|
Coal Power In China
In the People's Republic of China, electricity generated from coal represents over half of all electricity generated in the country. It is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions by China. China's installed coal-based power generation capacity was 1080 GW in 2021, about half the total installed capacity of power stations in China. Coal-fired power stations generated 57% of electricity in 2020. Over half the world's coal-fired power is generated in China. 5 GW of new coal power was approved in the first half of 2021. Quotas force utility companies to buy coal power over cheaper renewable power. China is the largest producer and consumer of coal in the world and is the largest user of coal-derived electricity. Despite China (like other G20 countries) pledging in 2009 to end inefficient fossil fuel subsidies, there are direct subsidies and the main way coal power is favored is by the rules guaranteeing its purchase – so dispatch order is not merit order. The think tank C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (also called the Paris Accords or Paris Climate Accords) is an international treaty on climate change that was signed in 2016. The treaty covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was negotiated by 196 parties at the 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference near Paris, France. As of February 2023, 195 members of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are parties to the agreement. Of the three UNFCCC member states which have not ratified the agreement, the only major emitter is Iran. The United States, the second largest emitter, withdrew from the agreement in 2020, rejoined in 2021, and announced its withdrawal again in 2025. The Paris Agreement has a long-term temperature goal which is to keep the rise in global surface temperature to well below above pre-industrial levels. The treaty also states that preferably the limit of the increase should only be . These limits are defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia–China Relations
Consular relations between China and Australia were first established in 1909, and diplomatic relations were established in 1941. Australia continued to recognise the Republic of China (ROC) government after it lost the Chinese Civil War and retreated to Taiwan in 1949, but switched recognition to the People's Republic of China (PRC) on 21 December 1972. Chinese Australians have been a significant minority group in the country since the Qing dynasty. The relationship between China and Australia has grown considerably over the years. They have strong political, economic, and cultural ties, including through multilateral organizations such as Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC, East Asia Summit and the G20. In 2023, Australia expressed its tentative support for China's application for membership of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership, CPTPP. China is Australia's List of the largest trading partners of Australia, largest two-way trading partn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Policy Of China
China is the world's largest exporter, a position it has maintained continuously since 2010. It is the largest trading partner of over 120 countries, as of at least early 2024. As a member of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), China is part of the world's largest trading bloc. China began promoting overseas investment through the Go Out policy, which Jiang Zemin formally announced as a national strategy in 2000. After its 2001 entry into the World Trade Organization, China focused on export-led growth and became a major link in global supply chains. Through this process, China developed large trade surpluses and foreign currency reserves. History In 1999, the Chinese government began promoting investment abroad through the Go Out policy 2006年03月15日 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Development And Reform Commission
The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) is the third-ranked executive department of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, which functions as a macroeconomic management agency. Established as the State Planning Commission, the NDRC has broad administrative and planning control over the economy of mainland China, and has a reputation of being the "mini-state council". History The body was first established in November 1952 as the State Planning Commission of the Central People's Government. It was modeled after Gosplan. Gao Gang was its first director. In 1954, it was transformed to the State Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. The NDRC's functions are to study and formulate policies for economic and social development, maintain the balance of economic development, and to guide restructuring of the economic system of mainland China. In March 1998, the commission was renamed into the State Development Planning Commission. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas-fired Power Plant
A gas-fired power plant, sometimes referred to as gas-fired power station, natural gas power plant, or methane gas power plant, is a thermal power station that burns natural gas to generate electricity. Gas-fired power plants generate almost a quarter of world electricity and are significant sources of greenhouse gas emissions. However, they can provide seasonal, dispatchable energy generation to compensate for variable renewable energy deficits, where hydropower or interconnectors are not available. In the early 2020s batteries became competitive with gas peaker plants. Basic concepts: heat into mechanical energy into electrical energy A gas-fired power plant is a type of fossil fuel power station in which chemical energy stored in natural gas, which is mainly methane, is converted successively into: thermal energy, mechanical energy and, finally, electrical energy. Although they cannot exceed the Carnot cycle limit for conversion of heat energy into useful work, the exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peaking Power Plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand. Although historically peaking power plants were frequently used in conjunction with coal baseload plants, peaking plants are now used less commonly. Combined cycle gas turbine plants have two or more cycles, the first of which is very similar to a peaking plant, with the second running on the waste heat of the first. That type of plant is often capable of rapidly starting up, albeit at reduced efficiency, and then over some hours transitioning to a more efficient baseload generation mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
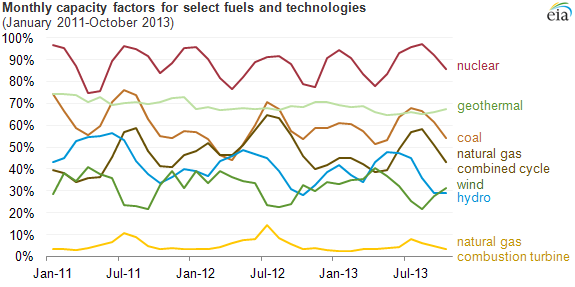
Capacity Factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind, the sun or hydro-electric installations. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production. The actual energy output during that period and the capacity factor vary greatly depending on a range of factors. The capacity factor can never exceed the availability factor, or uptime during the period. Uptime can be reduced due to, for example, reliability issues and maintenance, schedul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stranded Asset
Stranded assets are "assets that have suffered from unanticipated or premature write-downs, devaluations or conversion to liabilities". Stranded assets can be caused by a variety of factors and are a phenomenon inherent in the 'creative destruction' of economic growth, transformation and innovation; as such they pose risks to individuals and firms and may have systemic implications. Climate change is expected to cause a significant increase in stranded assets for carbon-intensive industries and investors, with a potential ripple effect throughout the world economy. The term is important to financial risk management in order to avoid economic loss after an asset has been converted to a liability. Accountants have measures to deal with the impairment of assets (e.g. IAS 16) which seek to ensure that an entity's assets are not carried at more than their recoverable amount. In this context, stranded assets are also defined as an asset that has become obsolete or non-performing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy And Climate Intelligence Unit
The Energy and Climate Intelligence Unit (ECIU) is a non-profit organisation based in the UK conducting independent research and analysis on energy and climate issues. The organisation was incorporated in 2014. According to their own about page, they are a "a non-profit organisation that supports informed debate on energy and climate change issues in the UK", supporting journalists, parliamentarians and other communicators with accurate briefings on key issues, and work with individuals and organisations that have interesting stories to tell, helping them connect to the national conversation. The ECIU has been referenced by British and global press when citing data about climate change. The organisation was founded by former BBC environment correspondent Richard Black. ECIU's Advisory Board includes climate scientists, energy policy experts, economists, MPs and peers. The Unit is solely funded by philanthropic foundations; they acknowledge support from the European Climate Foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |