|
Census Of Antarctic Marine Life
The Census of Antarctic Marine Life (CAML) is a field project of the Census of Marine Life that researches the marine biodiversity of Antarctica, how it is affected by climate change, and how this change is altering the ecosystem of the Southern Ocean. The program started in 2005 as a 5-year initiative with the scientific goal being to study the evolution of life in Antarctic waters, to determine how this has influenced the diversity of the present biota, and use these observations to predict how it might respond to future change. However, due to modern and extravagant changes within technology, we are able to witness and influence biodiversity reproduction and development. This enables us to gain further insight toward characteristics that allow such biodiversity to flourish within this barren desert referred to as the Arctic and Antarctic. CAML has collected its data from 18 Antarctic research vessels during the International Polar Year, which is freely accessible aScientific Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Antarctic Division
The Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) is a division of the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water. The Division undertakes science programs and research projects to contribute to an understanding of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. It conducts and supports collaborative research programs with other Australian and international organisations, such as the Bureau of Meteorology and Geoscience Australia, as well as administering and maintaining a presence in Australian Antarctic and sub-Antarctic territories. Their website includes articles on the Antarctic wildlife, threats, guidelines and they have blogs written by Australians at the three Australian bases in Antarctica: Mawson, Davis and Casey. Charter Under its charter the Australian Antarctic Division: * Administers the Australian Antarctic Territory and the Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands * Conducts research in high priority areas of Antarctic science * Coordinates and manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census Of Marine Life
The Census of Marine Life was a 10-year, US $650 million scientific initiative, involving a global network of researchers in more than 80 nations, engaged to assess and explain the diversity, distribution, and abundance of life in the oceans. The world's first comprehensive Census of Marine Life — past, present, and future — was released in 2010 in London. Initially supported by funding from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, the project was successful in generating many times that initial investment in additional support and substantially increased the baselines of knowledge in often underexplored ocean realms, as well as engaging over 2,700 different researchers for the first time in a global collaborative community united in a common goal, and has been described as "one of the largest scientific collaborations ever conducted". Project history According to Jesse Ausubel, Senior Research Associate of the Program for the Human Environment of Rockefeller University and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Committee On Antarctic Research
The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is an interdisciplinary body of the International Science Council (ISC). SCAR coordinates international scientific research efforts in Antarctica, including the Southern Ocean. SCAR's scientific work is administered through several discipline-themed ''science groups''. The organisation has observer status at, and provides independent advice to Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings, and also provides information to other international bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). History At the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU)’s Antarctic meeting held in Stockholm from 9–11 September 1957, it was agreed that a committee should be created to oversee scientific research in Antarctica. At the time there were 12 nations actively conducting Antarctic research and they were each invited to nominate one delegate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biota (ecology)
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader term than habitat and can comprise a variety of habitats. While a biome can cover large areas, a microbiome is a mix of organisms that coexist in a defined space on a much smaller scale. For example, the human microbiome is the collection of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that are present on or in a human body. A biota is the total collection of organisms of a geographic region or a time period, from local geographic scales and instantaneous temporal scales all the way up to whole-planet and whole-timescale spatiotemporal scales. The biotas of the Earth make up the biosphere. Etymology The term was suggested in 1916 by Clements, originally as a synonym for '' biotic community'' of Möbius (1877). Later, it gained its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Polar Year
The International Polar Years (IPY) are collaborative, international efforts with intensive research focus on the polar regions. Karl Weyprecht, an Austro-Hungarian naval officer, motivated the endeavor in 1875, but died before it first occurred in 1882–1883. Fifty years later (1932–1933) a second IPY took place. The International Geophysical Year was inspired by the IPY and was organized 75 years after the first IPY (1957–58). The fourth, and most recent, IPY covered two full annual cycles from March 2007 to March 2009. The First International Polar Year (1882–1883) The First International Polar Year was proposed by an Austro-Hungarian naval officer, Karl Weyprecht, in 1875 and organized by Georg Neumayer, director of the German Maritime Observatory. Rather than settling for traditional individual and national efforts, they pushed for a coordinated scientific approach to researching Arctic phenomena. Observers made coordinated geophysical measurements at multiple locati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Register Of Antarctic Marine Species
The Register of Antarctic Marine Species, also known as RAMS, is a taxonomic database that provides a list of marine species found in the Southern Ocean surrounding Antarctica. Its purpose is to provide authoritative and comprehensive information on the diversity of marine life in the region, which provides a reference point for marine science, research, conservation and sustainable management. The database includes marine species found on the sea floor, in the water column, and around sea-ice.{{Cite web, url=https://ipt.biodiversity.aq/resource?r=rams, title=The Register of Antarctic Marine Species, website=ipt.biodiversity.aq, access-date=2019-05-08 RAMS is a regionally-focused database within the World Register of Marine Species. References Database In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbes
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from μικρός, mikrós, "small" and βίος, bíos, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whales
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and porpoises. Dolphins and porpoises may be considered whales from a formal, cladistic perspective. Whales, dolphins and porpoises belong to the order Cetartiodactyla, which consists of even-toed ungulates. Their closest non-cetacean living relatives are the hippopotamuses, from which they and other cetaceans diverged about 54 million years ago. The two parvorders of whales, baleen whales (Mysticeti) and toothed whales (Odontoceti), are thought to have had their last common ancestor around 34 million years ago. Mysticetes include four extant (living) families: Balaenopteridae (the rorquals), Balaenidae (right whales), Cetotheriidae (the pygmy right whale), and Eschrichtiidae (the grey whale). Odontocetes include the Monodonti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
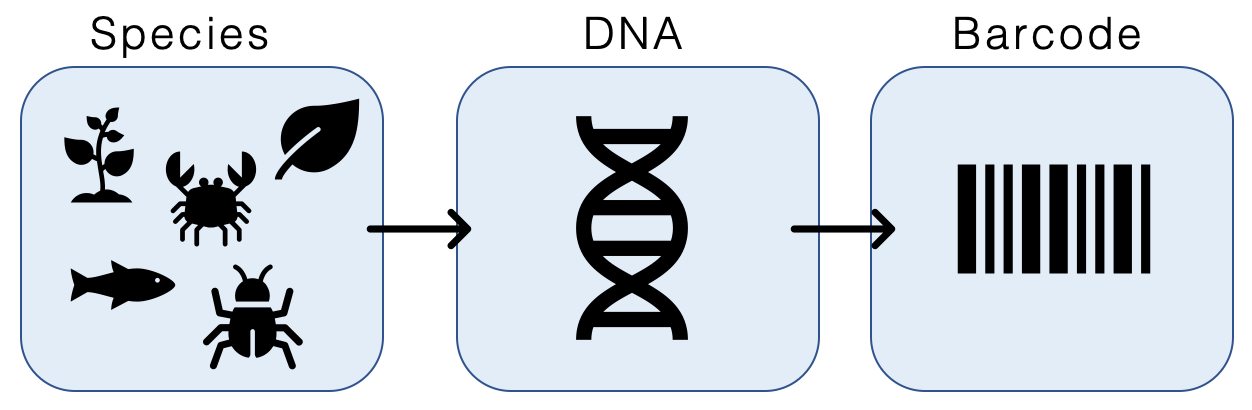
DNA Barcode
DNA barcoding is a method of species identification using a short section of DNA from a specific gene or genes. The premise of DNA barcoding is that by comparison with a reference library of such DNA sections (also called "sequences"), an individual sequence can be used to uniquely identify an organism to species, just as a supermarket scanner uses the familiar black stripes of the UPC barcode to identify an item in its stock against its reference database. These "barcodes" are sometimes used in an effort to identify unknown species or parts of an organism, simply to catalog as many taxa as possible, or to compare with traditional taxonomy in an effort to determine species boundaries. Different gene regions are used to identify the different organismal groups using barcoding. The most commonly used barcode region for animals and some protists is a portion of the cytochrome ''c'' oxidase I (COI or COX1) gene, found in mitochondrial DNA. Other genes suitable for DNA barcoding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
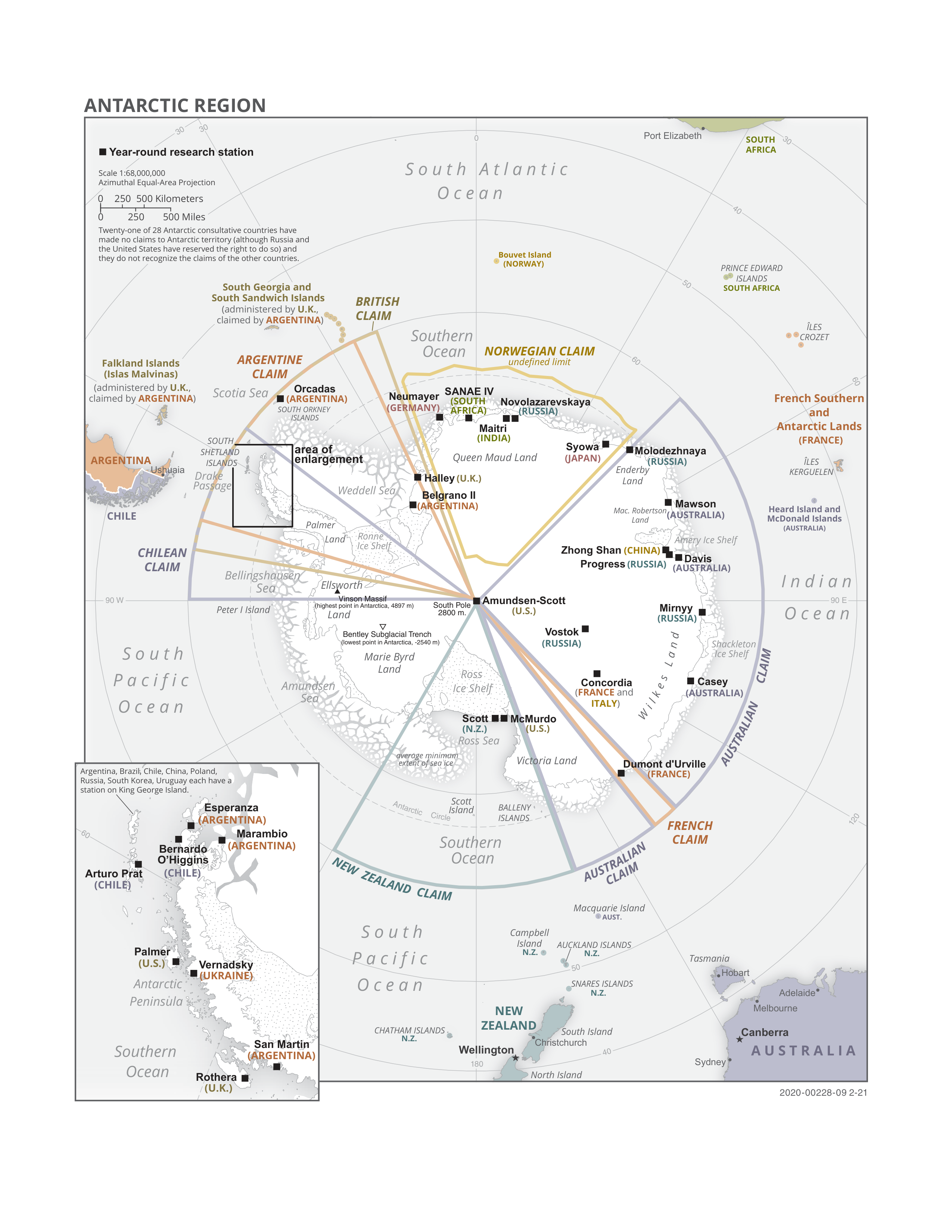
Antarctic Treaty
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_p252_Polar_Station_in_Sodankylä.jpg)