|
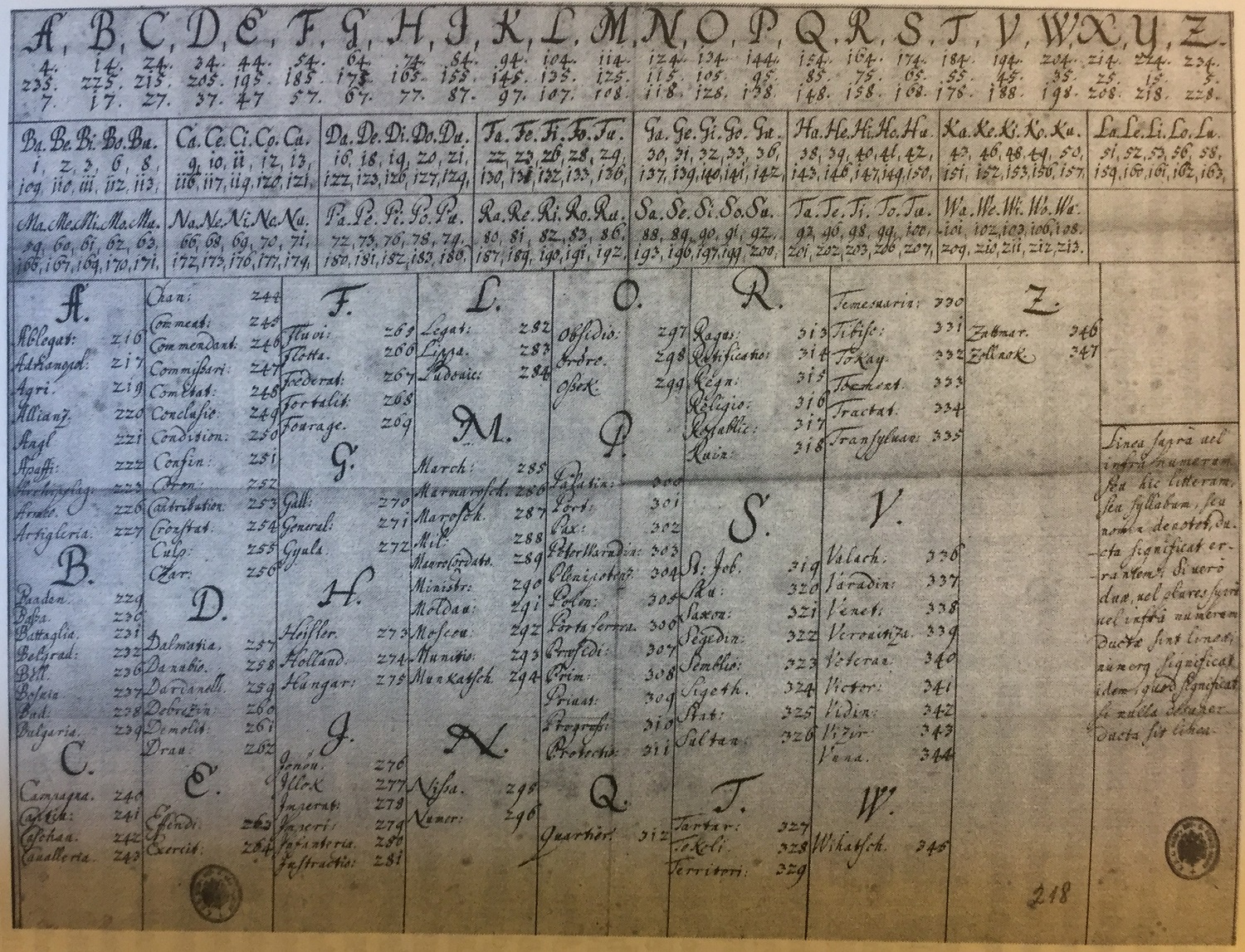
Classical Cipher
In cryptography, a classical cipher is a type of cipher that was used historically but for the most part, has fallen into disuse. In contrast to modern cryptographic algorithms, most classical ciphers can be practically computed and solved by hand. However, they are also usually very simple to break with modern technology. The term includes the simple systems used since Greek and Roman times, the elaborate Renaissance ciphers, World War II cryptography such as the Enigma machine and beyond. In contrast, modern strong cryptography relies on new algorithms and computers developed since the 1970s. Types of classical ciphers Classical ciphers are often divided into ''transposition ciphers'' and ''substitution ciphers'', but there are also '' concealment ciphers''. Substitution ciphers In a substitution cipher, letters, or groups of letters, are systematically replaced throughout the message for other letters, groups of letters, or symbols. A well-known example of a substitution c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logy, -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of Adversary (cryptography), adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing Communication protocol, protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security (confidentiality, data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, Smart card#EMV, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, password, computer passwords, and military communications. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Cipher
In cryptography, a product cipher combines two or more transformations in a manner intending that the resulting cipher is more secure than the individual components to make it resistant to cryptanalysis.Handbook of Applied Cryptography by Alfred J. Menezes, Paul C. van Oorschot, Scott A. Vanstone. Fifth Printing (August 2001) page 251. The product cipher combines a sequence of simple transformations such as substitution (S-box), permutation (P-box), and modular arithmetic. The concept of product ciphers is due to Claude Shannon, who presented the idea in his foundational paper, ''Communication Theory of Secrecy Systems''. A particular product cipher design where all the constituting transformation functions have the same structure is called an iterative cipher with the term " rounds" applied to the functions themselves. For transformation involving reasonable number of n message symbols, both of the foregoing cipher systems (the S-box and P-box) are by themselves wanting. Shannon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Known-plaintext Attack
The known-plaintext attack (KPA) is an attack model for cryptanalysis where the attacker has access to both the plaintext (called a crib) and its encrypted version (ciphertext). These can be used to reveal secret keys and code books. The term "crib" originated at Bletchley Park, the British World War II decryption operation, where it was defined as: History The usage "crib" was adapted from a slang term referring to cheating (e.g., "I cribbed my answer from your test paper"). A "crib" originally was a literal or interlinear translation of a foreign-language text—usually a Latin or Greek text—that students might be assigned to translate from the original language. The idea behind a crib is that cryptologists were looking at incomprehensible ciphertext, but if they had a clue about some word or phrase that might be expected to be in the ciphertext, they would have a "wedge," a test to break into it. If their otherwise random attacks on the cipher managed to sometimes produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasiski Examination
In cryptanalysis, Kasiski examination (also known as Kasiski's test or Kasiski's method) is a method of attacking polyalphabetic substitution ciphers, such as the Vigenère cipher. It was first published by Friedrich Kasiski in 1863, but seems to have been independently discovered by Charles Babbage as early as 1846. How it works In polyalphabetic substitution ciphers where the substitution alphabets are chosen by the use of a keyword, the Kasiski examination allows a cryptanalyst to deduce the length of the keyword. Once the length of the keyword is discovered, the cryptanalyst lines up the ciphertext in ''n'' columns, where ''n'' is the length of the keyword. Then each column can be treated as the ciphertext of a monoalphabetic substitution cipher. As such, each column can be attacked with frequency analysis. Similarly, where a rotor stream cipher machine has been used, this method may allow the deduction of the length of individual rotors. The Kasiski examination involves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vigenère Cipher
The Vigenère cipher () is a method of encryption, encrypting alphabetic text where each letter of the plaintext is encoded with a different Caesar cipher, whose increment is determined by the corresponding letter of another text, the key (cryptography), key. For example, if the plaintext is attacking tonight and the key is oculorhinolaryngology, then *the first letter of the plaintext, a, is shifted by 14 positions in the alphabet (because the first letter of the key, o, is the 14th letter of the alphabet, counting from zero), yielding o; *the second letter, t, is shifted by 2 (because the second letter of the key, c, is the 2nd letter of the alphabet, counting from zero) yielding v; *the third letter, t, is shifted by 20 (u), yielding n, with wrap-around; and so on. It is important to note that traditionally spaces and punctuation are removed prior to encryption and reintroduced afterwards. * In this example the tenth letter of the plaintext t is shifted by 14 position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Analysis
In cryptanalysis, frequency analysis (also known as counting letters) is the study of the frequency of letters or groups of letters in a ciphertext. The method is used as an aid to breaking classical ciphers. Frequency analysis is based on the fact that, in any given stretch of written language, certain letters and combinations of letters occur with varying frequencies. Moreover, there is a characteristic distribution of letters that is roughly the same for almost all samples of that language. For instance, given a section of English language, , , and are the most common, while , , and are rare. Likewise, , , , and are the most common pairs of letters (termed ''bigrams'' or ''digraphs''), and , , , and are the most common repeats. The nonsense phrase " ETAOIN SHRDLU" represents the 12 most frequent letters in typical English language text. In some ciphers, such properties of the natural language plaintext are preserved in the ciphertext, and these patterns have the poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substitution Ciphers
In cryptography, a substitution cipher is a method of encrypting in which units of plaintext are replaced with the ciphertext, in a defined manner, with the help of a key; the "units" may be single letters (the most common), pairs of letters, triplets of letters, mixtures of the above, and so forth. The receiver deciphers the text by performing the inverse substitution process to extract the original message. Substitution ciphers can be compared with transposition ciphers. In a transposition cipher, the units of the plaintext are rearranged in a different and usually quite complex order, but the units themselves are left unchanged. By contrast, in a substitution cipher, the units of the plaintext are retained in the same sequence in the ciphertext, but the units themselves are altered. There are a number of different types of substitution cipher. If the cipher operates on single letters, it is termed a simple substitution cipher; a cipher that operates on larger groups of letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brute Force Attack
In cryptography, a brute-force attack or exhaustive key search is a cryptanalytic attack that consists of an attacker submitting many possible Key (cryptography), keys or passwords with the hope of eventually guessing correctly. This strategy can theoretically be used to break any form of encryption that is not information-theoretically secure. However, in a properly designed cryptosystem the chance of successfully guessing the key is negligible. When Password cracking, cracking passwords, this method is very fast when used to check all short passwords, but for longer passwords other methods such as the dictionary attack are used because a brute-force search takes too long. Longer passwords, passphrases and keys have more possible values, making them exponentially more difficult to crack than shorter ones due to diversity of characters. Brute-force attacks can be made less effective by Obfuscation (software), obfuscating the data to be encoded making it more difficult for an att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciphertext-only Attack
In cryptography, a ciphertext-only attack (COA) or known ciphertext attack is an attack model for cryptanalysis where the attacker is assumed to have access only to a set of ciphertexts. While the attacker has no channel providing access to the plaintext prior to encryption, in all practical ciphertext-only attacks, the attacker still has some knowledge of the plaintext. For instance, the attacker might know the language in which the plaintext is written or the expected statistical distribution of characters in the plaintext. Standard protocol data and messages are commonly part of the plaintext in many deployed systems, and can usually be guessed or known efficiently as part of a ciphertext-only attack on these systems. Attack The attack is completely successful if the corresponding plaintexts can be deduced, or even better, the key. The ability to obtain any information at all about the underlying plaintext beyond what was pre-known to the attacker is still considered a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeneas Tacticus
Aeneas Tacticus (; fl. 4th century BC) was one of the earliest Greek writers on the art of war and is credited as the first author to provide a complete guide to securing military communications. Polybius described his design for a hydraulic semaphore system. According to Aelianus Tacticus and Polybius, he wrote a number of treatises () on the subject. The only extant one, ''How to Survive under Siege'' (, ), deals with the best methods of defending a fortified city. An epitome of the whole was made by Cineas, minister of Pyrrhus, king of Epirus. The work is chiefly valuable as containing a large number of historical illustrations. Aeneas was considered by Isaac Casaubon to have been a contemporary of Xenophon and identical with the Arcadian general Aeneas of Stymphalus, whom Xenophon (''Hellenica'', vii.3) mentions as fighting at the Battle of Mantinea (362 BC). References Further reading *''Aeneas Tacticus, Asclepiodotus, Onasander''. Translated by Illinois Greek Clu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in northeastern Essex, England. It is the second-largest settlement in the county, with a population of 130,245 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 Census. The demonym is ''Colcestrian''. Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first Colonia (Roman), major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colchester therefore claims to be Britain's first city. It has been an important military base since the Roman Empire, Roman era, with Colchester Garrison currently housing the 16th Air Assault Brigade (United Kingdom), 16th Air Assault Brigade. On the River Colne, Essex, River Colne, Colchester is northeast of London. It is connected to London by the A12 road (England), A12 road and the Great Eastern Main Line railway. Colchester is less than from London Stansted Airport and from the port of Harwich. Attractions in and around the city include St Botolph's Priory, Colchester Zoo, and several art galleries. Colchester Castle was constructe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, the struggle consisted of the First English Civil War and the Second English Civil War. The Anglo-Scottish war (1650–1652), Anglo-Scottish War of 1650 to 1652 is sometimes referred to as the ''Third English Civil War.'' While the conflicts in the three kingdoms of England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland had similarities, each had their own specific issues and objectives. The First English Civil War was fought primarily over the correct balance of power between Parliament of England, Parliament and Charles I of England, Charles I. It ended in June 1646 with Royalist defeat and the king in custody. However, victory exposed Parliamentarian divisions over the nature of the political settlemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |