|
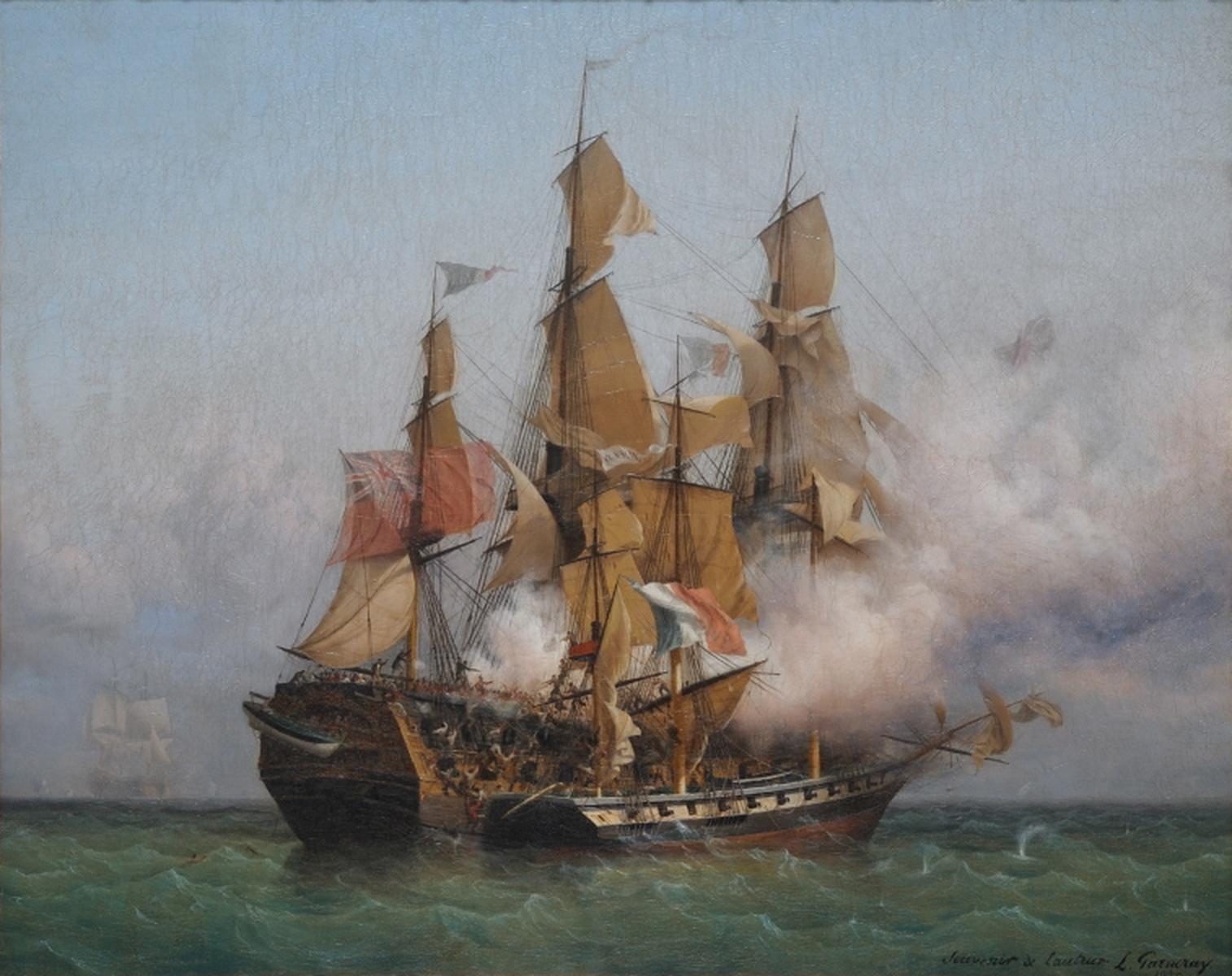
Capture Of Saint Martin (1633)
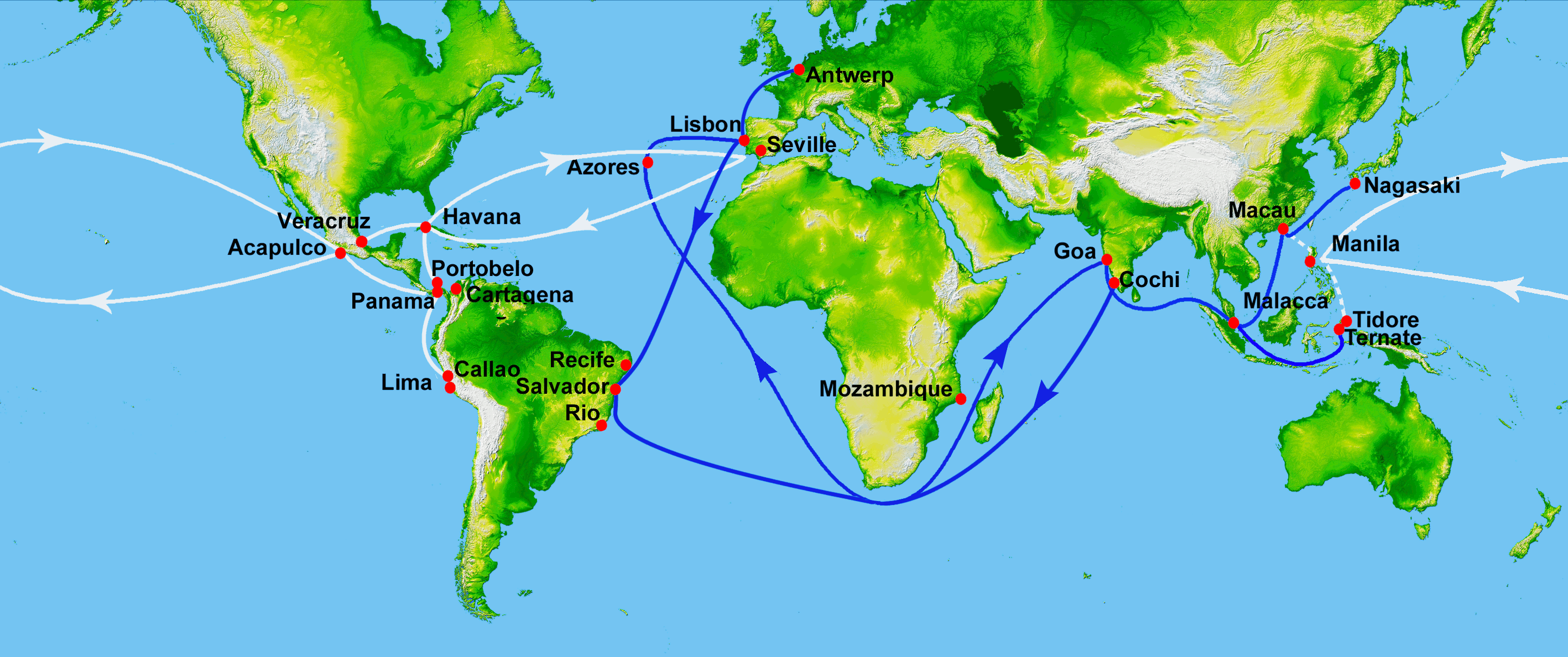
Part of the Eighty Years' War, the Capture of Saint Martin was a Spanish naval expedition against the island of Saint Martin, then occupied by the Dutch Republic. The island, claimed by Spain since Christopher Columbus' second voyage to the West Indies in 1493, lies a few hundred miles east of Puerto Rico. Its capture prevented Dutch privateers using it as a base for operations in the Caribbean. Background The Dutch Republic had been fighting Spain for its independence since the outbreak of the Eighty Years War in 1568, a conflict which extended into the Spanish Americas. By the 1620s, the Spanish were increasingly concerned by Dutch, French and English incursions into the Caribbean, culminating in the Battle in the Bay of Matanzas in 1628, when the Dutch captured the annual Spanish treasure fleet. The Spanish now decided to take action and targeted the Dutch garrison on Saint Martin, which threatened their colony in Puerto Rico. In April 1633, a fleet was sent from Cád ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish Empire, Spanish government. The Origins of the Eighty Years' War, causes of the war included the Reformation, Centralised state, centralisation, excessive taxation, and the rights and privileges of the Dutch nobility and cities. After Eighty Years' War, 1566–1572, the initial stages, Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Netherlands, deployed Army of Flanders, his armies and Eighty Years' War, 1572–1576, regained control over most of the rebel-held territories. However, Spanish Fury, widespread mutinies in the Spanish army caused a general uprising. Under the leadership of the exiled William the Silent, the Catholic and Protestant-dominated provinces sought to establish religious peace while jointly opposing the king's regime with the Pacification of Ghent, but the Eighty Years' War, 1576–1579, general rebelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as letters of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes and taking crews prisoner for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Most colonial powers, as well as other countries, engaged in privateering. Privateering allowed sovereigns to multiply their naval forces at relatively low cost by mobilizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire, closing a calamitous period of European history that killed approximately eight million people. Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand III, the kingdoms of France and Sweden, and their respective allies among the princes of the Holy Roman Empire, participated in the treaties.Clodfelter, Micheal (2017). ''Warfare and Armed Conflicts: A Statistical Encyclopedia of Casualty and Other Figures, 1492–2015.'' McFarland. p. 40. . The negotiation process was lengthy and complex. Talks took place in two cities, because each side wanted to meet on territory under its own control. A total of 109 delegations arrived to represent the belligerent states, but not all delegations were present at the same time. Two treaties were signed to end the war in the Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of navy, naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest quality, best known, or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Martin Island Topographic Map-en
Saint Martin may refer to: People * Saint Martin of Tours (c. 316–397), Bishop of Tours, France * Saint Martin of Braga (c. 520–580), archbishop of Bracara Augusta in Gallaecia (now Braga in Portugal) * Pope Martin I (c. 595–655), bishop of Rome * Saint Martin of Arades (died 726), canonized monk from Corbie Abbey whose feast day is November 26 * Saint Martin of Soure (died 1146), Portuguese cleric canonized after martyrdom to the Moors of Cordoba * Saint Martin de Porres (1579–1639), Peruvian lay brother of the Dominican Order * Saints Martin Tho and Martin Tinh Duc Ta, two Vietnamese Martyrs who died between 1745 and 1862 People with the surname * Alexis St. Martin (1802–1880), Canadian voyageur * Fernande Saint-Martin (1927–2019), Canadian art critic, museologist, semiologist, visual arts theorist and writer * Louis Claude de Saint-Martin (1743–1803), French mystic philosopher * Louis St. Martin (1820–1893), American politician from Louisiana * Paul Sain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cádiz
Cádiz ( , , ) is a city in Spain and the capital of the Province of Cádiz in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. It is located in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula off the Atlantic Ocean separated from neighbouring San Fernando, Cádiz, San Fernando by a narrow isthmus. Cádiz, one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, was founded by the Phoenicians as a trading post.Strabo, ''Geographica'' 3.5.5 In the 18th century, the Port in the Bay of Cádiz consolidated as the main harbour of mainland Spain, enjoying the virtual monopoly of trade with the Americas until 1778. It is also the site of the University of Cádiz. Situated on a narrow slice of land surrounded by the sea‚ Cádiz is, in most respects, a typical Andalusian city with well-preserved historical landmarks. The older part of Cádiz, within the remnants of the defensive wall, city walls, is commonly refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Settlement Of Puerto Rico
Spanish settlement of Puerto Rico began in the early 1500s shortly after the formation of the Spanish state in 1493 (continuing until 1898 as a colony of Spain) and continues to the present day. The most significant Spanish immigration wave occurred during the colonial period, continuing with smaller numbers arriving during the 20th century to the present day. The Spanish Spanish culture, heritage in Puerto Rico is palpable today in its customs and many traditions, Puerto Rican Spanish, language, and in the Spanish Colonial architecture, old and new architectural designs. Landing and first settlement On 25 September 1493, Christopher Columbus set sail on his Christopher Columbus#Second voyage (1493–1496), second voyage with 17 ships and 1,200–1,500 men from Cádiz, Spain. On 19 November 1493 he landed on the island, naming it San Juan Bautista in honor of Saint John the Baptist. The first Spanish settlement, Caparra Archaeological Site, Caparra, was founded on 8 August 150 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Treasure Fleet
The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet (, also called silver fleet or plate fleet; from the meaning "silver"), was a convoy system of sea routes organized by the Spanish Empire from 1566 to 1790, which linked Spain with its Spanish Empire, territories in the Americas across the Atlantic. The convoys were general purpose cargo fleets used for transporting a wide variety of items, including agricultural goods, lumber, various metal resources such as silver and gold, Gemstone, gems, pearls, spices, sugar, tobacco, silk, and other exotic goods from the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire to the Peninsular Spain, Spanish mainland. Spanish goods such as oil, wine, textiles, books and tools were transported in the opposite direction. The West Indies fleet was the first permanent transatlantic trade route in history. Similarly, the related Manila galleons, Manila galleon trade was the first permanent trade route across the Pacific. The Spanish West and East Indies fleets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle In The Bay Of Matanzas
The Battle in the Bay of Matanzas was a naval battle in Cuba during the Eighty Years' War in which a Dutch squadron was able to defeat and capture a Spanish treasure fleet. Overview In 1628, Admiral Piet Hein, with Witte de With as his flag captain, sailed out to capture the Spanish treasure fleet loaded with silver from their American colonies. With him was Admiral Hendrick Lonck, and he was later joined by a squadron of Vice-Admiral Joost Banckert. Part of the Spanish fleet in Venezuela had been warned because a Dutch cabin boy had lost his way on Blanquilla and was captured, betraying the plan, but the other half from Mexico continued its voyage, unaware of the threat. Sixteen Spanish ships were intercepted: one galleon was taken after a surprise encounter during the night, nine smaller merchantmen were talked into surrendering; two small ships were overtaken at sea, and four fleeing galleons were trapped on the Cuban coast in the Bay of Matanzas. After some musket vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, which would later become the United Kingdom. The Kingdom of England was among the most powerful states in Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern period, early modern periods. Beginning in the year 886 Alfred the Great reoccupied London from the Danish Vikings and after this event he declared himself King of the Anglo-Saxons, until his death in 899. During the course of the early tenth century, the various Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms were united by Alfred's descendants Edward the Elder (reigned 899–924) and Æthelstan (reigned 924–939) to form the Kingdom of the English. In 927, Æthelstan conquered the last remaining Viking kingdom, Scandinavian York, York, making him the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from the High Middle Ages to 1848 during its dissolution. It was also an early French colonial empire, colonial power, with colonies in Asia and Africa, and the largest being New France in North America geographically centred around the Great Lakes. The Kingdom of France was descended directly from the West Francia, western Frankish realm of the Carolingian Empire, which was ceded to Charles the Bald with the Treaty of Verdun (843). A branch of the Carolingian dynasty continued to rule until 987, when Hugh Capet was elected king and founded the Capetian dynasty. The territory remained known as ''Francia'' and its ruler as ('king of the Franks') well into the High Middle Ages. The first king calling himself ('King of France') was Philip II of Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Colonization Of The Americas
The Spanish colonization of the Americas began in 1493 on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (now Haiti and the Dominican Republic) after the initial 1492 voyage of Genoa, Genoese mariner Christopher Columbus under license from Queen Isabella I of Castile. These overseas territories of the Spanish Empire were under the jurisdiction of Crown of Castile until the last territory was lost in Spanish–American War, 1898. Spaniards saw the dense populations of indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples as an important economic resource and the territory claimed as potentially producing great wealth for individual Spaniards and the crown. Religion played an important role in the Spanish conquest and incorporation of indigenous peoples, bringing them into the Catholic Church peacefully or by force. The crown created civil and religious structures to administer the vast territory. Spanish men and women settled in greatest numbers where there were dense indigenous populations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |