral sensitivity, to supplement their characteristic curves that describe their responsivity. A database of camera spectral sensitivity is created and its space analyzed. For X-ray films, the spectral sensitivity is chosen t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmittance
Electromagnetic radiation can be affected in several ways by the medium in which it propagates. It can be Scattering, scattered, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed, and Fresnel equations, reflected and refracted at discontinuities in the medium. This page is an overview of the last 3. The transmittance of a material and any surfaces is its effectiveness in transmitting radiant energy; the fraction of the initial (incident) radiation which propagates to a location of interest (often an observation location). This may be described by the transmission coefficient. Surface Transmittance Hemispherical transmittance Hemispherical transmittance of a surface, denoted ''T'', is defined as :T = \frac, where *Φet is the radiant flux ''transmitted'' by that surface into the hemisphere on the opposite side from the incident radiation; *Φei is the radiant flux received by that surface. Hemispheric transmittance may be calculated as an integral over the directional trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmittance Tinted Lenses
Electromagnetic radiation can be affected in several ways by the medium in which it propagates. It can be scattered, absorbed, and reflected and refracted at discontinuities in the medium. This page is an overview of the last 3. The transmittance of a material and any surfaces is its effectiveness in transmitting radiant energy; the fraction of the initial (incident) radiation which propagates to a location of interest (often an observation location). This may be described by the transmission coefficient. Surface Transmittance Hemispherical transmittance Hemispherical transmittance of a surface, denoted ''T'', is defined as :T = \frac, where *Φet is the radiant flux ''transmitted'' by that surface into the hemisphere on the opposite side from the incident radiation; *Φei is the radiant flux received by that surface. Hemispheric transmittance may be calculated as an integral over the directional transmittance described below. Spectral hemispherical transmittance Spect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Perception
Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions. Depth sensation is the corresponding term for non-human animals, since although it is known that they can sense the distance of an object, it is not known whether they perceive it in the same way that humans do. Depth perception arises from a variety of depth cues. These are typically classified into binocular cues and monocular cues. Binocular cues are based on the receipt of sensory information in three dimensions from both eyes and monocular cues can be observed with just one eye. Binocular cues include retinal disparity, which exploits parallax and vergence. Stereopsis is made possible with binocular vision. Monocular cues include relative size (distant objects subtend smaller visual angles than near objects), texture gradient, occlusion, linear perspective, contrast differences, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulfrich Effect
The Pulfrich effect is a psychophysical percept wherein lateral motion of an object in the field of view is interpreted by the visual cortex as having a depth component, due to a relative difference in signal timings between the two eyes. Overview The effect is generally induced by placing a dark filter over one eye but can also occur spontaneously in several eye diseases such as cataract, optic neuritis, or multiple sclerosis. In such cases, symptoms such as difficulties judging the paths of oncoming cars have been reported. The phenomenon is named for German physicist Carl Pulfrich, who first described it in 1922. Carl Pulfrich was the brother-in-law of Heinrich Hertz. The effect has been exploited as the basis for some television, film, and game 3D presentations. Demonstration In the classic Pulfrich effect experiment, a subject views a pendulum swinging in a plane perpendicular to the observer's line of sight. When a neutral density filter (a darkened lens—typically gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |