|
Climate Change (general Concept)
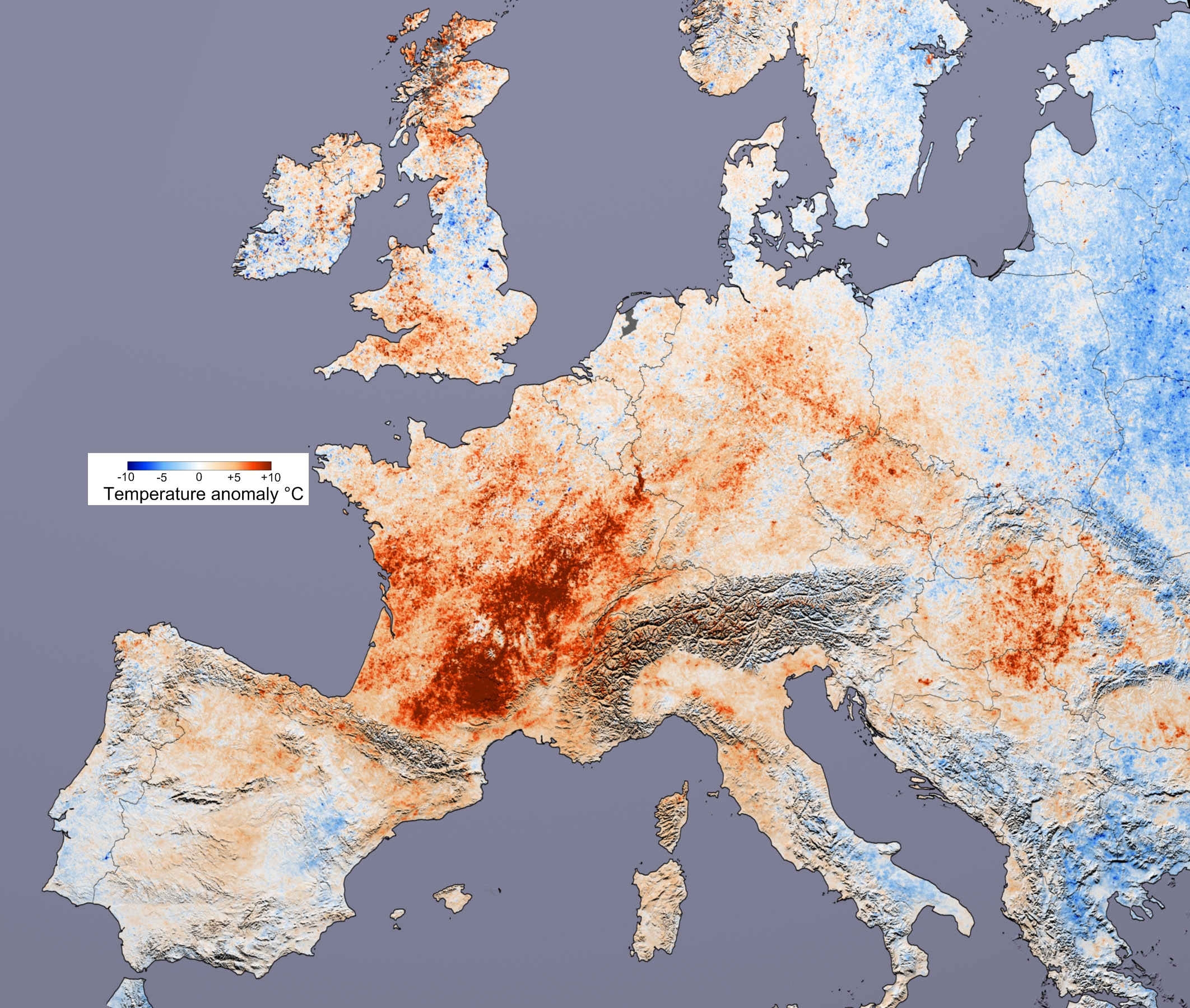
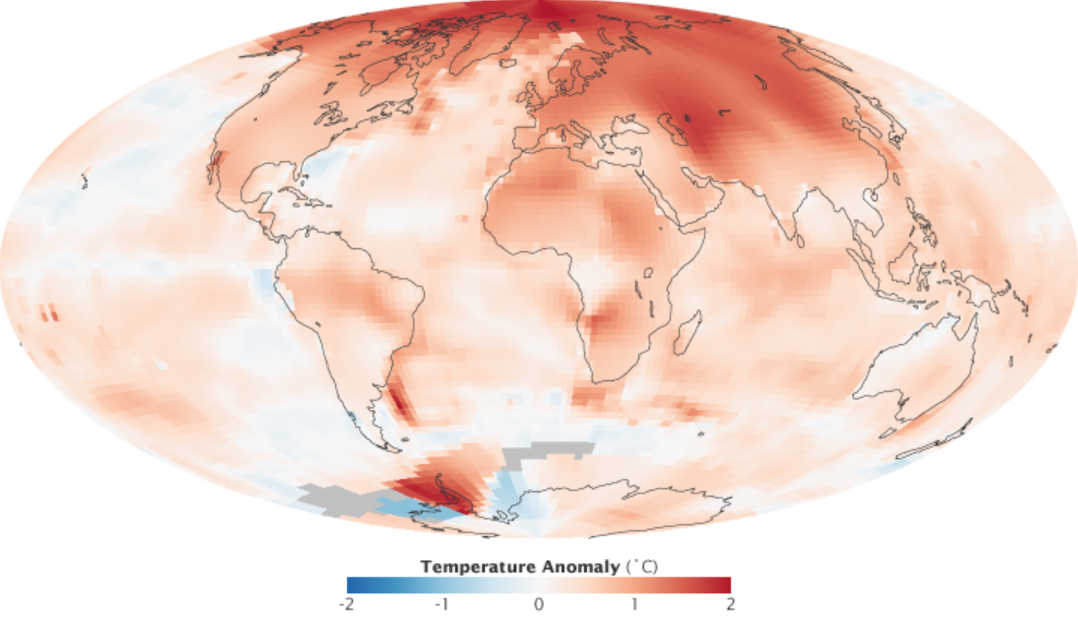
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Air Temperature
Atmospheric temperature is a measure of temperature at different levels of the Earth's atmosphere. It is governed by many factors, including insolation, incoming solar radiation, humidity, and altitude. The abbreviation MAAT is often used for Mean Annual Air Temperature of a geographical location. Near-surface air temperature The temperature of the air near the surface of the Earth is measured at meteorological observatories and weather stations, usually using thermometers placed in a shelter such as a Stevenson screen—a standardized, well-ventilated, white-painted instrument shelter. The thermometers should be positioned 1.25–2 m above the ground. Details of this setup are defined by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). A true daily mean could be obtained from a continuously recording thermograph. Commonly, it is approximated by the mean of discrete readings (e.g. 24 hourly readings, four 6-hourly readings, etc.) or by the mean of the daily minimum and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically perceived by humans as warmth) and ultraviolet (which can have physiological effects such as sunburn) lights. However, according to the American Meteorological Society, there are "conflicting conventions as to whether all three [...] are referred to as light, or whether that term should only be applied to the visible portion of the spectrum." Upon reaching the Earth, sunlight is light scattering by particles, scattered and attenuation, filtered through the atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon. When direct solar radiation is not blocked by clouds, it is experienced as sunshine, a combination of bright light and radiant heat (atmospheric). When cloud cover, blocked by clouds or dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montane Ecosystems
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures lapse rate, fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands and shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply. Life zones As elevation increases, the alpine climate, climate becomes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Weather
Extreme weather includes unexpected, unusual, severe weather, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Extreme events are based on a location's recorded weather history. The main types of extreme weather include heat waves, cold waves, droughts, and heavy precipitation or storm events, such as tropical cyclones. Extreme weather can have various effects, from natural hazards such as floods and landslides to social costs on human health and the economy. Severe weather is a particular type of extreme weather which poses risks to life and property. Weather patterns in a given region vary with time, and so extreme weather can be attributed, at least in part, to the natural Climate variability and change, climate variability that exists on Earth. For example, the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) or the North Atlantic oscillation (NAO) are climate phenomena that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclones And Climate Change
Climate change affects tropical cyclones in a variety of ways: an intensification of rainfall and wind speed, an increase in the frequency of very intense storms and a poleward extension of where the cyclones reach maximum Intensity mapping, intensity are among the consequences of human-induced climate change.IPCC, 2021Summary for Policymakers InClimate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M. I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J. B. R. Matthews, T. K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York City, US, pp. 8–9; 15–16, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.001. Tropical cyclones use warm, moist air as their source of energy or ''fuel''. As climate change is Ocean heat conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Sea Ice Decline
Sea ice in the Arctic region has declined in recent decades in area and volume due to climate change. It has been melting more in summer than it refreezes in winter. Global warming, caused by Radiative forcing#Forcing due to changes in atmospheric gases, greenhouse gas forcing is responsible for the decline in Arctic sea ice. The decline of sea ice in the Arctic has been accelerating during the early twenty-first century, with a decline rate of 4.7% per decade (it has declined over 50% since the first satellite records). Summertime sea ice will likely cease to exist sometime during the 21st century. The region is at its warmest in at least 4,000 years. Furthermore, the Arctic-wide melt season has lengthened at a rate of five days per decade (from 1979 to 2013), dominated by a later autumn freeze-up. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (2021) stated that Arctic sea ice area will likely drop below 1 million km2 in at least some Septembers before 2050.Fox-Kemper, B., H.T. Hewitt, C. Xia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retreat Of Glaciers Since 1850
The retreat of glaciers since 1850 is a well-documented effects of climate change, effect of climate change. The retreat of Mountain glacier, mountain glaciers provides evidence for the Instrumental temperature record, rise in global temperatures since the late 19th century. Examples include mountain glaciers in western North America, Asia, Alps, the Alps in central Europe, and tropical and subtropical regions of South America and Africa. Since glacial mass is affected by long-term climatic changes, e.g. Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, Temperature, mean temperature, and cloud cover, glacial mass changes are one of the most sensitive indicators of climate change. The retreat of glaciers is also a major reason for sea level rise. Excluding peripheral glaciers of Ice sheet, ice sheets, the total cumulated global glacial losses over the 26 years from 1993 to 2018 were likely 5500 gigatons, or 210 gigatons per year.Fox-Kemper, B., H.T. Hewitt, C. Xiao, G. Aðalgeirsdóttir, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
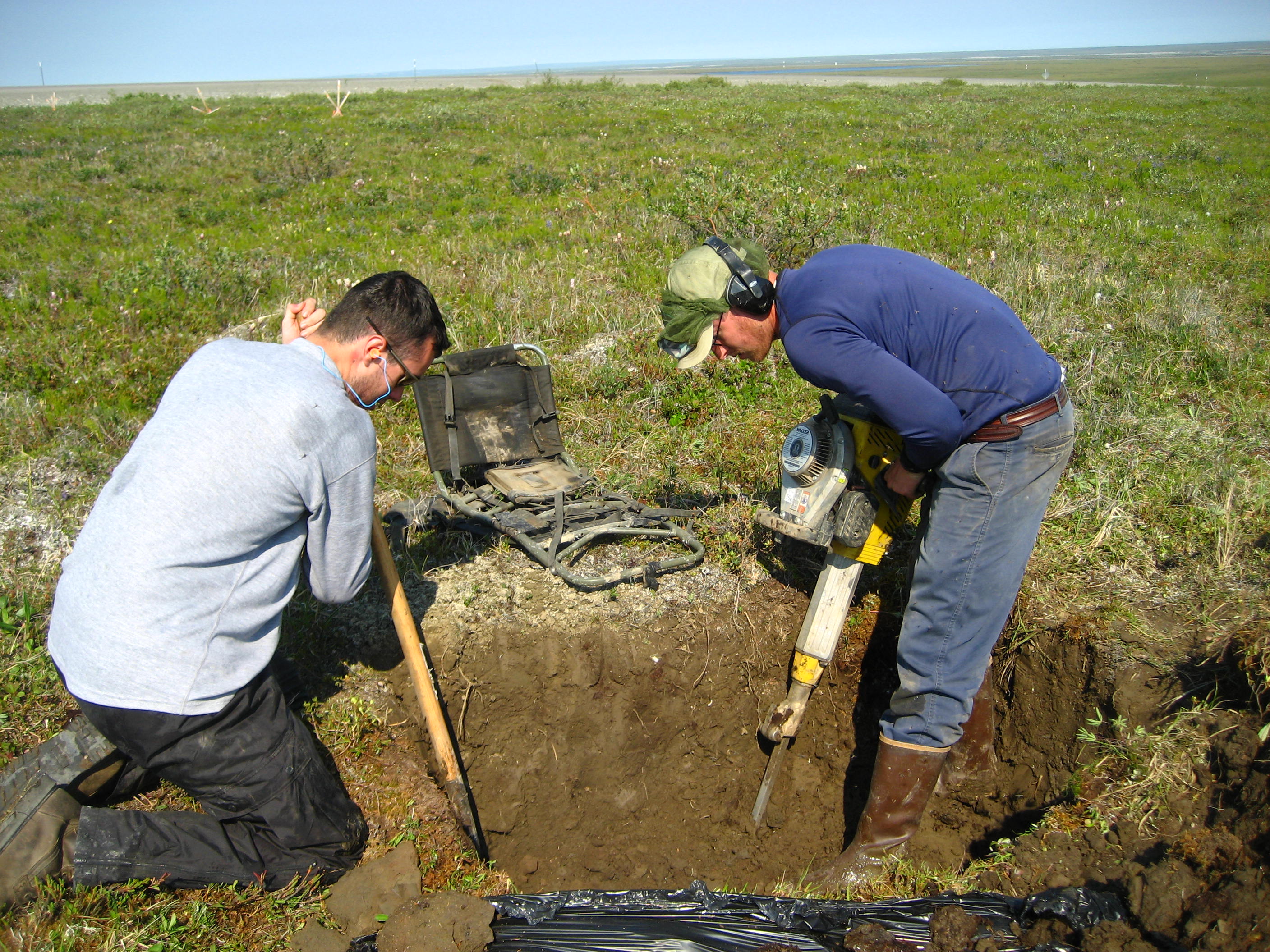
Permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below a meter (3 ft), the deepest is greater than . Similarly, the area of individual permafrost zones may be limited to narrow mountain summits or extend across vast Arctic regions. The ground beneath glaciers and ice sheets is not usually defined as permafrost, so on land, permafrost is generally located beneath a so-called active layer of soil which freezes and thaws depending on the season. Around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface is underlain by permafrost, covering a total area of around . This includes large areas of Alaska, Canada, Greenland, and Siberia. It is also located in high mountain regions, with the Tibetan Plateau being a prominent example. Only a minority of permafrost exists in the Southern Hemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Amplification
Polar amplification is the phenomenon that any change in the net radiation balance (for example greenhouse intensification) tends to produce a larger change in temperature near the poles than in the planetary average. This is commonly referred to as the ratio of polar warming to tropical warming. On a planet with an atmosphere that can restrict emission of longwave radiation to space (a greenhouse effect), surface temperatures will be warmer than a simple planetary equilibrium temperature calculation would predict. Where the atmosphere or an extensive ocean is able to transport heat polewards, the poles will be warmer and equatorial regions cooler than their local net radiation balances would predict. The poles will experience the most cooling when the global-mean temperature is lower relative to a reference climate; alternatively, the poles will experience the greatest warming when the global-mean temperature is higher. In the extreme, the planet Venus is thought to have experienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a bushfire (Bushfires in Australia, in Australia), desert fire, grass fire, hill fire, Peat#Peat fires, peat fire, prairie fire, vegetation fire, or veld fire. Some natural forest ecosystems Fire ecology, depend on wildfire. Modern forest management often engages in prescribed burns to mitigate fire risk and promote natural forest cycles. However, controlled burns can turn into wildfires by mistake. Wildfires can be classified by cause of ignition, physical properties, combustible material present, and the effect of weather on the fire. Wildfire severity results from a combination of factors such as available fuels, physical setting, and weather. Climatic cycles with wet periods that create substantial fuels, followed by drought and heat, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Wave
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather generally considered to be at least ''five consecutive days''. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and to normal temperatures for the season. The main difficulties with this broad definition emerge when one must quantify what the 'normal' temperature state is, and what the spatial extent of the event may or must be. Temperatures that humans from a hotter climate consider normal can be regarded as a heat wave in a cooler area. This would be the case if the warm temperatures are outside the normal climate pattern for that area. Heat waves have become more frequent, and more intense over land, across almost every area on Earth since the 1950s, the increase in frequency and duration being caused by climate change. Heat waves form when a high-pressure area in the upper atmosphere strengthens and remains over a region for several days up to seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities. The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This is driven by a number of factors, alone or in combination, such as drought, climatic shifts, tillage for agriculture, overgrazing and deforestation for fuel or construction materials. Though vegetation plays a major role in determining the Soil biology, biological composition of the soil, studies have shown that, in many environments, the rate of erosion and runoff decreases exponentially with increased vegetation cover. Unprotected, dry soil surfaces blow away with the wind or are washed away by flash floods, leaving infertile lower soil layers that bake in the sun and become an unproductive hardpan. At least 90% of the inhabitants of drylands live in Developing country, developing countries, where they also suffer from poor economic and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |