|
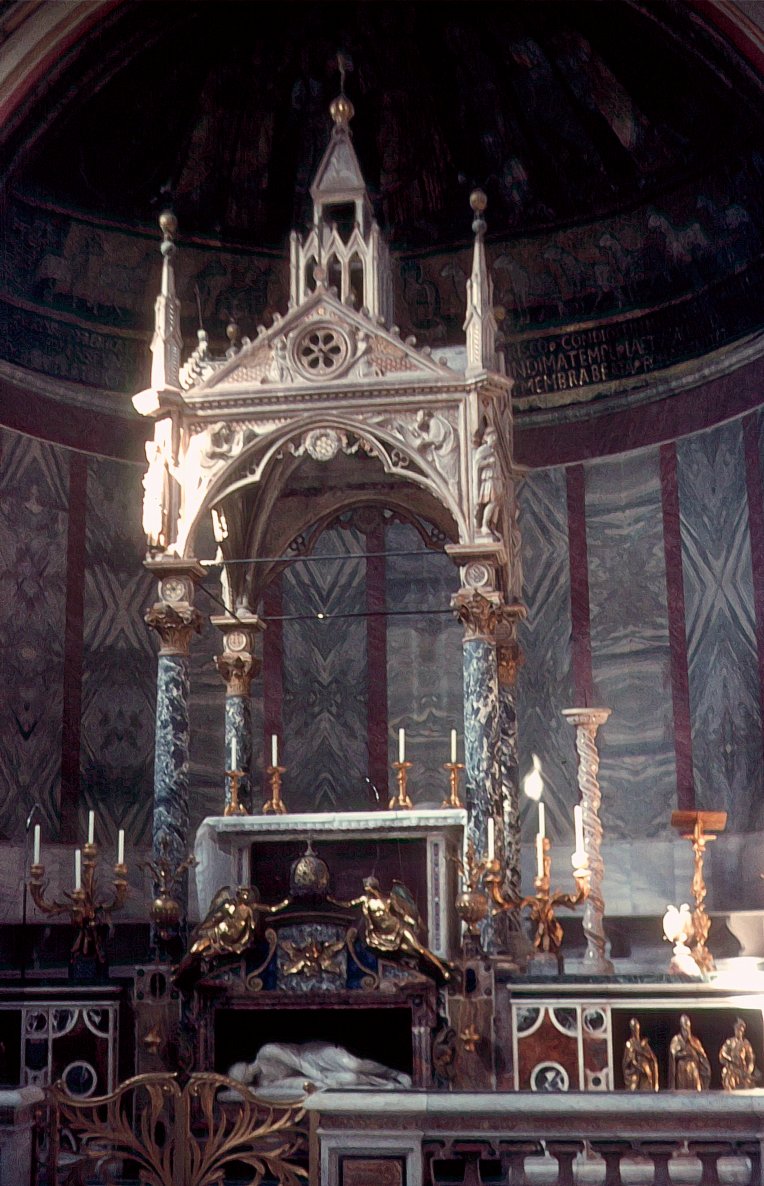
Catholic Church In Sichuan
The presence of the Catholic Church in the southwestern Chinese province of Sichuan and city of Chongqing dates back to 1640, when two missionaries, Lodovico Buglio and Gabriel de Magalhães, through Jesuit missions in China, entered the province and spent much of the 1640s evangelizing in Chengdu and its surrounding areas. The Paris Foreign Missions Society assumed full responsibility for the Sichuan Mission in the 18th century. The ''Basset–Su Chinese New Testament'' produced in Chengdu by the French missionary Jean Basset (died 1707), Jean Basset and the Sichuanese people, Sichuanese Conversion to Christianity, convert Johan Su during the first decade of the 18th century, became the prototype for Protestant Bible translations done by Robert Morrison (missionary), Robert Morrison, the first Protestant missionary to China in the early 19th century, which paved the way for the entire Protestant missionary enterprise in the country. In 1724, Yongzheng Emperor's "Amplified inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, Autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions of Guangxi and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet, as well as Southeast Asian countries Myanmar (Burma), Vietnam, and Laos. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014. Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the Northwest and low elevations in the Southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the altitude can vary from the mountain peaks to river valleys as much as . Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of Vascular plant, higher plants in China, Yunnan has perhaps 17, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family, collectively called the Southern Ming, survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjing were the largest in the world. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artus De Lionne
Artus de Lionne (1655–1713), abbé and Bishop of Rosalie ''in partibus infidelium'', in Turkey, was a French missionary of the Paris Foreign Missions Society. He was a son of Louis XIV's Foreign Minister, Hugues de Lionne.''Rituals of majesty: France, Siam, and court spectacle in royal image-building at Versailles in 1685 and 1686'' Canadian Journal of History, Aug 1996 by Love, Ronald /ref> Biography Artus de Lionne was born in Rome in 1655. He first left for Siam as a missionary in 1681. He returned to France in 1686, serving as translator to the embassy of the Siamese Kosa Pan to the court of Louis XIV.Smithies, Note 3, p.28 Artus de Lionne then returned to Siam with the Siamese embassy in 1687 on board the ships of the French ambassador Simon de la Loubère. He played a role in the negotiation between the French and Siamese sides during the 1688 Siamese Revolution, which resulted in the expulsion of the French forces. Artus de Lionne left Siam with General Desfarges fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel De Magalhães
Gabriel de Magalhães (; 1610 – 6 May 1677), or gallicized as Gabriel Magaillans, was an early Portuguese Jesuit missionary to China who was one of the first Catholic missionaries to reach Sichuan. He also worked in Peking and founded the original St. Joseph's Church there. Early life Magalhães was born in Pedrógão, Coimbra, Portugal, a member of the same family as Ferdinand Magellan.read on line on chineancienne.franhere. Mission to China After first spending six years in the Portuguese colony of Goa, Magalhães arrived in Hangzhou in 1640. He was then sent to Chengdu in Sichuan and arrived in August 1642. He began a close association with fellow Jesuit Lodovico Buglio in Chengdu, and started to study Chinese under Buglio's guidance. Buglio would become his biographer 35 years later. Both Magalhães and Buglio were pressed to serve under the rebel "King of the West", Zhang Xianzhong () after Zhang captured Sichuan in 1644. Initially Magalhães wrote sympathetically of Zh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodovico Buglio
Lodovico Buglio (26 January 1606 – 7 October 1682), Chinese name Li Leisi ( zh, t=利類思), was an Italian Jesuit mathematician and theologian. He was the first Catholic missionary to reach Sichuan, the then-westernmost province in China. Career Buglio was born at Mineo, Sicily, on 26 January 1606. He entered the Society of Jesus, on 29 January 1622, and, after a career as a professor of the humanities and rhetoric in the Roman College, asked to be sent to the Chinese mission. Buglio was a Jesuit and studied the Chinese language in the late 1630s at speed, using the abbreviated course of study. China Buglio preached the Gospel in the provinces of Sichuan, Fujian, and Jiangxi. He and fellow Jesuit Gabriel de Magalhães were pressed to serve the rebel leader Zhang Xianzhong who had conquered Sichuan in 1644. After Zhang was killed by Hooge, he was taken to Beijing in 1648. Here, after a short captivity, he was left free to exercise his ministry. He suffered in the persecutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a population of 20,937,757 at the 2020 Chinese census, 2020 census, it is the fourth most populous city in China, and it is the only city with a population of over 20 million apart from Direct-administered municipality, direct-administered municipalities. It is traditionally the hub of Western China. Chengdu is in central Sichuan. The surrounding Chengdu Plain is known as the "Country of Heaven" and the "Land of Abundance". Its prehistoric settlers included the Sanxingdui culture. The site of Dujiangyan, an ancient irrigation system, is designated as a World Heritage Site. The Jin River (Sichuan), Jin River flows through the city. Chengdu's culture reflects that of its province, Sichuan; in 2011, it was recognized by UNESCO as a city of ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Rite
The Roman Rite () is the most common ritual family for performing the ecclesiastical services of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. The Roman Rite governs Rite (Christianity), rites such as the Roman Mass and the Liturgy of the Hours as well as the manner in which Sacraments of the Catholic Church, sacraments and Blessing in the Catholic Church, blessings are performed. The Roman Rite developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while distinct Latin liturgical rites such as the Ambrosian Rite remain, the Roman Rite has gradually been adopted almost everywhere in the Latin Church. In medieval times there were numerous local variants, even if all of them did not amount to distinct rites, yet uniformity increased as a result of the invention of printing and in obedience to the decrees of the Council of Trent of 1545–1563 (see ''Quo primum''). Several Latin liturgical rites which had survived into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecclesiastical Latin
Ecclesiastical Latin, also called Church Latin or Liturgical Latin, is a form of Latin developed to discuss Christian theology, Christian thought in Late antiquity and used in Christianity, Christian liturgy, theology, and church administration to the present day, especially in the Catholic Church. It includes words from Vulgar Latin and Classical Latin (as well as Greek language, Greek and Hebrew language, Hebrew) re-purposed with Christian meaning. It is less stylized and rigid in form than Classical Latin, sharing vocabulary, forms, and syntax, while at the same time incorporating informal elements which had always been with the language but which were excluded by the literary authors of Classical Latin. Its pronunciation was partly standardized in the late 8th century during the Carolingian Renaissance as part of Charlemagne's educational reforms, and this new letter-by-letter pronunciation, used in France and England, was adopted in Iberia and Italy a couple of centuries aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuosu Language
Nuosu or Nosu (, transcribed as ), also known as Northern Yi, Liangshan Yi, and Sichuan Yi, is the prestige language of the Yi people; it has been chosen by the Chinese government as the standard Yi language () and as such is the only one taught in schools in both oral and written forms. It was spoken by two million people and was increasing (as of PRC census); 60% were monolingual (1994 estimate). Nuosu is the native Nuosu name for their own language and is not used in Mandarin Chinese, though it may sometimes be translated as ''Nuòsūyǔ'' (). The occasional terms "Black Yi" () and 'White Yi' () are castes of the Nuosu people, not dialects. Nuosu is one of several often mutually unintelligible varieties known as Yi, Lolo, Moso, or Noso. The six Yi languages recognized by the Chinese government have only 25% to 50% of their vocabulary in common. They share a common Yi script, traditional writing system, but that is used for shamanism, rather than daily accounting. According t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khams Tibetan
Khams Tibetan () is the Tibetic languages, Tibetic language used by the majority of the people in Kham. Khams is one of the three branches of the traditional classification of Tibetic languages (the other two being Amdo Tibetan and Ü-Tsang). In terms of mutual intelligibility, Khams could communicate at a basic level with the Ü-Tsang branch (including Lhasa Tibetan). Both Khams Tibetan and Lhasa Tibetan evolve to not preserve the word-initial consonant clusters, which makes them very far from Classical Tibetan, especially when compared to the more Linguistic conservatism, conservative Amdo Tibetan. Also, Kham and Lhasa Tibetan evolved to be tonal language, tonal, which Classical Tibetan was not. Khams Tibetan has 80% lexical similarity with Central Tibetan. Distribution Kham Tibetan is spoken in Kham, which is now divided between the eastern part of Tibet Autonomous Region, the southern part of Qinghai, the western part of Sichuan, and the northwestern part of Yunnan, China. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |