|
Chang'e 2
Chang'e 2 (; ) is a Chinese uncrewed lunar probe that was launched on 1 October 2010. It was a follow-up to the Chang'e 1 lunar probe, which was launched in 2007. Chang'e 2 was part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, and conducted research from a 100-km-high lunar orbit in preparation for the December 2013 soft landing by the Chang'e 3 lander and rover. Chang'e 2 was similar in design to Chang'e 1, although it featured some technical improvements, including a more advanced onboard camera. Like its predecessor, the probe was named after Chang'e, an ancient Chinese moon goddess. After completing its primary objective, the probe left lunar orbit for the Earth–Sun Lagrangian point, to test the Chinese tracking and control network, making the China National Space Administration the third space agency after NASA and ESA to have visited this point. It entered orbit around L2 on 25 August 2011, and began transmitting data from its new position in Septem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing Air And Space Museum
Beijing, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's most populous national capital city as well as China's second largest city by urban area after Shanghai. It is located in Northern China, and is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of the State Council with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province and neighbors Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jing-Jin-Ji cluster. Beijing is a global city and one of the world's leading centres for culture, diplomacy, politics, finance, business and economics, education, research, language, tourism, media, sport, science and technology, transportation, and art. It is home to the headquarters of most of China's largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Of The Moon
The physical exploration of the Moon began when ''Luna 2'', a space probe launched by the Soviet Union, made a deliberate impact on the surface of the Moon on 14 September, 1959. Prior to that the only available means of lunar exploration had been observations from Earth. The invention of the optical telescope brought about the first leap in the quality of lunar observations. Galileo Galilei is generally credited as the first person to use a telescope for astronomical purposes, having made his own telescope in 1609, the mountains and craters on the lunar surface were among his first observations using it. Human exploration of the Moon since Luna 2 has consisted of both crewed and uncrewed missions. NASA's Apollo program has been the only program to successfully land humans on the Moon, which it did six times on the near side in the 20th century. The first human landing took place in 1969, when the Apollo 11 astronauts Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong touched down on the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 5
Chang'e 5 () was the fifth lunar exploration mission in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program of CNSA, and China's first lunar sample-return mission. Like its predecessors, the spacecraft is named after the Chinese moon goddess, Chang'e. It launched at 20:30 UTC on 23 November 2020, from Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site on Hainan Island, landed on the Moon on 1 December 2020, collected ~ of lunar samples (including from a core ~1 m deep), and returned to the Earth at 17:59 UTC on 16 December 2020. Chang'e 5 was the first lunar sample-return mission since the Soviet Union's Luna 24 in 1976. New lunar minerals, including Changesite-(Y) and two different structures of the titanium compound Ti2O, were identified from the samples returned from the mission, making China the third country to discover a new lunar mineral. The mission also made China the third country to return samples from the Moon after the United States and the Soviet Union. Overview The Chinese Lunar Expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 4
Chang'e 4 (; ) is a robotic spacecraft mission in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program of the CNSA. It made a soft landing on the far side of the Moon, the first spacecraft to do so, on 3 January 2019. A communication relay satellite, , was first launched to a halo orbit near the Earth–Moon L2 point in May 2018. The robotic lander and '' Yutu-2'' () rover were launched on 7 December 2018 and entered lunar orbit on 12 December 2018, before landing on the Moon's far side. On 15 January it was announced that seeds had sprouted in the lunar lander's biological experiment, the first plants to sprout on the Moon. The mission is the follow-up to Chang'e 3, the first Chinese landing on the Moon. The spacecraft was originally built as a backup for Chang'e 3 and became available after Chang'e 3 landed successfully in 2013. The configuration of Chang'e 4 was adjusted to meet new scientific and performance objectives. Like its predecessors, the mission is named after Chang'e, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceNews
''SpaceNews'' is a print and digital publication that covers business and political news in the space and satellite industry. ''SpaceNews'' provides news, commentary and analysis to an audience of government officials, politicians and executives within the space industry. ''SpaceNews'' details topics in civil, military and space and the satellite communications business. ''SpaceNews'' covers important news in North America, Europe, Asia, Africa, the Middle East and South America from NASA, the European Space Agency, and private spaceflight firms such as Arianespace, International Launch Services, SpaceX and United Launch Alliance. The magazine regularly features profiles on relevant and important figures within the space industry. These profiles have featured numerous government leaders, corporate executives and other knowledgeable space experts, including NASA administrators Richard Truly, Daniel Goldin, Sean O’Keefe, Michael Griffin and Charles Boldin. Founded in 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
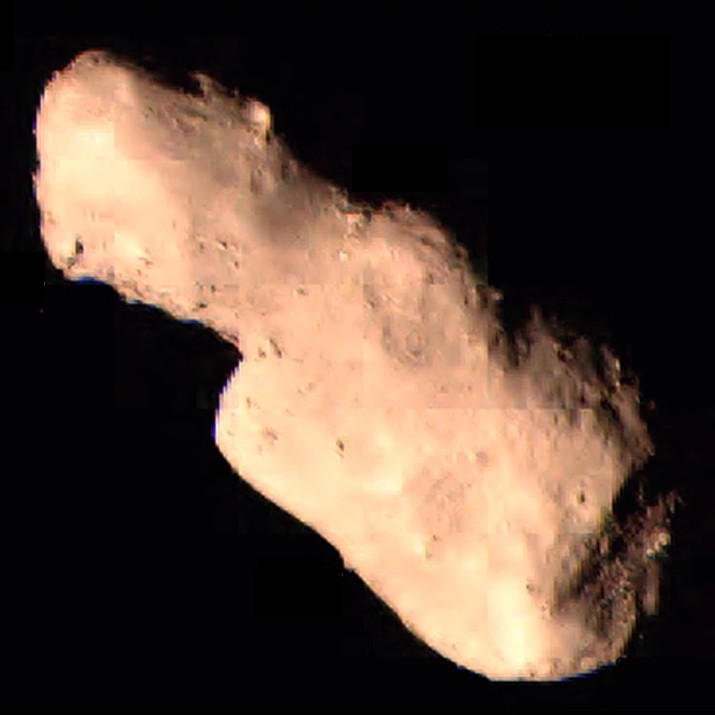
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). Asteroids are rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere, and are broadly classified into C-type asteroid, C-type (carbonaceous), M-type asteroid, M-type (metallic), or S-type asteroid, S-type (silicaceous). The size and shape of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from small rubble piles under a kilometer across to Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres, a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter. A body is classified as a comet, not an asteroid, if it shows a coma (tail) when warmed by solar radiation, although recent observations suggest a continuum between these types of bodies. Of the roughly one million known asteroids, the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 astronomical unit, AU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CNSA
The China National Space Administration (CNSA) is a government agency of the People's Republic of China headquartered in Haidian, Beijing, responsible for civil space administration and international space cooperation. These responsibilities include organizing or leading foreign exchanges and cooperation in the aerospace field. The CNSA is an administrative agency under the State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense. Founded in 1993, CNSA has pioneered a number of achievements in space for China despite its relatively short history, including becoming the first space agency to land on the far side of the Moon with Chang'e 4, bringing material back from the Moon with Chang'e 5 and 6, and being the second agency who successfully landed a rover on Mars with Tianwen-1. Tianwen-2 is enroute to explore the co-orbital near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa and the active asteroid 311P/PanSTARRS and collecting samples of the regolith of Kamo'oa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Society
The Planetary Society is an American internationally-active non-governmental nonprofit organization. It is involved in research, public outreach, and political space advocacy for engineering projects related to astronomy, planetary science, and space exploration. It was founded in 1980 by Carl Sagan, Bruce Murray, and Louis Friedman, and has about 60,000 members from more than 100 countries around the world. The Society is dedicated to the exploration of the Solar System, the search for near-Earth objects, and the search for extraterrestrial life. The society's mission is stated as: "Empowering the world’s citizens to advance space science and exploration." The Planetary Society is a strong advocate for space funding and missions of exploration within NASA. They lobby Congress and engage their membership in the United States to write and call their representatives in support of NASA funding. In addition to public outreach, The Planetary Society has sponsored solar sail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinhua
Xinhua News Agency (English pronunciation: ),J. C. Wells: Longman Pronunciation Dictionary, 3rd ed., for both British and American English or New China News Agency, is the official State media, state news agency of the China, People's Republic of China. It is a ministry-level institution of the State Council of China, State Council. Founded in 1931, it is the largest media organ in China. Xinhua is a publisher, as well as a news agency; it publishes in multiple languages and is a channel for the distribution of information related to the Chinese government and the ruling Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Its headquarters in Beijing are located close to the central government's headquarters at Zhongnanhai. Xinhua tailors its pro-Chinese government message to the nuances of each international audience. The organization has faced criticism for spreading Propaganda in China, propaganda and disinformation and for criticizing people, groups, or movements critical of the Chinese governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India Times
''The Times of India'' (''TOI'') is an Indian English-language daily newspaper and digital news media owned and managed by the Times Group. It is the third-largest newspaper in India by circulation and largest selling English-language daily in the world. It is the oldest English-language newspaper in India, and the second-oldest Indian newspaper still in circulation, with its first edition published in 1838. It is nicknamed as "The Old Lady of Bori Bunder", and is a newspaper of record. Near the beginning of the 20th century, Lord Curzon, the Viceroy of India, called ''TOI'' "the leading paper in Asia". In 1991, the BBC ranked ''TOI'' among the world's six best newspapers. It is owned and published by Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. (BCCL), which is owned by the Sahu Jain family. In the Brand Trust Report India study 2019, ''TOI'' was rated as the most trusted English newspaper in India. In a 2021 survey, Reuters Institute rated ''TOI'' as the most trusted media news brand amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |