|
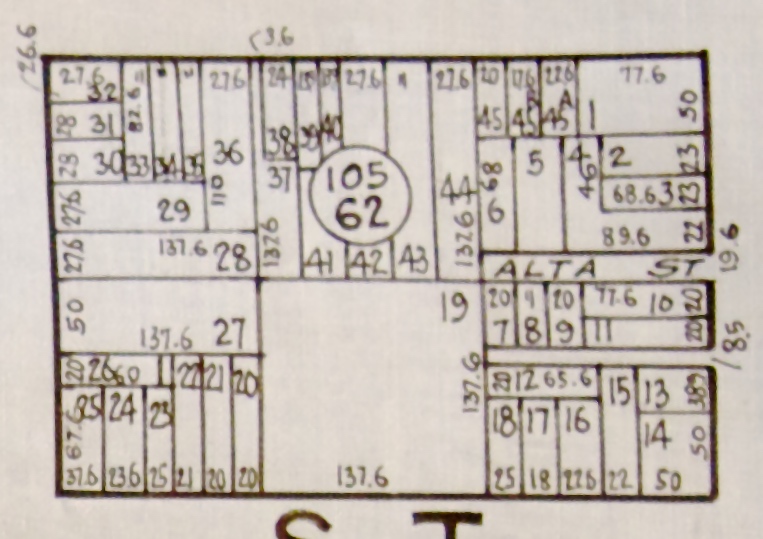
Chilean Units Of Measurement
A number of different units of measurement were used in Chile to measure quantities like length, mass, area, capacity, etc. From 1848, the metric system has been compulsory in Chile. Pre-metric units Spanish customary units were used before 1848. Length To measure length several units were used. Legally, one vara is equal to 0.836 m. Some of the units and their legal values as follows: * 1 línea = vara * 1 pulgada = vara * 1 pie = vara * 1 cuadra = 150 vara * 1 legua = 5400 vara Mass Several units were used to measure mass. One libra is equal to 0.460093 kg. Some other units are given below: * 1 grano = libra * 1 adarme = libra * 1 = libra * 1 onza = libra * 1 arroba = 25 libra * 1 quintal = 100 libra Capacity Mainly two systems, dry and liquid, were used to measure capacity in Chile. Dry One almud was equal to 8.083 L. 12 almud were equal to one fanega. Liquid One cuartillo was equal to 1.111 L. 32 cuartillo were equal to one arroba. References {{S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Measurement
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. For instance, when referencing "10 metres" (or 10 m), what is actually meant is 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to the present. A multitude of System of measurement, systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. In trade, weights and measures are often a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric System
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules governing the metric system have changed over time, the modern definition, the International System of Units (SI), defines the metric prefixes and seven base units: metre (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), Mole (unit), mole (mol), and candela (cd). An SI derived unit is a named combination of base units such as hertz (cycles per second), Newton (unit), newton (kg⋅m/s2), and tesla (unit), tesla (1 kg⋅s−2⋅A−1) and in the case of Celsius a shifted scale from Kelvin. Certain units have been Non-SI units mentioned in the SI#Units officially accepted for use with the SI, officially accepted for use with the SI. Some of these are decimalised, like the litre and electronvolt, and are considered "metric". Others, like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Customary Units
There are a number of Spanish units of measurement of length or area that are virtually obsolete due to metrication. They include the vara, the cordel, the league and the labor. The units of area used to express the area of land are still encountered in some transactions in land today. (unit of length) A (meaning "rod" or "pole", abbreviation: var) is an old Spanish unit of length. Varas are a surveying unit that appear in many deeds in the southern United States due to the land previously being part of Mexico, and becoming part of the United States under the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. Varas were also used in many parts of Latin America. It varied in size at various times and places; the Spanish unit was set at about in 1801. In Argentina, the vara measured about , and typical urban lots are wide (10 Argentine varas). At some time a value of was adopted in California. In Texas, a was defined as , or 1 yard = 1.08 . The and the corresponding unit of area, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League (unit)
A league is a unit of length. It was common in Europe and Latin America, but due to its highly inconsistent definition, it is no longer an official unit in any nation. Derived from an ancient Celtic unit and adopted by the Romans as the , the league became a common unit of measurement throughout western Europe. Since the Middle Ages, many values have been specified in several countries, ranging from 2.2 km (1.4 mi) to 7.9 km (4.9 mi). It may have originally represented, roughly, the distance a Preferred walking speed, person could walk in an hour. Definitions Ancient Rome The league was used in Ancient Rome, defined as 1½ mile#Roman, Roman miles (7,500 Foot (unit)#Historical origin, Roman feet, modern 2.2 km or 1.4 miles). The origin is the ''(also:'' '')'', the league of Gaul. Argentina The Argentine league () is or 6,666 : 1 is . England On land, the league is most commonly defined as three miles (4.83 km), although the length of a mile could vary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arroba
''Arroba'' is a Portuguese and Spanish customary unit of weight, mass or volume. Its symbol is @. History The word ''arroba'' has its origin in Arabic ''ar-rubʿ'' (الربع) or "quarter," specifically the fourth part (of a quintal), which defined the average load which a donkey could carry. Iberian Peninsula In weight it was equal to 32 pounds (14.7 kg) in Portugal and 25 pounds (11.5 kg) in Spain. The unit is still used in Portugal and Spain by cork merchants and pig farmers. Latin America The unit is still used in Brazil by the agricultural sector, mainly in the cotton and cattle business. The modern metric arroba used in these countries in everyday life is defined as . In Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru the arroba is equivalent to . In Bolivia nationally it is equivalent to . However locally there are many different values, ranging from in Inquisivi to in Baures. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almude
The almude is an obsolete Portuguese unit of measurement of volume used in Portugal, Brazil and other parts of the Portuguese Empire. Etymologically, it derives from the Arabic ''al-mudd'', and ultimately from Latin '' modius''. The almude appears in Portuguese documents since the first half of the 11th century. As in the Iberian regions under Arab rule, its capacity was in the Christian northwest 0.7 liters. In the system of the county of Portucale, the almude was equivalent to 2 alqueires (about 6.7 liters). In the system introduced by Afonso Henriques, first king of Portugal, and used almost until the end of the first dynasty, it seems that the almude was equivalent to the alqueire of that system (8.7 liters). In the system introduced by Pedro I, the almude was again equivalent to 2 alqueires (about 19.7 liters). In the Lisbon system, adapted and generalized to the whole kingdom by Manuel I, the almude was equivalent to about 16.8 liters. In modern times, the official almude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fanega
Fanega was a historical unit of volume used in colonial-era Costa Rica for measuring dry commodities, especially agricultural produce. Originating as a Spanish measure for grain, the fanega became the standard gauge for bulk goods in colonial administration and trade. In Costa Rica, it was most commonly applied to staple crops like maize and later to coffee. The term also appeared in legal decrees and records, specifying tribute payments or crop tithes. Pérez Zeledón, a key coffee-producing canton, exemplifies the fanega’s enduring role: coffee yields and export volumes there have long been quantified in fanegas, linking local agricultural practice to a colonial measurement tradition. The fanega’s usage persisted into the 19th and 20th centuries, notably in the coffee economy, even as the country transitioned to metric units. Etymology and origins The word fanega comes from the Spanish unit of measure of the same name, derived from the Andalusi Arabic faníqa (“measure for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Chile
The culture of Chile reflects the population and the geographic isolation of the country in relation to the rest of South America. Since colonial times, the Chilean culture has been a mix of Spain, Spanish colonial elements with elements of Indigenous people, indigenous (mostly Mapuche) culture, as well as that of other immigrant cultures. The Huasos of Zona Central, Chile, Central Chile and their native or folk music and dance are central to Chilean folk culture. Even though the folk traditions of Zona Central, Chile, Central Chile are central to Chilean cultural and national identity, Chile is both geographically and culturally diverse with both the North and the South having their own folk music and dance due to different indigenous peoples and different immigrant groups settling there. Additionally, while some regions of Chile have very strong indigenous heritage, such as Araucanía Region, Easter Island, and Arica and Parinacota Region, Arica y Parinacota Region, some regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |